
It’s no longer possible to deny that your life in the physical world and your digital life are one and the same. Coming to terms with this reality will help you make better decisions in many aspects of your life.
The same identity you use at work, at home, and with friends also exists in apps, inboxes, accounts, devices, and databases, whether you actively post online or prefer to stay quiet. Every purchase, login, location ping, and message leaves a trail. And that trail shapes what people, companies, and scammers can learn about you, how they can reach you, and what they might try to take.
That’s why digital security isn’t just an IT or a “tech person” problem. It’s a daily life skill. When you understand how your digital life works, what information you’re sharing, where it’s stored, and how it can be misused, you make better decisions. This guide is designed to help you build that awareness and translate it into practical habits: protecting your data, securing your accounts, and staying in control of your privacy in a world that’s always connected.
Being digitally secure doesn’t mean hiding from the internet or using complicated tools you don’t understand. It means having intentional control over your digital life to reduce risks while still being able to live, work, and communicate online safely. A digitally secure person focuses on four interconnected areas:
Your personal data is the foundation of your digital identity. Protecting it includes limiting how much data you share, understanding where it’s stored, and reducing how easily it can be collected, sold, or stolen. At its heart, personal information falls into two critical categories that require different levels of protection:
Account security ensures that only you can access them. Strong, unique passwords, multi-factor authentication, and secure recovery options prevent criminals from hijacking your email, banking, cloud storage, social media, and other online accounts, often the gateway to everything else in your digital life.
Privacy control means setting boundaries and deciding who can see what about you, and under what circumstances. This includes managing social media visibility, app permissions, browser tracking, and third-party access to your data.
Digital security is an ongoing effort as threats evolve, platforms change their policies, and new technologies introduce new risks. Staying digitally secure requires periodic check-ins, learning to recognize scams and manipulation, and adjusting your habits as the digital landscape changes.
Your personal information faces exposure risks through multiple channels during routine digital activities, often without your explicit knowledge.
Implementing comprehensive personal data protection requires a systematic approach that addresses the common exposure points. These practical steps provide layers of security that work together to minimize your exposure to identity theft and fraud.
Start by conducting a thorough audit of your online accounts and subscriptions to identify where you have unnecessarily shared more data than needed. Remove or minimize details that aren’t essential for the service to function. Moving forward, provide only the minimum required information to new accounts and avoid linking them across different platforms unless necessary.
Be particularly cautious with loyalty programs, surveys, and promotional offers that ask for extensive personal information, as they may share it with third parties. Read privacy policies carefully, focusing on sections that describe data sharing, retention periods, and your rights regarding your personal information.
If possible, consider using separate email addresses for different accounts to limit cross-platform tracking and reduce the impact if one account is compromised. Create dedicated email addresses for shopping, social media, newsletters, and important accounts like banking and healthcare.
Privacy protection requires regular attention to your account settings across all platforms and services you use. Social media platforms frequently update their privacy policies and settings, often defaulting to less private configurations that allow them to collect and share your data. For this reason, it is a good idea to review your privacy settings at least quarterly. Limit who can see your posts, contact information, and friend lists. Disable location tracking, facial recognition, and advertising customization features that rely on your personal data. Turn off automatic photo tagging and prevent search engines from indexing your profile.
On Google accounts, visit your Activity Controls and disable Web & App Activity, Location History, and YouTube History to stop this data from being saved. You can even opt out of ad personalization entirely if desired by adjusting Google Ad Settings. If you are more tech savvy, Google Takeout allows you to export and review what data Google has collected about you.
For Apple ID accounts, you can navigate to System Preferences on Mac or Settings on iOS devices to disable location-based Apple ads, limit app tracking, and review which apps have access to your contacts, photos, and other personal data.
Meanwhile, Amazon accounts store extensive purchase history, voice recordings from Alexa devices, and browsing behavior. Review your privacy settings to limit data sharing with third parties, delete voice recordings, and manage your advertising preferences.
Regularly audit the permissions you’ve granted to installed applications. Many apps request far more permissions to your location, contacts, camera, and microphone even though they don’t need them. Cancel these unnecessary permissions, and be particularly cautious about granting access to sensitive data.
Create passwords that actually protect you; they should be long and complex enough that even sophisticated attacks can’t easily break them. Combine uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters to make it harder for attackers to crack.
Aside from passwords, enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) on your most critical accounts: banking and financial services, email, cloud storage, social media, work, and healthcare. Use authenticator apps such as Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or Authy rather than SMS-based authentication when possible, as text messages can be intercepted through SIM swapping attacks. When setting up MFA, ensure you save backup codes in a secure location and register multiple devices when possible to keep you from being locked out of your accounts if your primary authentication device is lost, stolen, or damaged.
Alternatively, many services now offer passkeys which use cryptographic keys stored on your device, providing stronger security than passwords while being more convenient to use. Consider adopting passkeys for accounts that support them, particularly for your most sensitive accounts.
Device encryption protects your personal information if your smartphone, tablet, or laptop is lost, stolen, or accessed without authorization. Modern devices typically offer built-in encryption options that are easy to enable and don’t noticeably impact performance.
You can implement automatic backup systems such as secure cloud storage services, and ensure backup data is protected. iOS users can utilize encrypted iCloud backups, while Android users should enable Google backup with encryption. Regularly test your backup systems to ensure they’re working correctly and that you can successfully restore your data when needed.
Identify major data brokers that likely have your information and look for their privacy policy or opt-out procedures, which often involves submitting a request with your personal information and waiting for confirmation that your data has been removed.
In addition, review your subscriptions and memberships to identify services you no longer use. Request account deletion rather than simply closing accounts, as many companies retain data from closed accounts. When requesting deletion, ask specifically for all personal data to be removed from their systems, including backups and archives.
Keep records of your opt-out and deletion requests, and follow up if you don’t receive confirmation within the stated timeframe. In the United States, key data broker companies include Acxiom, LexisNexis, Experian, Equifax, TransUnion, Whitepages, Spokeo, BeenVerified, and PeopleFinder. Visit each company’s website.
Connect only to trusted, secure networks to reduce the risk of your data being intercepted by attackers lurking behind unsecured or fake Wi-Fi connections. Avoid logging into sensitive accounts on public networks in coffee shops, airports, or hotels, and use encrypted connections such as HTTPS or a virtual private network to hide your IP address and block third parties from monitoring your online activities.
Rather than using a free VPN service that often collects and sells your data to generate revenue, it is better to choose a premium, reputable VPN service that doesn’t log your browsing activities and offers servers in multiple locations.
Cyber threats evolve constantly, privacy policies change, and new services collect different types of personal information, making personal data protection an ongoing process rather than a one-time task. Here are measures to help regularly maintain your personal data protection:
By implementing these systematic approaches and maintaining regular attention to your privacy settings and data sharing practices, you significantly reduce your risk of identity theft and fraud while maintaining greater control over your digital presence and personal information.
You don’t need to dramatically overhaul your entire digital security in one day, but you can start making meaningful improvements right now. Taking action today, even small steps, builds the foundation for stronger personal data protection and peace of mind in your digital life. Choose one critical account, update its password, enable multi-factor authentication, and you’ll already be significantly more secure than you were this morning. Your future self will thank you for taking these proactive steps to protect what matters most to you.
Every step you take toward better privacy protection strengthens your overall digital security and reduces your risk of becoming a victim of scams, identity theft, or unwanted surveillance. You’ve already taken the first step by learning about digital security risks and solutions. Now it’s time to put that knowledge into action with practical steps that fit seamlessly into your digital routine.
The post What Does It Take To Be Digitally Secure? appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Social media platforms connect you to thousands of people worldwide. But while these platforms offer incredible opportunities for bonding, learning, and entertainment, they also present personal security challenges. Navigating them safely requires being aware of risks and proactively protecting your accounts.
The three most common risks you’ll encounter are privacy exposure, account takeover, and scams. Privacy exposure occurs when your personal information becomes visible to unintended audiences, potentially leading to identity theft, stalking, or professional damage. You have control over your social media security. By implementing safe social media practices, you can dramatically reduce your risk exposure.
This guide rounds up 15 practical, everyday tips to help you secure your accounts and use them more safely. It covers smart posting habits, safer clicking and app-permission choices, stronger privacy settings, and core security basics like using updated browsers, reliable protection tools, and identity-theft safeguards—so you can enjoy social media without making yourself an easy target.
Before we dive in, we want to remind you first that our strongest recommendation amid anything and everything unsolicited, unusual, or suspicious on social media is this: verify, verify, verify through separate communication channels such as phone, email, and official websites.
Not a day goes by when we don’t hear about a new hack. With 450,000 new pieces of malware released to the internet every day, security never sleeps. For your increased awareness, here’s a short list of the most common social media scams:
Social media is quite engaging, with all the funny status updates, photos, and comments. However, all these bits of information can reveal more about you than you intended to disclose. The examples below might be extreme, but they are real-world scenarios that continue to happen to real people daily on social media:
Oversharing on social media creates significant risks that extend beyond embarrassment or regret. Identity thieves actively monitor social platforms for personal information they can use to answer security questions, predict passwords, or impersonate you in social engineering attacks.
Avoid publicly answering questionnaires with details like your middle name, as this is the type of information financial institutions—and identity thieves—may use to verify your identity.
Third-party apps with excessive permissions can access your personal data, post to social media at any time on your behalf, or serve as entry points for attackers, regardless of whether you’re using the application. To limit app access and reduce your attack surface significantly, review all apps and services connected to your social media accounts. Revoke permissions to applications you no longer use or don’t remember authorizing.
Shortened links can be exploited in social media phishing attacks as they hide the final destination URL, making it difficult for you to determine where it actually leads. These tactics mimic legitimate communications from trusted sources and come in the form of direct messages, comments, sponsored posts, and fake verification alerts, all in an effort to steal your personal information, login credentials, or financial details. Often, these attacks appear as urgent messages claiming your account will be suspended or fake prize notifications.
When you identify phishing attempts, immediately report and block the suspicious accounts using the platform’s built-in reporting features. This will protect not only you but other users on the platform.
If the link is posted by a product seller or service provider, it is a good idea to:
You might think the video or link relates directly to you. But when you click it, you get a message saying that you need to upgrade your video player in order to see the clip. When you attempt to download the “upgrade,” the malicious page will instead install malware that tracks and steals your data. As mentioned, don’t click suspicious links or download files from unknown sources before verifying independently. Visit the official websites by directly typing the URL yourself or using trusted search engines.
This also brings us to the related topic of being tagged on other people’s content. If you don’t want certain content to be associated with you, adjust the settings that enable you to review posts and photos before they appear on your profile. This allows you to maintain control over your digital presence and prevents embarrassing or inappropriate content associations.
If one of your friends posts, “We’re stuck in Cambodia and need money,” keep your radar up as it’s most likely a scam. It is possible that a scammer has taken over your friend’s account, and is using it to impersonate them, spread malicious content, or extract sensitive information from their contacts, including you. Don’t engage with this post or the fraudster, otherwise the next account takeover could be yours.
In this kind of scam, some critical areas of your life are affected:
When you encounter suspicious activity, always use official support pages rather than responding to questionable messages. Major social media platforms provide dedicated help centers and verified contact methods.
Select the most secure options and check periodically for changes that can open up your profile to the public. Depending on your preference and the privacy level you are comfortable with, you can choose from these options:
We suggest that you review your privacy settings every three months, as platforms frequently update their policies and default settings. While you are at it, take the opportunity to audit your friend lists and remove inactive or suspicious accounts.
Posting real-time locations or check-ins can alert potential stalkers to your whereabouts and routine patterns, while geo-tagged photos can reveal where you live, study, work, shop, or work out. Location sharing creates patterns that criminals can exploit for security threats such as stalking, harassment, and other physical crimes.
To avoid informing scammers of your whereabouts, turn off location tagging in your social media apps and avoid posting about your routine. You might also consider disabling “last seen” or “active now” indicators that show when you’re online. This prevents others from monitoring your social media activity patterns and reduces unwanted contact attempts, significantly improving your personal and family safety while maintaining your ability to share experiences.
Older browsers tend to have more security flaws and often don’t recognize newer scam patterns, while updated versions are crucial for security by patching vulnerabilities. Updates add or improve privacy controls such as tracking prevention, cookie partitioning, third-party cookie blocking, stronger HTTPS enforcement, transparent permission prompts. They also support newer HTML/CSS/JavaScript features, video and audio codecs, payment and login standards, and accessibility features.
In terms of performance, new browser versions offer faster performance, better memory management, and more efficient rendering, so you get fewer freezes, less fan noise, and longer battery life and better extension compatibility.
Consider using password managers, which can create and store secure passwords for you. Never reuse passwords across platforms. This practice ensures that if one account is compromised, your other accounts remain secure. Password managers also help you monitor for breached credentials and update passwords regularly.
In addition, implement multi-factor authentication (MFA)on every social media account using authenticator apps. This single step can protect social media accounts from 99% of automated attacks. MFA enforcement should be non-negotiable for both personal and business accounts, as it adds critical security that makes account takeovers exponentially more difficult.
Scammers build fake login pages that look identical to real ones. The only obvious difference is usually the domain. They want you to type your username/password into their site, so they can steal it. So if you’re visiting a Facebook page, make sure you look for the https://www.facebook.com address.
The rule is to read the domain from right to left because the real domain is usually the last two meaningful segments before the slash. For instance, https://security.facebook.com—read from right to left—is legitimate because the main domain is facebook.com, and “security” is just a subdomain.
Watch out for scam patterns such as:
Within the social media platform, scammers often insert a “second” sign-in step to capture your credentials. A common trick is sending you to a page that looks like a normal email, business, or bank website but then suddenly asks you to log in again “to continue,” “to verify your identity,” or “because your session expired.” That extra login prompt is frequently a fake overlay or a malicious look-alike page designed to steal passwords.
Clicking a shared document link, viewing a receipt, or checking a delivery status usually shouldn’t require you to re-enter your email and password—especially if you’re already signed in elsewhere. Another example is a fake security notification claiming your account has been compromised, directing you to another page or website that requires a new login. Attackers usually rely on urgency, panic, and habit; you might be so used to logging in all the time, that you could do it automatically without noticing the context is wrong.
A safer habit is to stop and reset the flow. If something unexpectedly asks for another login, don’t use the embedded prompt. Instead, open a new tab, type the site’s official address yourself, check account status, and log in there if needed. If the request was legitimate, it will still work once you’re signed in through the official site; if it was a trap, you’ve just avoided handing over your credentials.
Your suite should include an antivirus, anti-spyware, anti-spam, a firewall, and a website safety advisor. Keeping your security suite up to date is essential as threats evolve daily, and outdated protection can miss new malware, phishing kits, ransomware variants, and scam techniques. Updates also patch security weaknesses in the software itself, improve detection technologies, and add protections for newer attack methods.
The McAfee Social Privacy Manager extends “security updates” beyond your device and into your social media footprint by scanning your privacy settings across supported platforms, flagging exposures, and recommending safer configurations. Because social platforms frequently change their settings and defaults, Social Privacy Manager also needs to stay updated to recognize and apply the right privacy protections.
Regardless of how careful you may be or any security systems you put in place, there is always a chance that you can be compromised in some way. It’s nice to have identity theft protection watching your back.
McAfee+ combines every day device security with identity monitoring in one suite. Depending on the plan, McAfee+ can watch for your personal info on the dark web and breach databases, monitor financial and credit activity, and send real-time alerts for anomalies. The Advanced and Ultimate plans add wider support such as credit monitoring and tracking for bank or investment accounts, as well as tools that reduce your exposure such as Personal Data Cleanup that removes your info from data broker sites. It doesn’t just warn you after a breach; it helps shrink the chances your data gets misused in the first place.
Social media brings incredible opportunities, but privacy exposure, scams, and account takeovers remain real challenges that can impact your finances, reputation, and personal security. The tips outlined above give you practical ways to recognize the risks and protect your social media accounts. By raising your level of awareness and applying safe social media practices, you are building a stronger defense against evolving threats.
Make security a family affair by sharing these safe social media practices with everyone in your household—especially children and teens who use social media—so they can enjoy a safer experience.
The post 15 Critical Tips to Stay Safe on Social Media appeared first on McAfee Blog.

The malware landscape is growing more complex and costly by the minute, as indicated by the rising number of cyberattacks that grow each year. According to the Federal Bureau of Investigation, in 2024, approximately $1.4 million in losses were reported due to malware. Meanwhile, complaints of ransomware, a type of malware that locks your files until a ransom is paid to release them, rose by 9% from the year prior, with losses totaling nearly $12.5 million.
With the continued growth of e-commerce, online banking, and artificial intelligence, we can count on even more new cyber threats for all kinds of devices—be it Android, iPhone, PC, or Mac. No device under your family’s roof is immune to cyberattacks. As we speak, one or more of your devices may have already been infected. But would you know it?
In this blog, we’ll dive into the types of viruses and malware that infiltrate devices and their indications, the ways you can remove them, and tips to protect your phones moving forward.
Malware is malicious software designed to harm your device, steal your personal information, or disrupt your digital life. On mobile devices, malware can take many forms—from apps that secretly collect your data to programs that bombard you with unwanted ads or even lock your device for ransom.
Mobile devices, including smartphones and tablets, can be infected with malware and other digital threats, even when their operating systems have built-in security features. How does this happen? Your phone can catch viruses and malware in several ways:
Malware doesn’t always announce itself with a big flashing sign. On the contrary, it slips quietly into your devices and starts causing trouble behind the scenes. Before long, you will see noticeable changes in its behavior. Here are five key signs of malware or a virus to watch for and catch the problem early, before the damage spreads:
As our phones and tablets become extensions of our daily lives, cybercriminals have developed sophisticated malware explicitly designed to infiltrate them, such as:
Sometimes the warning signs are obvious, but at other times, malware operates quietly in the background, stealing data or draining resources without drawing attention. Find out for sure if your device has a virus or malware by following these steps:
Here are more specific measures to ascertain the presence of a virus or malware, based on your mobile device’s operating system:
If you discover malicious apps and profiles in your phone, a clear, step-by-step action plan will help you remove them and restore your device to a secure state. Here’s how to tackle mobile malware confidently and get your device back to normal:
With a few smart habits and simple tools, you can create a safer digital environment for your family members. Here are some practical ways to safeguard family devices and keep threats at bay.
While the threat of malware and viruses continues to evolve, you now have the knowledge and tools to stay digitally protected. The signs we’ve discussed—from unexpected device behavior to suspicious pop-ups—serve as warnings, helping you catch problems before they escalate into major security incidents.
Your best defense combines proactive security measures and vigilant behavior. Applying simple, solid digital habits such as updating software, using strong passwords, and staying alert to suspicious activity will thwart the vast majority of common threats. By incorporating these practices into your routine, along with the right online security tools, you are building a robust defense that works around the clock.
The post 5 Signs Your Device May be Infected with Malware or a Virus appeared first on McAfee Blog.

From their original design as simple broadcast receivers, today’s televisions have evolved into powerful, internet-connected entertainment hubs. Combining traditional viewing with online capabilities, smart TVs provide instant access to streaming platforms, web browsing, voice assistants, and personalized recommendations.
As our TVs have grown smarter, however, they’ve also become gateways to new privacy and security challenges. In a chilling echo of George Orwell’s dystopian novel 1984, it’s possible that Big Brother, or in this case, Big Hacker, might be surveilling you through your own television.
In 2013, evidence emerged that smart TVs can be just as vulnerable to hacking as home computers, following an investigation by security analysts Aaron Grattafiori and Josh Yavor at iSEC Partners. Working with smart TV manufacturers to address potential vulnerabilities, the analysts presented their findings at the Black Hat network security conference in Las Vegas. Their demonstration highlighted the concerning possibility of smart TVs not only physically surveilling you through the built-in camera but also prying deeper into your personal life by collecting data on your web searches, app usage, and preferences.
Smart TVs can be hacked in several ways, but the gateway that opens your smart TV to these attacks is the IP address, which links with internet-driven apps such as Facebook and YouTube, as well as video streaming services, microphones, and even internal cameras. Because smart TVs often run the same code as computers and smartphones, such as JavaScript or HTML5, they are also susceptible to malware and spyware attacks. These are some of the ways your device can be hacked:
Once a hacker has compromised your smart TV, they can spy on you through several built-in technologies that collect data on your viewing habits, conversations, and online activities.
The key to managing these privacy risks is understanding what data your TV collects and taking control through privacy settings, network restrictions, and informed usage decisions.
Your smart TV data typically flows to multiple parties. It starts with the device manufacturer for product improvements, then to streaming app providers for content recommendations, on to advertising networks for targeted marketing, and analytics companies for usage insights. Recent regulatory guidance emphasizes that you should have clear visibility into these data-sharing relationships through your TV’s privacy policy.
You can limit data collection by disabling Automatic Content Recognition (ACR) in your TV’s privacy settings, turning off personalized advertising, and regularly reviewing app permissions. Consumer protection agencies require smart TV manufacturers to provide opt-out mechanisms for advertising personalization and data sharing with third parties.
Fortunately, you can significantly reduce your smart TV risks with some simple preventive measures:
Most smart TVs don’t fully turn off when you press the power button; they enter standby mode to enable quick startup. In this state, certain components may remain active and continue collecting data. It might maintain network connectivity to receive software updates, keep microphones and voice assistants ready to respond to wake words, or continue ACR that tracks your viewing habits.
To truly disconnect your TV from potential monitoring, you have several options:
It depends on your specific smart TV model and its manufacturing date. Most modern smart TVs manufactured after 2022 do not include built-in cameras. Major manufacturers such as Samsung, LG, Sony, and TCL have largely moved away from integrating cameras directly into their television sets due to privacy concerns and limited consumer adoption.
Some premium models and older smart TVs from 2018-2021 may still feature built-in cameras designed typically used for:
If your smart TV does have a camera, you still have control, as most smart TVs with cameras include physical privacy shutters, software controls to disable the camera, or the option to cover the lens. For external USB cameras, simply unplugging it ensures that no one can see you through the smart TV.
To determine if your smart TV has a camera, check the following:
If you discover your smart TV has a camera, you can take control of your privacy by disabling it in your TV’s settings, covering it with tape when not in use, or using any built-in privacy shutters.
Aside from the precautions listed above, there are other ways you can disable your smart TV’s camera:
If the thought of your living room turning into a hacker’s surveillance paradise sends a chill down your spine, you’re not alone. Fortunately, you can take some protective measures that keep your smart TV safe.
One of the best ways to protect yourself is to stay informed about the latest developments in smart TV security. Attend webinars, read articles, and follow experts in the field to stay current with the latest security threats and fixes.
Just as importantly, small but effective digital habits will also fortify your smart TV security: keep your TV’s firmware updated, stick to official app stores, secure your home Wi-Fi with strong encryption, use unique passwords for your devices, limit the use of social media and messaging apps on your TV, and be cautious about what you plug into your TV’s ports.
By following these recommendations, you can continue to relax in your living room and enjoy your digital entertainment experience without compromising your privacy and security.
The post How To Tell If Your Smart TV Spying on You appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Malicious software, also called malware, refers to any program or code engineered to harm or exploit computer systems, networks and devices. It affects your phone’s functionality, especially if you jailbreak your device—that is, opening your iOS to additional features, apps, and themes.
The risks associated with a malware infection can range from poor device performance to stolen data. Cybercriminals typically use it to extract data—from financial data and healthcare records to emails and passwords—that they can leverage over victims for financial gain.
Thanks to their closed ecosystem, built-in security features, and strict policies on third-party apps, Apple devices tend to be generally resilient against malware infections. It’s important to note, however, that they’re not completely without vulnerabilities.
Read on to learn how you can detect malware on your iPhone and how to remove these infections so you can get back to enjoying your digital activities.
While traditional self-replicating viruses are rare on iPhones, malware is a genuine threat for Apple devices. Malware typically enters through links in deceptive texts or emails or through downloaded, unvetted apps rather than system-wide infection. These are some types of malware that could infect your iPhone:
To keep you safe against malware and other threats, Apple engineers the iPhone with multiple security layers, including:
Together, these features create a highly secure environment for iPhones. However, this robust shield does not eliminate all risks, as threats can still bypass these defenses through phishing scams or by tricking a user into installing a malicious configuration profile.
If your iPhone is exhibiting these odd activities listed below, a manual scan is your first point of order. These quick actions are free to do as they are already integrated into your device.
The disadvantage of doing a manual scan is that it requires effort. In addition, it does not detect sophisticated malware, and only identifies symptoms rather than root causes.
If your iPhone persistently exhibits any of the red flags above despite your quick actions, you may have to investigate using a third-party security app to find the threats that manual checks don’t catch.
Compared with manual or built-in scans, third-party solutions like McAfee Mobile Security offer automated, comprehensive malware scans by detecting a wider range of threats before they enter your digital space. While available at a premium, third-party security suites offer great value as they include full-scale protection that includes a safe browsing feature to protect your digital life and a virtual private network (VPN) for a more secure internet connection.
If the scan confirms the presence of malware on your iPhone, don’t worry. There’s still time to protect yourself and your data. Below is an action plan you can follow to remove malware from your device.
In many cases, hackers exploit outdated versions of iOS to launch malware attacks. If you don’t have the latest version of your operating system, it’s a good idea to update your iOS immediately to close this potential vulnerability. To do this, go to Settings > General > Software Update and follow the instructions to update your iPhone.
It might sound simple, but restarting your device can fix certain issues. The system will restart on its own when updating the iOS. If you already have the latest version, restart your iPhone now.
If updating the iOS and restarting your device didn’t fix the issue, try clearing your phone’s browsing history and data. If you’re using Safari, go to Settings > Clear History and Website Data > Clear History and Data. Keep in mind that the process is similar for Google Chrome and most other popular web browsers.
Malicious software, such as spyware and ransomware, often end up on phones by masquerading as legitimate apps. To err on the side of caution, delete any apps that you don’t remember downloading or installing.
The option to restore to a previous backup is one of the most valuable features found on the iPhone and iPad. This allows you to restore your device to an iCloud backup version that was made before the malware infection. Go to Settings > General > Transfer or Reset iPhone > Erase All Content and Settings > Restore from iCloud Backup.
A factory reset should be your last resort when other removal methods have failed, as it is a complete data wipe. That means it will erase all content and settings, including any malicious apps, profiles, or files, returning the software to its original, out-of-the-box state. That’s why it’s crucial to back up your essential data such as photos and contacts first. Also, remember to restore to an iCloud backup version *before* the malware infection to avoid reintroducing the infection. For the highest level of security, set the iPhone up as new and manually redownload trusted apps from the App Store. When you are ready to reset, go to Settings > General > Transfer or Reset iPhone > Erase All Content and Settings > Set Up as New iPhone.
Spyware is designed to be sneaky, but it leaves subtle traces. Pay attention to your iPhone’s behavior, such as the camera or microphone unexpectedly activating as indicated by a green or orange dot in the status bar, sudden battery drain, or your device overheating for no reason. Another major red flag is a spike in data usage when you aren’t actively using your phone.
For a deeper look, do this 5-minute check to see which apps have accessed your data, camera, and microphone. Look for any activity that seems suspicious or that you don’t recall authorizing.
If you suspect your iPhone has been compromised, it’s important to act quickly. Here’s a step-by-step process to remove it, restore your privacy, and prevent future threats.
A common tactic used by scammers is the fake virus pop-up. These alarming messages appear while you are browsing, often using logos from Apple or other trusted companies, and claim your iPhone is infected. Their goal is to create panic, urging you to click a link, download a fake app, or call a fraudulent support number. Never interact with these pop-ups. Here’s a quick response plan when dealing with fake virus pop-up ads:
Never enter personal information, passwords, or payment details on a page that appears from a pop-up ad.
The best way to protect your iOS device is to avoid malware in the first place. Follow these security measures to safeguard your device:
Can my iPhone get a virus from opening an email?
Simply opening an email is very unlikely to infect your iPhone. However, clicking a malicious link or downloading an attachment from a phishing email can lead you to a harmful website or trick you into compromising your information. It’s the action you take, not opening the email itself, that creates the risk.
How do I know if a virus warning is real or fake?
Any pop-up in your browser that claims your iPhone has a virus is fake. Apple does not send notifications like this. These are scare tactics designed to trick you into clicking a link or calling a fake support number. The safest response is to close the browser tab and clear your browsing data.
Does my iPhone really need antivirus software?
It’s a misconception that iPhones are immune to all viruses. While Apple’s built-in security provides a strong defense, it doesn’t offer complete protection. Cybercriminals are increasingly using phishing, smishing, AI voice cloning, deepfake videos and other social engineering methods to target iPhone users. A comprehensive security app provides layered protection beyond the iOS integrated security. Think of it as adding a professional security guard to already-strong walls.
What is the best way to check my iPhone for a virus or malware for free?
You can perform manual checks for free by looking for suspicious apps, checking for unusual battery drain and data usage, and reviewing your App Privacy Report. While helpful for spotting obvious issues, these manual checks aren’t foolproof. A dedicated security app offers a more reliable and thorough analysis.
Can an iPhone get malware without jailbreaking it?
Yes. While jailbreaking significantly increases the risk, malware can still infect a non-jailbroken iPhone. This typically happens through sophisticated phishing attacks, installing malicious configuration profiles from untrusted sources, or, in very rare cases, by exploiting an unknown vulnerability in iOS, known as a “zero-day” attack.
Is an iPhone malware scan truly necessary?
Given the value of the personal data on our phones, a regular malware scan provides significant peace of mind. A reputable security app can identify vulnerabilities you might miss, such as outdated software or risky system settings, helping you maintain a strong security posture.
Keeping your iPhone secure from malware is an achievable goal that puts you in control of your digital safety. By combining smart habits with powerful security tools, you can confidently protect your personal information from emerging threats.
McAfee is committed to empowering you with the resources and protection needed to navigate the online world safely. McAfee Mobile Security provides full protection against various types of malware targeting the Apple ecosystem. With safe browsing features, a secure VPN, and antivirus software, McAfee Security for iOS delivers protection against emerging threats, so you can continue to use your iPhone with peace of mind. Download the McAfee Mobile Security app today and get all-in-one protection.
The post A Guide to Remove Malware From Your iPhone appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Phishing attacks increased nearly 40 percent in the year ending August 2024, with much of that growth concentrated at a small number of new generic top-level domains (gTLDs) — such as .shop, .top, .xyz — that attract scammers with rock-bottom prices and no meaningful registration requirements, new research finds. Meanwhile, the nonprofit entity that oversees the domain name industry is moving forward with plans to introduce a slew of new gTLDs.

Image: Shutterstock.
A study on phishing data released by Interisle Consulting finds that new gTLDs introduced in the last few years command just 11 percent of the market for new domains, but accounted for roughly 37 percent of cybercrime domains reported between September 2023 and August 2024.
Interisle was sponsored by several anti-spam organizations, including the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG), the Coalition Against Unsolicited Commercial Email (CAUCE), and the Messaging, Malware, and Mobile Anti-Abuse Working Group (M3AAWG).
The study finds that while .com and .net domains made up approximately half of all domains registered in the past year (more than all of the other TLDs combined) they accounted for just over 40 percent of all cybercrime domains. Interisle says an almost equal share — 37 percent — of cybercrime domains were registered through new gTLDs.
Spammers and scammers gravitate toward domains in the new gTLDs because these registrars tend to offer cheap or free registration with little to no account or identity verification requirements. For example, among the gTLDs with the highest cybercrime domain scores in this year’s study, nine offered registration fees for less than $1, and nearly two dozen offered fees of less than $2.00. By comparison, the cheapest price identified for a .com domain was $5.91.
Currently, there are around 2,500 registrars authorized to sell domains by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN), the California nonprofit that oversees the domain industry.
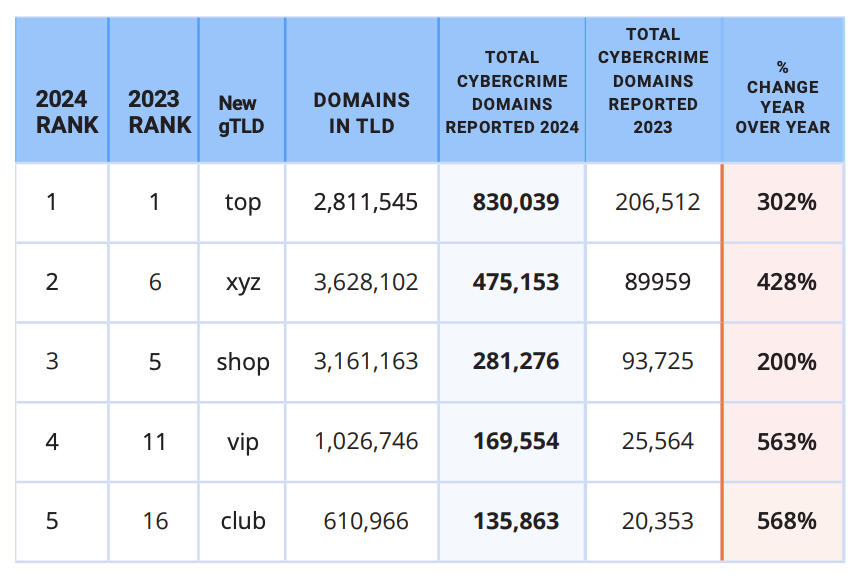
The top 5 new gTLDs, ranked by cybercrime domains reported. Image: Interisle Cybercrime Supply Chain 2014.
Incredibly, despite years of these reports showing phishers heavily abusing new gTLDs, ICANN is shuffling forward on a plan to introduce even more of them. ICANN’s proposed next round envisions accepting applications for new gTLDs in 2026.
John Levine is author of the book “The Internet for Dummies” and president of CAUCE. Levine said adding more TLDs without a much stricter registration policy will likely further expand an already plentiful greenfield for cybercriminals.
“The problem is that ICANN can’t make up their mind whether they are the neutral nonprofit regulator or just the domain speculator trade association,” Levine told KrebsOnSecurity. “But they act a lot more like the latter.”
Levine said the vast majority of new gTLDs have a few thousand domains — a far cry from the number of registrations they would need just to cover the up-front costs of operating a new gTLD (~$180,000-$300,000). New gTLD registrars can quickly attract customers by selling domains cheaply to customers who buy domains in bulk, but that tends to be a losing strategy.
“Selling to criminals and spammers turns out to be lousy business,” Levine said. “You can charge whatever you want on the first year, but you have to charge list price on domain renewals. And criminals and spammers never renew. So if it sounds like the economics makes no sense it’s because the economics makes no sense.”
In virtually all previous spam reports, Interisle found the top brands referenced in phishing attacks were the largest technology companies, including Apple, Facebook, Google and PayPal. But this past year, Interisle found the U.S. Postal Service was by far the most-phished entity, with more than four times the number of phishing domains as the second most-frequent target (Apple).
At least some of that increase is likely from a prolific cybercriminal using the nickname Chenlun, who has been selling phishing kits targeting domestic postal services in the United States and at least a dozen other countries.
Interisle says an increasing number of phishers are eschewing domain registrations altogether, and instead taking advantage of subdomain providers like blogspot.com, pages.dev, and weebly.com. The report notes that cyberattacks hosted at subdomain provider services can be tough to mitigate, because only the subdomain provider can disable malicious accounts or take down malicious web pages.
“Any action upstream, such as blocking the second-level domain, would have an impact across the provider’s whole customer base,” the report observes.
Interisle tracked more than 1.18 million instances of subdomains used for phishing in the past year (a 114 percent increase), and found more than half of those were subdomains at blogspot.com and other services operated by Google.
“Many of these services allow the creation of large numbers of accounts at one time, which is highly exploited by criminals,” the report concludes. “Subdomain providers should limit the number of subdomains (user accounts) a customer can create at one time and suspend automated, high-volume automated account sign-ups – especially using free services.”
Dec. 4, 10:21 a.m. ET: Corrected link to report.

McAfee threat researchers have identified several consumer brands and product categories most frequently used by cybercriminals to trick consumers into clicking on malicious links in the first weeks of this holiday shopping season. As holiday excitement peaks and shoppers hunt for the perfect gifts and amazing deals, scammers are taking advantage of the buzz. The National Retail Federation projects holiday spending will reach between $979.5 and $989 billion this year, and cybercriminals are capitalizing by creating scams that mimic the trusted brands and categories consumers trust. From October 1 to November 12, 2024, McAfee safeguarded its customers from 624,346 malicious or suspicious URLs tied to popular consumer brand names – a clear indication that bad actors are exploiting trusted brand names to deceive holiday shoppers.
McAfee’s threat research also reveals a 33.82% spike in malicious URLs targeting consumers with these brands’ names in the run-up to Black Friday and Cyber Monday. This rise in fraudulent activity aligns with holiday shopping patterns during a time when consumers may be more susceptible to clicking on offers from well-known brands like Apple, Yeezy, and Louis Vuitton, especially when deals seem too good to be true – pointing to the need for consumers to stay vigilant, especially with offers that seem unusually generous or come from unverified sources.
McAfee threat researchers have identified a surge in counterfeit sites and phishing scams that use popular luxury brands and tech products to lure consumers into “deals” on fake e-commerce sites designed to appear as official brand pages. While footwear and handbags were identified as the top two product categories exploited by cybercrooks during this festive time, the list of most exploited brands extends beyond those borders:
By mimicking trusted brands like these, offering unbelievable deals, or posing as legitimate customer service channels, cybercrooks create convincing traps designed to steal personal information or money. Here are some of the most common tactics scammers are using this holiday season:
With holiday shopping in full swing, it’s essential for consumers to stay one step ahead of scammers. By understanding the tactics cybercriminals use and taking a few precautionary measures, shoppers can protect themselves from falling victim to fraud. Here are some practical tips for safe shopping this season:
McAfee’s threat research team analyzed malicious or suspicious URLs that McAfee’s web reputation technology identified as targeting customers, by using a list of key company and product brand names—based on insights from a Potter Clarkson report on frequently faked brands—to query the URLs. This methodology captures instances where users either clicked on or were directed to dangerous sites mimicking trusted brands. Additionally, the team queried anonymized user activity from October 1st through November 12th.
The image below is a screenshot of a fake / malicious / scam site: Yeezy is a popular product brand formerly from Adidas found in multiple Malicious/Suspicious URLs. Often, they present themselves as official Yeezy and/or Adidas shopping sites.

The image below is a screenshot of a fake / malicious / scam site: The Apple brand was a popular target for scammers. Many sites were either knock offs, scams, or in this case, a fake customer service page designed to lure users into a scam.

The image below is a screenshot of a fake / malicious / scam site: This particular (fake) Apple sales site used Apple within its URL and name to appear more official. Oddly, this site also sells Samsung Android phones.

The image below is a screenshot of a fake / malicious / scam site: This site, now taken down, is a scam site purporting to sell Nike shoes.

The image below is a screenshot of a fake / malicious / scam site: Louis Vuitton is a popular brand for counterfeit and scams. Particularly their handbags. Here is one site that was entirely focused on Louis Vuitton Handbags.

The image below is a screenshot of a fake / malicious / scam site: This site presents itself as the official Louis Vuitton site selling handbags and clothes.

The image below is a screenshot of a fake / malicious / scam site: This site uses too-good-to-be-true deals on branded items including this Louis Vuitton Bomber jacket.

The image below is a screenshot of a fake / malicious / scam site: Rolex is a popular watch brand for counterfeits and scams. This site acknowledges it sells counterfeits and makes no effort to indicate this on the product.

The post This Holiday Season, Watch Out for These Cyber-Grinch Tricks Used to Scam Holiday Shoppers appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Two-step verification, two-factor authentication, multi-factor authentication…whatever your social media platform calls it, it’s an excellent way to protect your accounts.
There’s a good chance you’re already using multi-factor verification with your other accounts — for your bank, your finances, your credit card, and any number of things. The way it requires an extra one-time code in addition to your login and password makes life far tougher for hackers.
It’s increasingly common to see nowadays, where all manner of online services only allow access to your accounts after you’ve provided a one-time passcode sent to your email or smartphone. That’s where two-step verification comes in. You get sent a code as part of your usual login process (usually a six-digit number), and then you enter that along with your username and password.
Some online services also offer the option to use an authenticator app, which sends the code to a secure app rather than via email or your smartphone. Authenticator apps work much in the same way, yet they offer three unique features:
Google, Microsoft, and others offer authenticator apps if you want to go that route. You can get a good list of options by checking out the “editor’s picks” at your app store or in trusted tech publications.
Whichever form of authentication you use, always keep that secure code to yourself. It’s yours and yours alone. Anyone who asks for that code, say someone masquerading as a customer service rep, is trying to scam you. With that code, and your username/password combo, they can get into your account.
Passwords and two-step verification work hand-in-hand to keep you safer. Yet not any old password will do. You’ll want a strong, unique password. Here’s how that breaks down:
Now, with strong passwords in place, you can get to setting up multi-factor verification on your social media accounts.
When you set up two-factor authentication on Facebook, you’ll be asked to choose one of three security methods:
And here’s a link to the company’s full walkthrough: https://www.facebook.com/help/148233965247823
When you set up two-factor authentication on Instagram, you’ll be asked to choose one of three security methods: an authentication app, text message, or WhatsApp.
And here’s a link to the company’s full walkthrough: https://help.instagram.com/566810106808145
And here’s a link to the company’s full walkthrough: https://faq.whatsapp.com/1920866721452534
And here’s a link to the company’s full walkthrough: https://support.google.com/accounts/answer/185839?hl=en&co=GENIE.Platform%3DDesktop
1. TapProfileat the bottom of the screen.
2. Tap the Menu button at the top.
3. Tap Settings and Privacy, then Security.
4. Tap 2-step verification and choose at least two verification methods: SMS (text), email, and authenticator app.
5. Tap Turn on to confirm.
And here’s a link to the company’s full walkthrough: https://support.tiktok.com/en/account-and-privacy/personalized-ads-and-data/how-your-phone-number-is-used-on-tiktok
The post How to Protect Your Social Media Passwords with Multi-factor Verification appeared first on McAfee Blog.

What is malware? A dictionary-like definition is “malicious software that attacks computers, smartphones, and other connected devices.”
In fact, “malware” is a mash-up of “malicious software.” It describes any type of software or code specifically designed to exploit a connected device or network without consent. And, unsurprisingly, hackers design most of it for financial gain.
Think of malware as an umbrella term that covers an entire host of “bad stuff,” such as:
Spyware that tracks activity, like what you type and where you type it. (Think snooping on your bank account logins.
Ransomware that holds devices or the data on them hostage, that hackers only release for a price. (And even so, payment is no guarantee you’ll get back your access.)
Adware that serves up spammy ads on your device. (The hacker gets paid for the number of “impressions” the ads have. The more they show up on people’s devices, the more they get paid.)
Botnet software, that hijacks a device into a remote-controlled network of other devices. (These networks are used to shut down websites or even shut down large portions of the internet, just to mention two of the things they can do.)
Rootkit that attacks that give hackers remote-control access to a device. (And with that control, they can wage all manner of attacks — on the device and on other devices too.)
Viruses that modify the way a device and its apps function. Also, they can effectively bring a device or network to a grinding halt. (Yes, viruses are a subset of malware. They can copy, delete, and steal data, among other things.)
You might know malware by its more commonly used name — viruses.
There’s a pretty good reason why people commonly refer to malware as a “virus.” Viruses have been on our collective minds for some time.
Viruses have a long history. You could call it “the original malware.” And depending on how you define what a virus is, the first one took root in 1971 — more than 50 years ago. It was known as Creeper, and rather than being malicious in nature, the creator designed it to show how a self-replicating program could spot other devices on a network, transfer itself to them, and find yet more devices to repeat the process. Later, the same programmer who created a refined version of Creeper developed Reaper, a program that could remove the Creeper program. In a way, Reaper could be considered the first piece of antivirus software.[i]
From there, it wasn’t until the 1980s that malware started affecting the broader population, a time when computers became more commonplace in businesses and people’s homes.
At first, malware typically spread by infected floppy disks, much like the “Brain” virus in 1986. While recognized today as the first large-scale computer virus, its authors say they never intended it to work that way. Rather, they say they created Brain as an anti-piracy measure to protect their proprietary software from theft. However, Brain got loose. It went beyond their software and affected computers worldwide. Although not malicious or destructive in nature, Brain most certainly put the industry, businesses, and consumers on notice. Computer viruses were a thing.[ii]
Another piece of malware that got passed along via floppy disks was the “PC Cyborg” attack that targeted the medical research community in and around 1989. There, the malware would lie in wait until the user rebooted their computer for the 90th time and was presented with a digital ransom note.[iii]
An early example of ransomware – Source, Wikipedia
Upon that 90th boot, PC Cyborg encrypted the computer’s files, which would only get unencrypted if the victim paid a fee, making it the first documented form of ransomware.
Shortly thereafter, the internet started connecting computers, which opened millions of doors for hackers as people went online. Among the most noteworthy was 1999’s “Melissa” virus, which spread by way of infected email attachments and overloaded hundreds of corporate and governmental email servers worldwide.
It was quickly followed in 2000 by what’s considered among the most damaging malware to date — ILOVEYOU, which also spread by way of an attachment, this one posing as a love letter. Specifically, it was a self-replicating worm that installed itself on the victim’s computer where it destroyed some info and stole other info, then spread to other computers. One estimate put the global cost of ILOVEYOU at $10 billion. It further speculated that it infected 10% of the world’s internet-connected computers at the time.[iv]
With that history, it’s no surprise that anti-malware software is commonly called “antivirus.”
Antivirus forms a major cornerstone of online protection software. It protects your devices against malware through a combination of prevention, detection, and removal. Our antivirus uses AI to detect the absolute latest threats — and has for several years now.
Today, McAfee registers more than a million new malicious programs and potentially unwanted apps (PUA) each day, which contributes to the millions and millions already in existence. Now with the arrival of AI-powered coding tools, hackers can create new strains at rates unseen before.
That’s another reason why we use AI in our antivirus software. We use AI to protect against AI-created malware. It does so in three ways:
Once again, it’s important to remind ourselves that today’s malware is created largely for profit. Hackers use it to gain personal and financial info, either for their own purposes or to sell it for profit. The files you have stored on your devices have a street value. That includes tax returns, financial docs, payment info, and so on. Moreover, when you consider all the important things you keep on your devices, like your photos and documents, those have value too. Should you get caught up in a ransomware attack, a hacker puts a price tag on them for their return.
Needless to say, and you likely know this already, antivirus is essential for you and your devices.
You’ll find our AI-powered antivirus in all our McAfee+ plans. Better yet, our plans have dozens of protections that block the ways hackers distribute malware. To name just a few, our Text Scam Detector blocks links to suspicious sites that host malware and other attacks — and our Web Protection does the same for your browser. It also includes our industry-first online protection score that shows you just how safe you are, along with suggestions that can make you safer still. Together, our McAfee+ plans offer more than just antivirus. They protect your devices, your privacy, and your identity overall.
[i] https://www.historyofinformation.com/detail.php?entryid=2860
[ii] https://www.historyofinformation.com/detail.php?id=1676
[iii] https://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2016/05/the-computer-virus-that-haunted-early-aids-researchers/481965/
[iv] https://www.forbes.com/sites/daveywinder/2020/05/04/this-20-year-old-virus-infected-50-million-windows-computers-in-10-days-why-the-iloveyou-pandemic-matters-in-2020
The post What is Malware? appeared first on McAfee Blog.