
Unfortunately, scammers today are coming at us from all angles, trying to trick us into giving up our hard-earned money. We all need to be vigilant in protecting ourselves online. If you aren’t paying attention, even if you know what to look for, they can still catch you off guard. There are numerous ways to detect fake sites, phishing, and other scams, including emails.
Before we delve into the signs of fake websites, we will first take a closer look at the common types of scams that use websites, what happens when you accidentally access a fake website, and what you can do in case you unknowingly purchased items from it.
Fake or scam websites are fraudulent sites that look legitimate while secretly attempting to steal your personal information, money, or account access.
These deceptive platforms masquerade as trustworthy businesses or organizations, sending urgent messages that appear to be from popular shopping websites offering fantastic limited-time deals, banking websites requesting immediate account verification, government portals claiming you owe taxes or are eligible for refunds, and shipping companies asking for delivery fees.
The urgency aims to trick you into logging in and sharing sensitive information, such as credit card numbers, Social Security details, login credentials, and personal data. Once you submit your data, the scammers will steal your identity, drain your accounts, or sell your details to other criminals on the dark web.
These scam websites have become increasingly prevalent because they’re relatively inexpensive to create and can reach millions of potential victims quickly through email and text campaigns, social media ads, and search engine manipulation.
Cybersecurity researchers and consumer protection agencies discover these fraudulent sites through various methods, including monitoring suspicious domain registrations, analyzing reported phishing attempts, and tracking unusual web traffic patterns. According to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center, losses from cyber-enabled fraud totaled $13.7 billion, with fake websites accounting for a significant portion of these losses.
Visiting a fake website, accidentally or intentionally, can expose you to several serious security risks that can impact your digital life and financial well-being:
Scammers employ various tactics to create fake websites that appear authentic, but most of these techniques follow familiar patterns. Knowing the main types of scam sites helps you recognize danger faster. This section lists the most common categories of scam websites, explains how they operate, and identifies the red flags that alert you before they can steal your information or money.
Understanding these common scam types helps you recognize fake sites before they can steal your information or money. When in doubt, verify legitimacy by visiting official websites directly through bookmarks or search engines rather than clicking suspicious links.
For the latest warnings and protection guidance, check resources from the Federal Trade Commission and the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center.
You can protect yourself by learning to recognize the warning signs of fake sites. By understanding what these scams look like and how they operate, you’ll be better equipped to shop, bank, and browse online with confidence. Remember, legitimate companies will never pressure you to provide sensitive information through unsolicited emails or urgent pop-up messages.
Most scams typically start with social engineering tactics, such as phishing, smishing, and fake social media messages containing suspicious links, before directing you to a fake website.
From these communications, the scammers impersonate legitimate organizations before finally executing their malevolent intentions. To avoid being tricked, it is essential to recognize the warning signs wherever you encounter them.
Fake emails are among the most common phishing attempts you’ll encounter. If you see any of these signs in an unsolicited email, it is best not to engage:
Smishing messages bear the same signs as phishing emails and have become increasingly sophisticated. These fake messages often appear to come from delivery services, banks, or government agencies. Common tactics include fake package delivery notifications, urgent banking alerts, or messages claiming you’ve won prizes or need to verify account information.
Legitimate organizations typically don’t include clickable links in unsolicited text messages, especially for account-related actions. When in doubt, don’t click the link—instead, open your banking app directly or visit the official website by typing the URL manually.
Social media platforms give scammers new opportunities to create convincing fake profiles and pages. They might impersonate customer service accounts, create fake giveaways, or send direct messages requesting personal information. These fake sites often use profile pictures and branding that closely resemble legitimate companies.
Unusual sender behavior is another indicator of a scam across all platforms. This includes messages from contacts you haven’t heard from in years, communications from brands you don’t typically interact with, or requests that seem out of character for the supposed sender.
Scammers have become increasingly cunning in creating fake websites that closely mimic legitimate businesses and services. Here are some real-life examples of how cybercriminals use fake websites to victimize consumers:
Scammers exploit your trust in the United States Postal Service (USPS), designing sophisticated fake websites to steal your personal information, payment details, or money. They know you’re expecting a package or need to resolve a delivery issue, making you more likely to enter sensitive information without carefully verifying the site’s authenticity.
USPS-themed smishing attacks arrive as text messages stating your package is delayed, undeliverable, or requires immediate action. Common phrases include “Pay $1.99 to reschedule delivery” or “Your package is held – click here to release.”
Scammers use various URL manipulation techniques to make their fake sites appear official. Watch for these red flags:
Always verify package information and delivery issues through official USPS channels before taking any action on suspicious websites or messages:
Reporting fake USPS websites helps protect others from falling victim to these scams and assists law enforcement in tracking down perpetrators.
Remember that legitimate USPS services are free for standard delivery confirmation and tracking. Any website demanding payment for basic package tracking or delivery should be treated as suspicious and verified through official USPS channels before providing any personal or financial information.
According to the Federal Trade Commission, tech support scams cost Americans nearly $1.5 billion in 2024. These types of social engineering attacks are increasingly becoming sophisticated, making it more important than ever to verify security alerts through official channels.
Sadly, many scammers are misusing the McAfee name to create fake tech support pop-up scams and trick you into believing your computer is infected or your protection has expired, and hoping you’ll act without thinking.
These pop-ups typically appear while you’re browsing and claim your computer is severely infected with viruses, malware, or other threats. They use official-looking McAfee logos, colors, and messaging to appear legitimate to get you to call a fake support number, download malicious software, or pay for unnecessary services.
Learning to detect fake sites and pop-ups protects you from scams. Be on the lookout for these warning signs:
If you see a suspicious pop-up claiming to be from McAfee, here’s exactly what you should do:
To check if your McAfee protection is genuinely active and up-to-date:
Remember, legitimate McAfee software updates and notifications come through the installed program itself, not through random browser pop-ups. Your actual McAfee protection works quietly in the background without bombarding you with alarming messages.
Stay protected by trusting your installed McAfee software and always verifying security alerts through official McAfee channels, such as your installed McAfee dashboard or the official website.
Be prepared and know how to respond quickly when something doesn’t feel right. If you suspect you’ve encountered a fake website, trust your instincts and take these protective steps immediately.
Recognizing fake sites and emails becomes easier with practice. The key is to trust your instincts—if something feels suspicious or too good to be true, take a moment to verify through official channels. With the simple verification techniques covered in this guide, you can confidently navigate the digital world and spot fake sites and emails before they cause harm.
Your best defense is to make these quick security checks a regular habit—verify URLs, look for secure connections, and trust your instincts when something feels off. Go directly to the source or bookmark your most frequently used services and always navigate to them. Enable two-factor authentication on important accounts, and remember that legitimate companies will never ask for sensitive information via email. Maintaining healthy skepticism about unsolicited communications will protect not only your personal information but also help create a safer online environment for everyone.
For the latest information on fake websites and scams and to report them, visit the Federal Trade Commission’s scam alerts or the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center.
The post Ways to Tell if a Website Is Fake appeared first on McAfee Blog.
KrebsOnSecurity recently heard from a reader whose boss’s email account got phished and was used to trick one of the company’s customers into sending a large payment to scammers. An investigation into the attacker’s infrastructure points to a long-running Nigerian cybercrime ring that is actively targeting established companies in the transportation and aviation industries.

Image: Shutterstock, Mr. Teerapon Tiuekhom.
A reader who works in the transportation industry sent a tip about a recent successful phishing campaign that tricked an executive at the company into entering their credentials at a fake Microsoft 365 login page. From there, the attackers quickly mined the executive’s inbox for past communications about invoices, copying and modifying some of those messages with new invoice demands that were sent to some of the company’s customers and partners.
Speaking on condition of anonymity, the reader said the resulting phishing emails to customers came from a newly registered domain name that was remarkably similar to their employer’s domain, and that at least one of their customers fell for the ruse and paid a phony invoice. They said the attackers had spun up a look-alike domain just a few hours after the executive’s inbox credentials were phished, and that the scam resulted in a customer suffering a six-figure financial loss.
The reader also shared that the email addresses in the registration records for the imposter domain — roomservice801@gmail.com — is tied to many such phishing domains. Indeed, a search on this email address at DomainTools.com finds it is associated with at least 240 domains registered in 2024 or 2025. Virtually all of them mimic legitimate domains for companies in the aerospace and transportation industries worldwide.
An Internet search for this email address reveals a humorous blog post from 2020 on the Russian forum hackware[.]ru, which found roomservice801@gmail.com was tied to a phishing attack that used the lure of phony invoices to trick the recipient into logging in at a fake Microsoft login page. We’ll come back to this research in a moment.
DomainTools shows that some of the early domains registered to roomservice801@gmail.com in 2016 include other useful information. For example, the WHOIS records for alhhomaidhicentre[.]biz reference the technical contact of “Justy John” and the email address justyjohn50@yahoo.com.
A search at DomainTools found justyjohn50@yahoo.com has been registering one-off phishing domains since at least 2012. At this point, I was convinced that some security company surely had already published an analysis of this particular threat group, but I didn’t yet have enough information to draw any solid conclusions.
DomainTools says the Justy John email address is tied to more than two dozen domains registered since 2012, but we can find hundreds more phishing domains and related email addresses simply by pivoting on details in the registration records for these Justy John domains. For example, the street address used by the Justy John domain axisupdate[.]net — 7902 Pelleaux Road in Knoxville, TN — also appears in the registration records for accountauthenticate[.]com, acctlogin[.]biz, and loginaccount[.]biz, all of which at one point included the email address rsmith60646@gmail.com.
That Rsmith Gmail address is connected to the 2012 phishing domain alibala[.]biz (one character off of the Chinese e-commerce giant alibaba.com, with a different top-level domain of .biz). A search in DomainTools on the phone number in those domain records — 1.7736491613 — reveals even more phishing domains as well as the Nigerian phone number “2348062918302” and the email address michsmith59@gmail.com.
DomainTools shows michsmith59@gmail.com appears in the registration records for the domain seltrock[.]com, which was used in the phishing attack documented in the 2020 Russian blog post mentioned earlier. At this point, we are just two steps away from identifying the threat actor group.
The same Nigerian phone number shows up in dozens of domain registrations that reference the email address sebastinekelly69@gmail.com, including 26i3[.]net, costamere[.]com, danagruop[.]us, and dividrilling[.]com. A Web search on any of those domains finds they were indexed in an “indicator of compromise” list on GitHub maintained by Palo Alto Networks‘ Unit 42 research team.
According to Unit 42, the domains are the handiwork of a vast cybercrime group based in Nigeria that it dubbed “SilverTerrier” back in 2014. In an October 2021 report, Palo Alto said SilverTerrier excels at so-called “business e-mail compromise” or BEC scams, which target legitimate business email accounts through social engineering or computer intrusion activities. BEC criminals use that access to initiate or redirect the transfer of business funds for personal gain.
Palo Alto says SilverTerrier encompasses hundreds of BEC fraudsters, some of whom have been arrested in various international law enforcement operations by Interpol. In 2022, Interpol and the Nigeria Police Force arrested 11 alleged SilverTerrier members, including a prominent SilverTerrier leader who’d been flaunting his wealth on social media for years. Unfortunately, the lure of easy money, endemic poverty and corruption, and low barriers to entry for cybercrime in Nigeria conspire to provide a constant stream of new recruits.
BEC scams were the 7th most reported crime tracked by the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) in 2024, generating more than 21,000 complaints. However, BEC scams were the second most costly form of cybercrime reported to the feds last year, with nearly $2.8 billion in claimed losses. In its 2025 Fraud and Control Survey Report, the Association for Financial Professionals found 63 percent of organizations experienced a BEC last year.
Poking at some of the email addresses that spool out from this research reveals a number of Facebook accounts for people residing in Nigeria or in the United Arab Emirates, many of whom do not appear to have tried to mask their real-life identities. Palo Alto’s Unit 42 researchers reached a similar conclusion, noting that although a small subset of these crooks went to great lengths to conceal their identities, it was usually simple to learn their identities on social media accounts and the major messaging services.
Palo Alto said BEC actors have become far more organized over time, and that while it remains easy to find actors working as a group, the practice of using one phone number, email address or alias to register malicious infrastructure in support of multiple actors has made it far more time consuming (but not impossible) for cybersecurity and law enforcement organizations to sort out which actors committed specific crimes.
“We continue to find that SilverTerrier actors, regardless of geographical location, are often connected through only a few degrees of separation on social media platforms,” the researchers wrote.
Palo Alto has published a useful list of recommendations that organizations can adopt to minimize the incidence and impact of BEC attacks. Many of those tips are prophylactic, such as conducting regular employee security training and reviewing network security policies.
But one recommendation — getting familiar with a process known as the “financial fraud kill chain” or FFKC — bears specific mention because it offers the single best hope for BEC victims who are seeking to claw back payments made to fraudsters, and yet far too many victims don’t know it exists until it is too late.
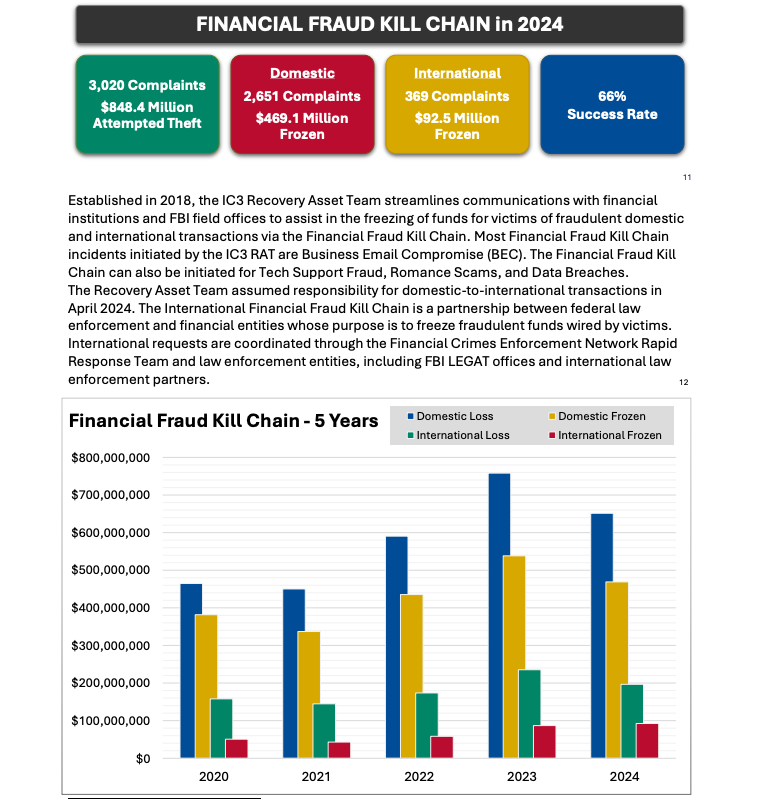
Image: ic3.gov.
As explained in this FBI primer, the International Financial Fraud Kill Chain is a partnership between federal law enforcement and financial entities whose purpose is to freeze fraudulent funds wired by victims. According to the FBI, viable victim complaints filed with ic3.gov promptly after a fraudulent transfer (generally less than 72 hours) will be automatically triaged by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN).
The FBI noted in its IC3 annual report (PDF) that the FFKC had a 66 percent success rate in 2024. Viable ic3.gov complaints involve losses of at least $50,000, and include all records from the victim or victim bank, as well as a completed FFKC form (provided by FinCEN) containing victim information, recipient information, bank names, account numbers, location, SWIFT, and any additional information.
🐫 CAMEL is an open-source community dedicated to finding the scaling laws of agents. We believe that studying these agents on a large scale offers valuable insights into their behaviors, capabilities, and potential risks. To facilitate research in this field, we implement and support various types of agents, tasks, prompts, models, and simulated environments.
The framework is designed to support systems with millions of agents, ensuring efficient coordination, communication, and resource management at scale.
Agents maintain stateful memory, enabling them to perform multi-step interactions with environments and efficiently tackle sophisticated tasks.
Every line of code and comment serves as a prompt for agents. Code should be written clearly and readably, ensuring both humans and agents can interpret it effectively.
We are a community-driven research collective comprising over 100 researchers dedicated to advancing frontier research in Multi-Agent Systems. Researchers worldwide choose CAMEL for their studies based on the following reasons.
| ✅ | Large-Scale Agent System | Simulate up to 1M agents to study emergent behaviors and scaling laws in complex, multi-agent environments. |
| ✅ | Dynamic Communication | Enable real-time interactions among agents, fostering seamless collaboration for tackling intricate tasks. |
| ✅ | Stateful Memory | Equip agents with the ability to retain and leverage historical context, improving decision-making over extended interactions. |
| ✅ | Support for Multiple Benchmarks | Utilize standardized benchmarks to rigorously evaluate agent performance, ensuring reproducibility and reliable comparisons. |
| ✅ | Support for Different Agent Types | Work with a variety of agent roles, tasks, models, and environments, supporting interdisciplinary experiments and diverse research applications. |
| ✅ | Data Generation and Tool Integration | Automate the creation of large-scale, structured datasets while seamlessly integrating with multiple tools, streamlining synthetic data generation and research workflows. |
Installing CAMEL is a breeze thanks to its availability on PyPI. Simply open your terminal and run:
pip install camel-ai
This example demonstrates how to create a ChatAgent using the CAMEL framework and perform a search query using DuckDuckGo.
bash pip install 'camel-ai[web_tools]'
bash export OPENAI_API_KEY='your_openai_api_key'
```python from camel.models import ModelFactory from camel.types import ModelPlatformType, ModelType from camel.agents import ChatAgent from camel.toolkits import SearchToolkit
model = ModelFactory.create( model_platform=ModelPlatformType.OPENAI, model_type=ModelType.GPT_4O, model_config_dict={"temperature": 0.0}, )
search_tool = SearchToolkit().search_duckduckgo
agent = ChatAgent(model=model, tools=[search_tool])
response_1 = agent.step("What is CAMEL-AI?") print(response_1.msgs[0].content) # CAMEL-AI is the first LLM (Large Language Model) multi-agent framework # and an open-source community focused on finding the scaling laws of agents. # ...
response_2 = agent.step("What is the Github link to CAMEL framework?") print(response_2.msgs[0].content) # The GitHub link to the CAMEL framework is # https://github.com/camel-ai/camel. ```
For more detailed instructions and additional configuration options, check out the installation section.
After running, you can explore our CAMEL Tech Stack and Cookbooks at docs.camel-ai.org to build powerful multi-agent systems.
We provide a demo showcasing a conversation between two ChatGPT agents playing roles as a python programmer and a stock trader collaborating on developing a trading bot for stock market.
Explore different types of agents, their roles, and their applications.
Please reach out to us on CAMEL discord if you encounter any issue set up CAMEL.
Core components and utilities to build, operate, and enhance CAMEL-AI agents and societies.
| Module | Description |
|---|---|
| Agents | Core agent architectures and behaviors for autonomous operation. |
| Agent Societies | Components for building and managing multi-agent systems and collaboration. |
| Data Generation | Tools and methods for synthetic data creation and augmentation. |
| Models | Model architectures and customization options for agent intelligence. |
| Tools | Tools integration for specialized agent tasks. |
| Memory | Memory storage and retrieval mechanisms for agent state management. |
| Storage | Persistent storage solutions for agent data and states. |
| Benchmarks | Performance evaluation and testing frameworks. |
| Interpreters | Code and command interpretation capabilities. |
| Data Loaders | Data ingestion and preprocessing tools. |
| Retrievers | Knowledge retrieval and RAG components. |
| Runtime | Execution environment and process management. |
| Human-in-the-Loop | Interactive components for human oversight and intervention. |
| --- |
We believe that studying these agents on a large scale offers valuable insights into their behaviors, capabilities, and potential risks.
Explore our research projects:
Research with US
We warmly invite you to use CAMEL for your impactful research.
Rigorous research takes time and resources. We are a community-driven research collective with 100+ researchers exploring the frontier research of Multi-agent Systems. Join our ongoing projects or test new ideas with us, reach out via email for more information.

For more details, please see our Models Documentation.
Data (Hosted on Hugging Face)
| Dataset | Chat format | Instruction format | Chat format (translated) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI Society | Chat format | Instruction format | Chat format (translated) |
| Code | Chat format | Instruction format | x |
| Math | Chat format | x | x |
| Physics | Chat format | x | x |
| Chemistry | Chat format | x | x |
| Biology | Chat format | x | x |
| Dataset | Instructions | Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| AI Society | Instructions | Tasks |
| Code | Instructions | Tasks |
| Misalignment | Instructions | Tasks |
Practical guides and tutorials for implementing specific functionalities in CAMEL-AI agents and societies.
| Cookbook | Description |
|---|---|
| Creating Your First Agent | A step-by-step guide to building your first agent. |
| Creating Your First Agent Society | Learn to build a collaborative society of agents. |
| Message Cookbook | Best practices for message handling in agents. |
| Cookbook | Description |
|---|---|
| Tools Cookbook | Integrating tools for enhanced functionality. |
| Memory Cookbook | Implementing memory systems in agents. |
| RAG Cookbook | Recipes for Retrieval-Augmented Generation. |
| Graph RAG Cookbook | Leveraging knowledge graphs with RAG. |
| Track CAMEL Agents with AgentOps | Tools for tracking and managing agents in operations. |
| Cookbook | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Generation with CAMEL and Finetuning with Unsloth | Learn how to generate data with CAMEL and fine-tune models effectively with Unsloth. |
| Data Gen with Real Function Calls and Hermes Format | Explore how to generate data with real function calls and the Hermes format. |
| CoT Data Generation and Upload Data to Huggingface | Uncover how to generate CoT data with CAMEL and seamlessly upload it to Huggingface. |
| CoT Data Generation and SFT Qwen with Unsolth | Discover how to generate CoT data using CAMEL and SFT Qwen with Unsolth, and seamlessly upload your data and model to Huggingface. |
| Cookbook | Description |
|---|---|
| Role-Playing Scraper for Report & Knowledge Graph Generation | Create role-playing agents for data scraping and reporting. |
| Create A Hackathon Judge Committee with Workforce | Building a team of agents for collaborative judging. |
| Dynamic Knowledge Graph Role-Playing: Multi-Agent System with dynamic, temporally-aware knowledge graphs | Builds dynamic, temporally-aware knowledge graphs for financial applications using a multi-agent system. It processes financial reports, news articles, and research papers to help traders analyze data, identify relationships, and uncover market insights. The system also utilizes diverse and optional element node deduplication techniques to ensure data integrity and optimize graph structure for financial decision-making. |
| Customer Service Discord Bot with Agentic RAG | Learn how to build a robust customer service bot for Discord using Agentic RAG. |
| Customer Service Discord Bot with Local Model | Learn how to build a robust customer service bot for Discord using Agentic RAG which supports local deployment. |
| Cookbook | Description |
|---|---|
| Video Analysis | Techniques for agents in video data analysis. |
| 3 Ways to Ingest Data from Websites with Firecrawl | Explore three methods for extracting and processing data from websites using Firecrawl. |
| Create AI Agents that work with your PDFs | Learn how to create AI agents that work with your PDFs using Chunkr and Mistral AI. |
For those who'd like to contribute code, we appreciate your interest in contributing to our open-source initiative. Please take a moment to review our contributing guidelines to get started on a smooth collaboration journey.🚀
We also welcome you to help CAMEL grow by sharing it on social media, at events, or during conferences. Your support makes a big difference!
For more information please contact camel-ai@eigent.ai
GitHub Issues: Report bugs, request features, and track development. Submit an issue
Discord: Get real-time support, chat with the community, and stay updated. Join us
X (Twitter): Follow for updates, AI insights, and key announcements. Follow us
Ambassador Project: Advocate for CAMEL-AI, host events, and contribute content. Learn more
@inproceedings{li2023camel,
title={CAMEL: Communicative Agents for "Mind" Exploration of Large Language Model Society},
author={Li, Guohao and Hammoud, Hasan Abed Al Kader and Itani, Hani and Khizbullin, Dmitrii and Ghanem, Bernard},
booktitle={Thirty-seventh Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems},
year={2023}
}
Special thanks to Nomic AI for giving us extended access to their data set exploration tool (Atlas).
We would also like to thank Haya Hammoud for designing the initial logo of our project.
We implemented amazing research ideas from other works for you to build, compare and customize your agents. If you use any of these modules, please kindly cite the original works: - TaskCreationAgent, TaskPrioritizationAgent and BabyAGI from Nakajima et al.: Task-Driven Autonomous Agent. [Example]
PersonaHub from Tao Ge et al.: Scaling Synthetic Data Creation with 1,000,000,000 Personas. [Example]
Self-Instruct from Yizhong Wang et al.: SELF-INSTRUCT: Aligning Language Models with Self-Generated Instructions. [Example]
The source code is licensed under Apache 2.0.
OWASP Maryam is a modular open-source framework based on OSINT and data gathering. It is designed to provide a robust environment to harvest data from open sources and search engines quickly and thoroughly.
$ pip install maryam
Alternatively, you can install the latest version with the following command (Recommended):
pip install git+https://github.com/saeeddhqan/maryam.git
# Using dns_search. --max means all of resources. --api shows the results as json.
# .. -t means use multi-threading.
maryam -e dns_search -d ibm.com -t 5 --max --api --form
# Using youtube. -q means query
maryam -e youtube -q "<QUERY>"
maryam -e google -q "<QUERY>"
maryam -e dnsbrute -d domain.tld
# Show framework modules
maryam -e show modules
# Set framework options.
maryam -e set proxy ..
maryam -e set agent ..
maryam -e set timeout ..
# Run web API
maryam -e web api 127.0.0.1 1313
Here is a start guide: Development Guide You can add a new search engine to the util classes or use the current search engines to write a new module. The best help to write a new module is checking the current modules.
To report bugs, requests, or any other issues please create an issue.